如何实现下载大文件,解决网络中断等问题
下载东西很容易,但是如何优化?
先抛出几个问题
1.下载完后,文件都要存在内存吗? 比如我下载两个g的文件需要两个g的内存?
2.下载文件后,如何存进硬盘,需要拷贝几次? 能不能实现零拷贝?
3.下载的过程中多线程下载会提高速度吗?
4.下载的过程中如果网络中断了怎么办?
分别回答这几个问题
1.没必要存在内存,我们可以用流来下载,但是用流来下载的痛点是:网络断开了怎么办? 我们知道流只能读取一次,网络断开后,其实是要往回读取的,这样就会抛出错误。
public static File getApkByUrl(String urlString) throws IOException {
URL url = null;
ReadableByteChannel readableByteChannel = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
File apkFile = File.createTempFile("source", "apk");
try{
url = new URL(urlString);
//通过http请求获得文件的大小
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("HEAD");
conn.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows 7; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/47.0.2526.73 Safari/537.36 YNoteCef/5.8.0.1 (Windows)");
//System.out.println(conn.getContentLength());
//url通道
readableByteChannel = Channels.newChannel(url.openStream());
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(apkFile);
FileChannel fileChannel=fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//下载 连接两个通道
//fileChannel.transferFrom(readableByteChannel, 0 , Long.MAX_VALUE);
//fileCopy_TransferFrom(fileChannel, readableByteChannel);
long index=0;
long Memory=20971520;
while(fileChannel.size()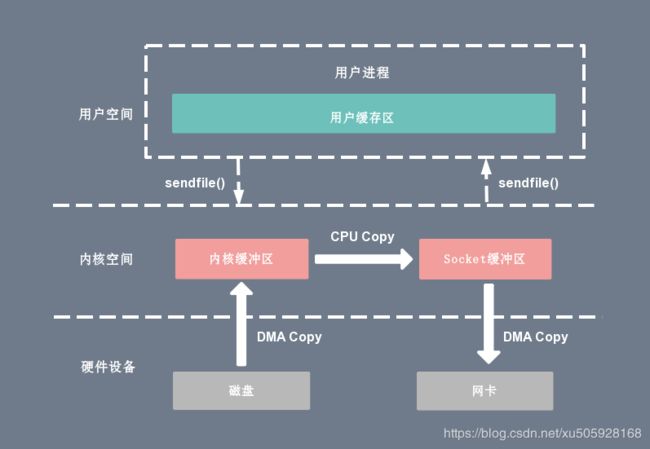
图从网上找的,就是我们现在可以不用经过用户空间来拷贝了。用得就是
fileChannel.transferFrom
这个方法。
3.下载过程中用多线程是会提速的。
我们下载的速度实际就是实时抢占网络宽带的大小。实际上!!!
用户进程实时抢占的带宽 ≤实时网络可用带宽
那现在我们要做的就是无限接近实时网络可用带宽对吧?
可是!TCP有流量探测机制,一旦检测到有丢包就会减速!来个图!
很显然,指数级降速,线性增速,这很不公平!降速很快,但升速却很漫长!造成的直接恶果就是真实的传输速率远远小于实时可用带宽。 这没办法,为了避免网络拥塞对吧?这就有点牺牲小我成全大家的精神,我的减速是为了大家能用。
多线程相比单线程的优势是,由于有多个线程在竞争实时可用带宽。尽管多线程逻辑上是并行的,但其实还是按时序的串行处理。所以每个线程处于的阶段并不一致。 在任意时刻,有的线程处于丢包被罚1/2降速,有的线程处于2倍增速阶段(SlowStart),而有的线程处于线性增长阶段。通过多个线程的下载速率的加权平均,得到的是一根相对平滑的下载曲线。这条平滑曲线在大多数时候应该位于单线程下载速率的上方。这就是多线程下载速率更有优势的体现。!!! 但是,如果TCP流量探测机制更加智能,比如BBR算法。BBR算法最大的进步,就是摒弃传统TCP流量调度算法(基于是否丢包而升速或降速), BBR采取的是,实时测量网络最大的可用带宽,并将发送速率与之相匹配,一直在实时可用带宽附近小范围徘徊,避免大起大落的情况发生。测量速率能无限接近实时可用带宽,多线程相比单线程,优势就体现不出来了。
所以在是TCP是传统的拥塞算法的情况下,多线程还是有优势的。
4.下载的过程中如果网络中断了怎么办?
因为我们用的是流嘛,所以不能重复读取。简单的解决办法就是,如果是一次性获取,而不是像我上面那样分段获取,是不会报错的!!!注意! 所以我们要判断文件是否下载完整,我们可以先发个请求获取文件的大小,下载完成后再判断一下。
上面是简单的方法。那我肯定希望不要重新下载,如果下载一个100g的,网络断开就要重新下载,那我要疯了吧?
那如何实现?
其实最核心的方法就是,不要在下载链接中请求文件的全部,分段请求,举个例子,0-9,我分5段请求,第一段0-1第二段2-3.…… 这样如果其中一段网络断开,那我就重新请求那一段就行,流重新读。
package com.company;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/*
* Encode:UTF-8
*
* Author:GFC
*
* 根据输入的url和设定的线程数,来完成断点续传功能。
*
* 每个线程支负责某一小段的数据下载;再通过RandomAccessFil e完成数据的整合。
*/
public class MultiTheradDownLoad {
//下载地址
private String urlStr = null;
private String filename = null;
//临时文件名
private String tmpfilename = null;
private File file=null;
private int threadNum = 0;
private CountDownLatch latch = null;//设置一个计数器,代码内主要用来完成对缓存文件的删除
private long fileLength = 0l;
private long threadLength = 0l;
private long[] startPos;//保留每个线程下载数据的起始位置。
private long[] endPos;//保留每个线程下载数据的截止位置。
private boolean bool = false;
private URL url = null;
//有参构造函数,先构造需要的数据
public MultiTheradDownLoad(String urlStr, int threadNum,File file) {
this.urlStr = urlStr;
this.threadNum = threadNum;
startPos = new long[this.threadNum];
endPos = new long[this.threadNum];
latch = new CountDownLatch(this.threadNum);
this.file=file;
this.filename=file.getName();
}
/*
* 组织断点续传功能的方法
*/
public File downloadPart() {
//File file = null;
File tmpfile = null;
//设置HTTP网络访问代理
System.setProperty("http.proxySet", "true");
System.setProperty("http.proxyHost", "proxy3.bj.petrochina");
System.setProperty("http.proxyPort", "8080");
//从文件链接中获取文件名,此处没考虑文件名为空的情况,此种情况可能需使用UUID来生成一个唯一数来代表文件名。
// filename = urlStr.substring(urlStr.lastIndexOf('/') + 1, urlStr
// .contains("?") ? urlStr.lastIndexOf('?') : urlStr.length());
tmpfilename = filename + "_tmp";
try {
//创建url
url = new URL(urlStr);
//打开下载链接,并且得到一个HttpURLConnection的一个对象httpcon
HttpURLConnection httpcon = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
httpcon.setRequestMethod("GET");
//获取请求资源的总长度。
fileLength = httpcon.getContentLengthLong();
//下载文件和临时文件
//file = new File(filename);//相对目录
tmpfile = new File(tmpfilename);
//每个线程需下载的资源大小;由于文件大小不确定,为避免数据丢失
threadLength = fileLength%threadNum == 0 ? fileLength/threadNum : fileLength/threadNum+1;
//打印下载信息
System.out.println("fileName: " + filename + " ," + "fileLength= "
+ fileLength + " the threadLength= " + threadLength);
//各个线程在exec线程池中进行,起始位置--结束位置
if (file.exists() && file.length() == fileLength) {
System.out.println("文件已存在!!");
return file;
} else {
setBreakPoint(startPos, endPos, tmpfile);
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
exec.execute(new DownLoadThread(startPos[i], endPos[i],
this, i, tmpfile, latch));
}
latch.await();//当你的计数器减为0之前,会在此处一直阻塞。
exec.shutdown();
}
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//下载完成后,判断文件是否完整,并删除临时文件
//System.out.println(file.length());
if (file.length() == fileLength) {
if (tmpfile.exists()) {
System.out.println("删除临时文件!!");
tmpfile.delete();
}
return file;
}
return file;
}
/*
* 断点设置方法,当有临时文件时,直接在临时文件中读取上次下载中断时的断点位置。没有临时文件,即第一次下载时,重新设置断点。
*
* Rantmpfile.seek()跳转到一个位置的目的是为了让各个断点存储的位置尽量分开。
*
* 这是实现断点续传的重要基础。
*/
private void setBreakPoint(long[] startPos, long[] endPos, File tmpfile) {
RandomAccessFile rantmpfile = null;
try {
if (tmpfile.exists()) {
System.out.println("继续下载!!");
rantmpfile = new RandomAccessFile(tmpfile, "rw");
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
rantmpfile.seek(8 * i + 8);
startPos[i] = rantmpfile.readLong();
rantmpfile.seek(8 * (i + 1000) + 16);
endPos[i] = rantmpfile.readLong();
System.out.println("the Array content in the exit file: ");
System.out.println("thre thread" + (i + 1) + " startPos:"
+ startPos[i] + ", endPos: " + endPos[i]);
}
} else {
System.out.println("the tmpfile is not available!!");
rantmpfile = new RandomAccessFile(tmpfile, "rw");
//最后一个线程的截止位置大小为请求资源的大小
for (int i = 0; i < threadNum; i++) {
startPos[i] = threadLength * i;
if (i == threadNum - 1) {
endPos[i] = fileLength;
} else {
endPos[i] = threadLength * (i + 1) - 1;
}
rantmpfile.seek(8 * i + 8);
rantmpfile.writeLong(startPos[i]);
rantmpfile.seek(8 * (i + 1000) + 16);
rantmpfile.writeLong(endPos[i]);
System.out.println("the Array content: ");
System.out.println("thre thread" + (i + 1) + " startPos:"
+ startPos[i] + ", endPos: " + endPos[i]);
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (rantmpfile != null) {
rantmpfile.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*
* 实现下载功能的内部类,通过读取断点来设置向服务器请求的数据区间。
*/
class DownLoadThread implements Runnable {
private long startPos;
private long endPos;
private MultiTheradDownLoad task = null;
private RandomAccessFile downloadfile = null;
private int id;
private File tmpfile = null;
private RandomAccessFile rantmpfile = null;
private CountDownLatch latch = null;
public DownLoadThread(long startPos, long endPos,
MultiTheradDownLoad task, int id, File tmpfile,
CountDownLatch latch) {
this.startPos = startPos;
this.endPos = endPos;
this.task = task;
this.tmpfile = tmpfile;
try {
//用这个来下载
this.downloadfile = new RandomAccessFile(file,"rw");
this.rantmpfile = new RandomAccessFile(this.tmpfile, "rw");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.id = id;
this.latch = latch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
HttpURLConnection httpcon = null;
InputStream is = null;
int length = 0;
System.out.println("线程" + id + " 开始下载!!");
while (true) {
try {
httpcon = (HttpURLConnection) task.url.openConnection();
httpcon.setRequestMethod("GET");
//防止网络阻塞,设置指定的超时时间;单位都是ms。超过指定时间,就会抛出异常
httpcon.setReadTimeout(20000);//读取数据的超时设置
httpcon.setConnectTimeout(20000);//连接的超时设置
if (startPos < endPos) {
//向服务器请求指定区间段的数据,这是实现断点续传的根本。
httpcon.setRequestProperty("Range", "bytes=" + startPos+ "-" + endPos);
System.out.println("线程 " + id+ " 长度:---- "+ (endPos - startPos));
downloadfile.seek(startPos);
if (httpcon.getResponseCode() != HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK
&& httpcon.getResponseCode() != HttpURLConnection.HTTP_PARTIAL) {
this.task.bool = true;
httpcon.disconnect();
downloadfile.close();
System.out.println("线程 ---" + id + " 下载完成!!");
latch.countDown();//计数器自减
break;
}
is = httpcon.getInputStream();//获取服务器返回的资源流
long count = 0l;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while (!this.task.bool && (length = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
count += length;
downloadfile.write(buf, 0, length);
//不断更新每个线程下载资源的起始位置,并写入临时文件;为断点续传做准备
startPos += length;
rantmpfile.seek(8 * id + 8);
rantmpfile.writeLong(startPos);
}
System.out.println("线程 " + id
+ " 总下载大小: " + count);
//关闭流
is.close();
httpcon.disconnect();
downloadfile.close();
rantmpfile.close();
}
latch.countDown();//计数器自减
System.out.println("线程 " + id + " 下载完成!!");
break;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
上面代码来自
https://blog.csdn.net/Adelaide_Guo/article/details/77757132
