ID3决策树(Java实现)
说明
参考文章-归纳决策树ID3(Java实现),完成代码编写。
在原代码的基础上补充了预测函数,实现利用模型对新数据进行分类预测。
作者对ID3决策树的介绍-ID3决策树
决策树采用xml文件保存,使用Dom4J类库,点击下载
让Dom4J支持按XPath选择节点,还得引入包jaxen.jar,点击下载
源代码汇总,点击下载
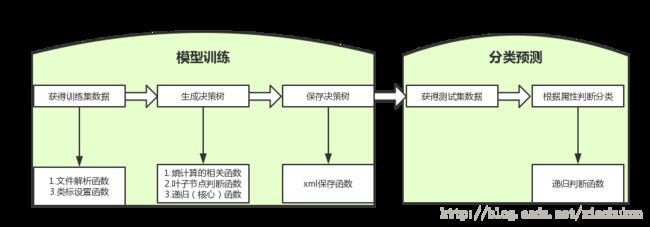
思路
代码
输入文件采用ARFF格式,使用的训练数据文件如下:
train.arff
@relation weather.symbolic
@attribute outlook {sunny,overcast,rainy}
@attribute temperature {hot,mild,cool}
@attribute humidity {high,normal}
@attribute windy {TRUE,FALSE}
@attribute play {yes,no}
@data
sunny,hot,high,FALSE,no
sunny,hot,high,TRUE,no
overcast,hot,high,FALSE,yes
rainy,mild,high,FALSE,yes
rainy,cool,normal,FALSE,yes
rainy,cool,normal,TRUE,no
overcast,cool,normal,TRUE,yes
sunny,mild,high,FALSE,no
sunny,cool,normal,FALSE,yes
rainy,mild,normal,FALSE,yes
sunny,mild,normal,TRUE,yes
overcast,mild,high,TRUE,yes
overcast,hot,normal,FALSE,yes
rainy,mild,high,TRUE,no
ARFF(Attribute-Relation File Format):格式简单明了,分为两部分,第一部分交代属性及取值范围,第二部分则是数据部分(data)。
由于只是测试代码效果,测试集(predict.arff)也是上述数据,只是将类标相关的数据移除了。
ID3类
package ID3;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.Character.Subset;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
public class ID3 {
// 同时保留训练集和测试集的数据在模型中,防止训练集和测试集的列顺序不同
private ArrayList trainAttribute = new ArrayList(); // 存储训练集属性的名称
private ArrayList> train_attributeValue = new ArrayList>(); // 存储训练集每个属性的取值
private ArrayList predictAttribute = new ArrayList(); // 存储测试集属性的名称
private ArrayList> predict_attributeValue = new ArrayList>(); // 存储测试集每个属性的取值
private ArrayList train_data = new ArrayList(); // 训练集数据 ,即arff文件中的data字符串
private ArrayList predict_data = new ArrayList(); // 测试集数据
private String[] preLable;
int decatt; // 决策变量在属性集中的索引(即类标所在列)
public static final String patternString = "@attribute(.*)[{](.*?)[}]";
//正则表达,其中*? 表示重复任意次,但尽可能少重复,防止匹配到更后面的"}"符号
Document xmldoc;
Element root;
public ID3() {
//创建并初始化xml文件,以用于储存决策树结构
xmldoc = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
root = xmldoc.addElement("root");
root.addElement("DecisionTree").addAttribute("value", "null");
}
/**
* 模型训练函数
* @param class_name 类标变量
* @param data_pathname 训练集
* @return xml决策树文件
*/
public Document train(String class_name,String data_pathname){
read_trainARFF(new File(data_pathname));
setDec(class_name);
LinkedList ll=new LinkedList(); //LinkList用于增删比ArrayList有优势
for(int i=0;iif(i!=decatt) ll.add(i); //防止类别变量不在最后一列发生错误
}
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i"DecisionTree", "null", al, ll);
return xmldoc;
}
/**
* 预测/分类函数(利用保留在类里的xml决策时模型进行预测)
* @param data_pathname 测试集
* @return 预测结果集
*/
public String[] predict(String data_pathname){
read_predictARFF(new File(data_pathname));
preLable=new String[predict_data.size()];
ArrayList subset=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i"DecisionTree");
giveLable(DecisionTree, subset);
return preLable;
}
/**
* 用于计算分类结果的递归函数
* @param node 节点
* @param subset 子集(存储序号)
*/
public void giveLable(Element node, ArrayList subset) {
List list=node.elements();
if (list.size()==0) { //叶子节点
System.out.println("节点:"+node.getName()+"是叶子节点");
String lable=node.getTextTrim();
for(int index:subset ){
preLable[index]=lable;
}
}else{ //非叶子节点
for(Element e:list){
String name=e.getName();
String value=e.attribute("value").getValue();
int index=predictAttribute.indexOf(name);
ArrayList temp=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i//筛选subset
if(predict_data.get(subset.get(i))[index].equals(value)){
temp.add(subset.get(i));
}
}
giveLable(e, temp);
}
}
}
//读取arff文件,给attribute、attributevalue、data赋值
public void read_trainARFF(File file) {
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString);
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(line);
if (matcher.find()) {
trainAttribute.add(matcher.group(1).trim()); //获取第一个括号里的内容
//涉及取值,尽量加.trim(),后面也可以看到,即使是换行符也可能会造成字符串不相等
String[] values = matcher.group(2).split(",");
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(values.length);
for (String value : values) {
al.add(value.trim());
}
train_attributeValue.add(al);
} else if (line.startsWith("@data")) {
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
if(line=="")
continue;
String[] row = line.split(",");
train_data.add(row);
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
//读取arff文件,给attribute、attributevalue、data赋值
public void read_predictARFF(File file) {
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString);
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(line);
if (matcher.find()) {
predictAttribute.add(matcher.group(1).trim()); //获取第一个括号里的内容
//涉及取值,尽量加.trim(),后面也可以看到,即使是换行符也可能会造成字符串不相等
String[] values = matcher.group(2).split(",");
ArrayList al = new ArrayList(values.length);
for (String value : values) {
al.add(value.trim());
}
predict_attributeValue.add(al);
} else if (line.startsWith("@data")) {
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
if(line=="")
continue;
String[] row = line.split(",");
predict_data.add(row);
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
//设置决策变量
public void setDec(int n) {
if (n < 0 || n >= trainAttribute.size()) {
System.err.println("决策变量指定错误。");
System.exit(2);
}
decatt = n;
}
public void setDec(String name) {
int n = trainAttribute.indexOf(name);
setDec(n);
}
//给一个样本(数组中是各种情况的计数),计算它的熵
public double getEntropy(int[] arr) {
double entropy = 0.0;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { //关于Double.MIN_VALUE好像和浮点精度有关,不是很懂
entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
sum += arr[i];
}
entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
entropy /= sum;
return entropy;
}
//给一个样本数组及样本的算术和,计算它的熵
public double getEntropy(int[] arr, int sum) {
double entropy = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
}
entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
entropy /= sum;
return entropy;
}
//判断类标是否统一,统一则之后即为叶节点(也可以设置为类别比例达到某一程度等其他指标)
public boolean infoPure(ArrayList subset) {
String value = train_data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt];
for (int i = 1; i < subset.size(); i++) {
String next=train_data.get(subset.get(i))[decatt];
if (!value.trim().equals(next.trim()))
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 给定原始数据的子集(subset中存储行号),当以第index个属性为节点时计算它的信息熵
public double calNodeEntropy(ArrayList subset, int index) {
int sum = subset.size();
//System.out.println("sum="+sum);
//System.out.println("index="+index);
double entropy = 0.0;
int[][] info = new int[train_attributeValue.get(index).size()][];
for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++)
info[i] = new int[train_attributeValue.get(decatt).size()];
int[] count = new int[train_attributeValue.get(index).size()];
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
int n = subset.get(i);
String nodevalue = train_data.get(n)[index];
int nodeind = train_attributeValue.get(index).indexOf(nodevalue);
count[nodeind]++;
String decvalue = train_data.get(n)[decatt];
//System.out.println(attributevalue.get(decatt).indexOf("no"));
int decind = train_attributeValue.get(decatt).indexOf(decvalue.trim());
info[nodeind][decind]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) {
entropy += getEntropy(info[i]) * count[i] / sum;
}
return entropy;
}
/**
* 构建决策树 (核心函数)
* @param node 节点名称
* @param value 节点值
* @param subset 数据子集
* @param selatt 属性子集
*/
public void buildDT(String node, String value, ArrayList subset,
LinkedList selatt) {
Element ele = null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List list = root.selectNodes("//"+node);
Iterator iter=list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
ele=iter.next();
if(ele.attributeValue("value").equals(value))
break;
}
if (infoPure(subset)) {
ele.setText(train_data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt]); //类标单一,直接写分类
return;
}
int minIndex = -1;
double minEntropy = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < selatt.size(); i++) {
if (i == decatt)
continue;
double entropy = calNodeEntropy(subset, selatt.get(i));
if (entropy < minEntropy) {
minIndex = selatt.get(i);
minEntropy = entropy;
}
}
String nodeName= trainAttribute.get(minIndex);
selatt.remove(new Integer(minIndex));
ArrayList attvalues = train_attributeValue.get(minIndex);
for (String val : attvalues) {
//System.out.println(nodeName+"="+val);
ele.addElement(nodeName).addAttribute("value", val);
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < subset.size(); i++) {
if (train_data.get(subset.get(i))[minIndex].equals(val)) {
al.add(subset.get(i));
}
}
buildDT(nodeName, val, al, selatt);
}
}
/**
* 把xml写入文件
* @param filename
*/
public void writeXML(String filename) {
try {
File file = new File(filename);
if (!file.exists())
file.createNewFile();
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint(); // 美化格式
XMLWriter output = new XMLWriter(fw, format);
output.write(xmldoc);
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
} 主函数
package ID3;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ID3 inst=new ID3();
inst.train("play", "files/ID3/train.arff");
inst.writeXML("files/ID3/ID3_Tree.xml");
String[] preLable=inst.predict("files/ID3/predict.arff");
for(int i=0;iout.println(i+preLable[i]);
}
}
} 决策树xml文件
<root>
<DecisionTree value="null">
<outlook value="sunny">
<humidity value="high">nohumidity>
<humidity value="normal">yeshumidity>
outlook>
<outlook value="overcast">yesoutlook>
<outlook value="rainy">
<windy value="TRUE">nowindy>
<windy value="FALSE">yeswindy>
outlook>
DecisionTree>
root>