谦虚其心,宏大其量
上午主要学习了JDBC
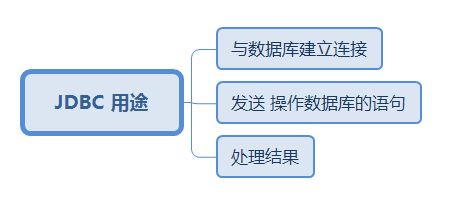
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity,即java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。JDBC提供了一种基准,据此可以构建更高级的工具和接口,使数据库开发人员能够编写数据库应用程序。
(JDBC用socket技术实现 是典型的两个进程之间的通信)
基于昨天学的MySQL知识
http://www.jianshu.com/p/c98059693e5d
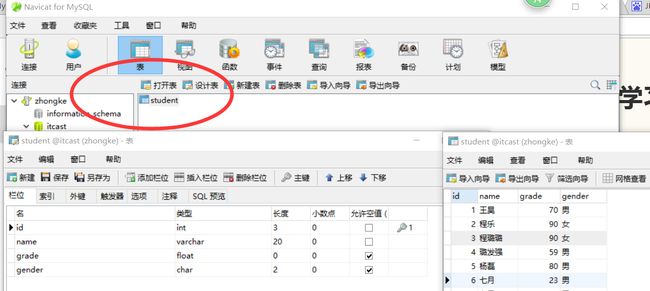
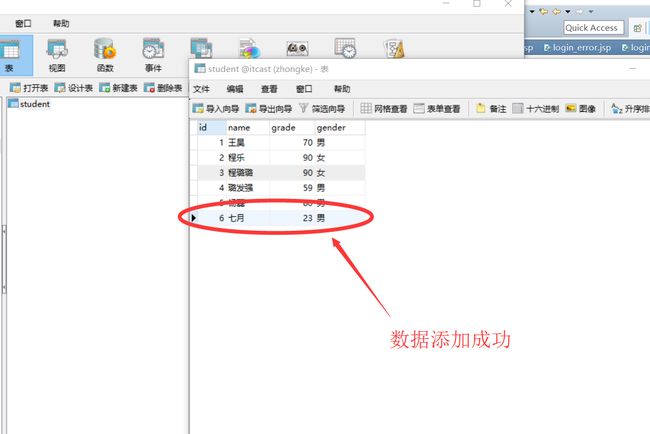
在itcast数据库中建立的student表:
在MyEclispse中建立Web项目:
下载老师给的mysql-connector-java-5.1.30.jar文件
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1bp1tb7h
(用于连接java和mysql数据库关键文件)
选中文件 (左上角):
复制文件后直接粘贴到 Web工程中WebRoot\WEB-INF\lib文件夹下:
安装的MySQL数据库为服务器端(左)
打开的MySQL命令行是客户端程序(右):
我们在客户端(shell)下输入指令:
传给MySQL服务器端后 其接收指令——解释指令——执行指令——返回给shell结果
Java 所有的API都是为了让我们方便编程设计的,让程序员不用再去考虑很复杂的问题,但要知道其原理! JDBC就是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API。
使用JDBC来操作数据库用到的类:
1 Connection 连接 (接头人)
2 Statement 语句 (送信的)
3 ResultSet 结果集 (查询需要)
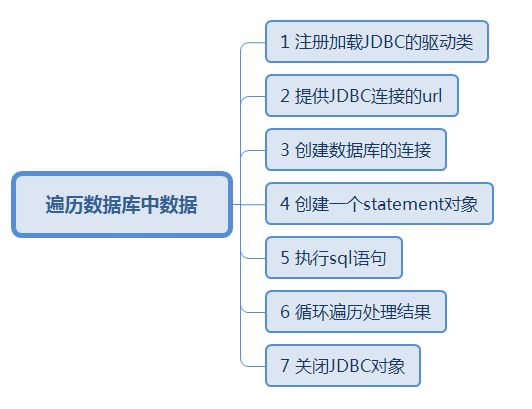
连接遍历数据库的大致步骤:
遍历打印数据库中数据 代码:
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Connection;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Statement;
public class TestJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
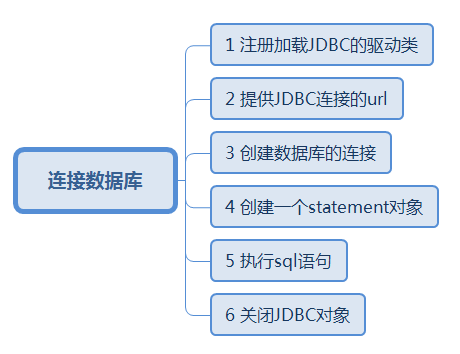
// 第一步 先加载注册JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接(利用驱动器管理器DriverManager的getConnection方法)
Connection conn = (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
Statement stmt = (Statement) conn.createStatement();
// 第五步 执行sql语句
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from student");
// 第六步 循环遍历处理结果
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(rs.getFloat("grade"));
}
// 第七步 关闭JDBC对象
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}
注:
第一步 加载注册JDBC的驱动类 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 不同数据库不一样(这里用的是mysql) 需要其他数据库的话 直接去查即可
stmt.executeQuery 返回一个结果集 用于查询
关键语句:
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from student");
另外要注意第七步关闭顺序(反着来)
上面代码版本异常处理为main函数处抛出:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { }
这种做法不好,若后面代码中间一旦异常停止
则其后面的代码不会执行。
改进的版本:(增加try catch)
import java.sql.*;
public class TestJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 第五步 执行sql语句 获取结果集合
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from student");
// 第六步 循环遍历结果集 处理
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(rs.getFloat("grade"));
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入日志操作
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第七步 关闭JDBC对象 释放资源
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
首先是try后两个catch分支 分别处理不同异常,try catch后的finally里执行关闭JDBC对象操作(此更符合事件处理逻辑)
又考虑到对象rs stmt为空关闭会导致异常
改进finally中处理办法:
...
}finally{
try{
// 第七步 关闭JDBC对象
if(rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if(stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
最终较完美代码:
import java.sql.*;
public class TestJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 第五步 执行sql语句
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from student");
// 第六步 循环遍历处理结果
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(rs.getFloat("grade"));
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入异常操作
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第七步 关闭JDBC对象 释放资源
if(rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if(stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
也可以再优化一下结构:
import java.sql.*;
public class TestJDBC22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
String Driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
// 对应 第二步
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName(Driver);
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 第五步 执行sql语句
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from student");
// 第六步 循环遍历处理结果
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(rs.getFloat("grade"));
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入异常操作
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第七步 关闭JDBC对象 释放资源
if(rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if(stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
重要说明:
将:
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Connection;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Statement;
...
改为:
import java.sql.*;
...
则代码中很多不用强转类型:
不遍历的话 则大致步骤:
数据插入操作代码:
import java.sql.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 第五步 执行sql语句
String sql = "insert into student values(0,'七月',23,'男')";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入日志等操作 所以要分开两个异常类别 都要 catch
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第六步 关闭JDBC对象
if(stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
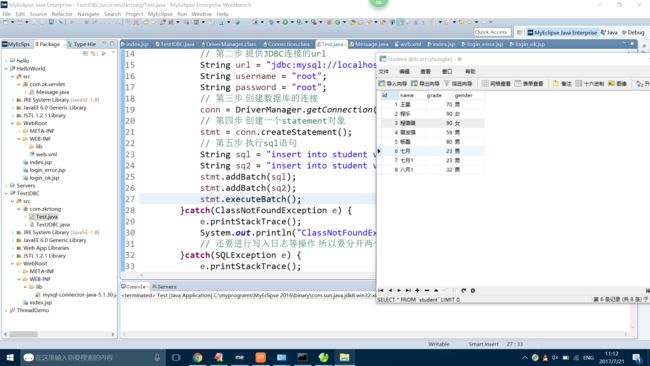
批量插入方法:
import java.sql.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 第五步 执行sql语句
String sql = "insert into student values(0,'七月1',23,'男')";
String sq2 = "insert into student values(0,'八月1',32,'男')";
stmt.addBatch(sql);
stmt.addBatch(sq2);
stmt.executeBatch();
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入日志等操作 所以要分开两个异常类别 都要 catch
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第六步 关闭JDBC对象
if(stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
此方法中关键语句:
// 执行sql语句
String sql = "insert into student values(0,'七月1',23,'男')";
String sq2 = "insert into student values(0,'八月1',32,'男')";
stmt.addBatch(sql);
stmt.addBatch(sq2);
stmt.executeBatch();
用Statement对象中的addBatch() 函数方法将SQL命令语句都添加到Batch中 然后用executeBatch() 方法整体将Batch 中的语句提交给数据库管理系统。
添加两条数据成功:
注:
我们可以使用Statement对象用来做测试 但是在生产环境下一定要考虑使用 PreparedStatement(见下)
下午
学习了 PreparedStatement 对象,用其可以使得update数据更灵活:
import java.sql.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
String sql = "insert into student values(?,?,?,?)";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 第五步 执行sql语句
pstmt.setInt(1,8);
pstmt.setString(2,"nihao");
pstmt.setFloat(3, 55);
pstmt.setString(4,"男");
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入日志等操作 所以要分开两个异常类别 都要 catch
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第六步 关闭JDBC对象
if(pstmt != null) {
pstmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
PreparedStatement 批量insert数据:
import java.sql.*;
public class TestJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
String sql = "insert into student values(?,?,?,?)";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 第五步 执行sql语句
pstmt.setInt(1,9);
pstmt.setString(2,"9");
pstmt.setFloat(3, 55);
pstmt.setString(4,"男");
pstmt.addBatch();
pstmt.setInt(1,10);
pstmt.setString(2,"10");
pstmt.setFloat(3, 68);
pstmt.setString(4,"男");
pstmt.addBatch();
pstmt.executeBatch();
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入日志等操作 所以要分开两个异常类别 都要 catch
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第六步 关闭JDBC对象
if(pstmt != null) {
pstmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
PreparedStatement 查询:
import java.sql.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
// 第一步 先加载JDBC的驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 第二步 提供JDBC连接的url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/itcast";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
// 第三步 创建数据库的连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
String sql = "select * from student";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 第五步 执行sql语句 获取结果集合
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
// 第六步 循环遍历处理结果
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(rs.getInt("age"));
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException");
// 还要进行写入日志等操作 所以要分开两个异常类别 都要 catch
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("SQLException");
}finally{
try{
// 第七步 关闭JDBC对象
if(pstmt != null) {
pstmt.close();
}
if(conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch(SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
注意PreparedStatement 和 Statement 创建一个statement对象(第4步) 和 执行sql语句(第5步)语句的区别:
Statement:
String sql = "select * from student";
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 第五步 执行sql语句
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
PreparedStatement:
String sql = "select * from student";
// 第四步 创建一个statement对象
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 第五步 执行sql语句 获取结果集合
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
PreparedStatement优势绝不仅仅是更灵活的参数化查询
请参见:PreparedStatement VS Statement
拓展阅读:
1 - 通过JDBC进行简单的增删改查(以MySQL为例)
2 - JDBC详解
世界上所有的追求都是因为热爱
一枚爱编码 爱生活 爱分享的IT信徒
— hongXkeX