攻防世界crypto新手练习区通关教程
base64
下载附件后去解密base64即可
cyberpeace{Welcome_to_new_World!}
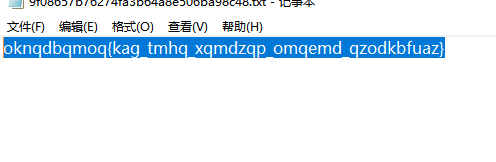
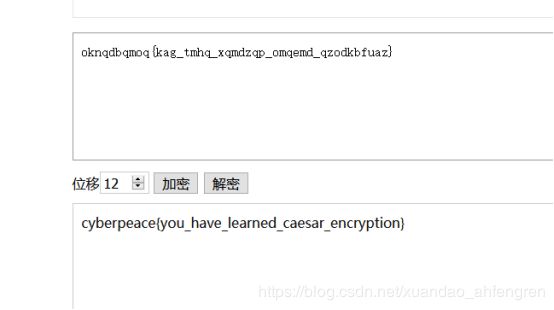
Caesar
下载附件后去解密,是凯撒密码
位移12即可
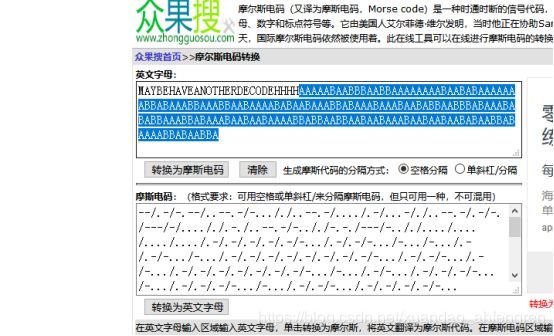
Morse
这是一串摩斯密码,拿去解密即可
cyberpeace{morsecodeissointeresting}
混合编码
首先base64解密
然后进行unicode编码转换
接着再进行一次base64解密
最后在ascii解密
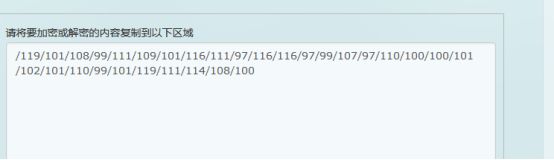
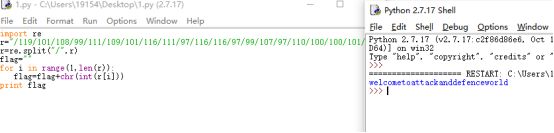
import re
r="/119/101/108/99/111/109/101/116/111/97/116/116/97/99/107/97/110/100/100/101/102/101/110/99/101/119/111/114/108/100"
r=re.split("/",r)
flag=""
for i in range(1,len(r)):
flag=flag+chr(int(r[i]))
print flag加上格式Cyberpeace{welcometoattackanddefenceworld}
幂数加密
运行脚本进行解密即可
a=["88421","0122","048","02244","04","0142242","0248","0122"]
flag="" for j in range(0,len(a)):
str = a[j]
list=[]
sum=0
for i in str:
list.append(i)
length = len(list)
for i in range(0,length):
sum+=int(list[i])
flag+=chr(64+sum) print flag
cyberpeace{WELLDONE}
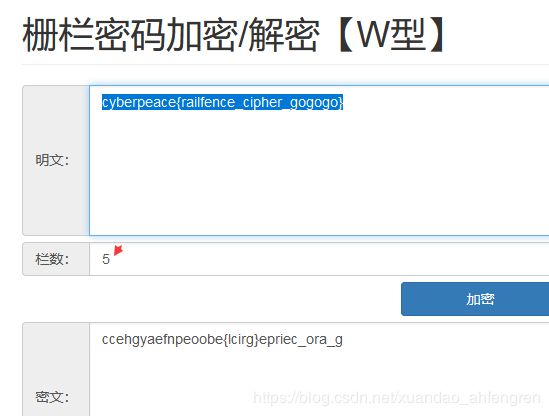
Railfence
这是栅栏密码,栏数为5
cyberpeace{railfence_cipher_gogogo}
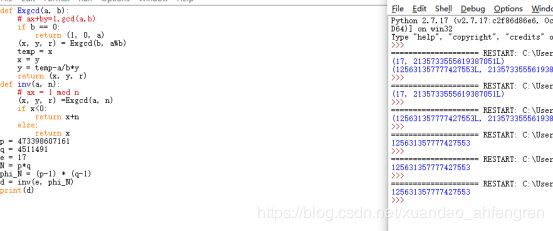
easy_RSA
运行python即可
def Exgcd(a, b):
# ax+by=1,gcd(a,b)
if b == 0:
return (1, 0, a)
(x, y, r) = Exgcd(b, a%b)
temp = x
x = y
y = temp-a/b*y
return (x, y, r)
def inv(a, n):
# ax = 1 mod n
(x, y, r) =Exgcd(a, n)
if x<0:
return x+n
else:
return x
p = 473398607161
q = 4511491
e = 17
N = p*q
phi_N = (p-1) * (q-1)
d = inv(e, phi_N)
print(d)不仅仅是Morse
首先摩斯密码解密然后把HHH后面的拿去培根解密即可
然后就是把小写的字符串就是flag了
cyberpeace{attackanddefenceworldisinteresting}
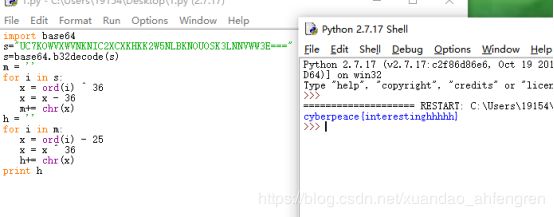
Easychallenge
需要先把python的pyc文件进行反编译
之后运行代码即可
import base64
s="UC7KOWVXWVNKNIC2XCXKHKK2W5NLBKNOUOSK3LNNVWW3E==="
s=base64.b32decode(s)
m = ''
for i in s:
x = ord(i) ^ 36
x = x - 36
m+= chr(x)
h = ''
for i in m:
x = ord(i) - 25
x = x ^ 36
h+= chr(x)
print hNormal_RSA
PCTF{256b_i5_m3dium}
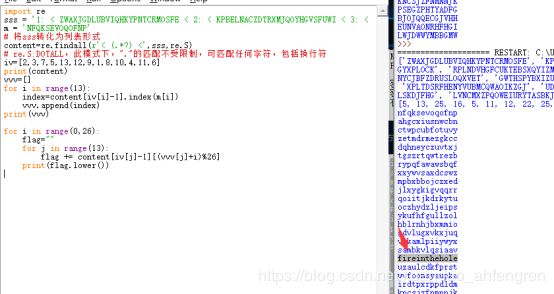
转轮机加密
import re
sss = '1: < ZWAXJGDLUBVIQHKYPNTCRMOSFE < 2: < KPBELNACZDTRXMJQOYHGVSFUWI < 3: < BDMAIZVRNSJUWFHTEQGYXPLOCK < 4: < RPLNDVHGFCUKTEBSXQYIZMJWAO < 5: < IHFRLABEUOTSGJVDKCPMNZQWXY < 6: < AMKGHIWPNYCJBFZDRUSLOQXVET < 7: < GWTHSPYBXIZULVKMRAFDCEONJQ < 8: < NOZUTWDCVRJLXKISEFAPMYGHBQ < 9: < XPLTDSRFHENYVUBMCQWAOIKZGJ < 10: < UDNAJFBOWTGVRSCZQKELMXYIHP < 11 < MNBVCXZQWERTPOIUYALSKDJFHG < 12 < LVNCMXZPQOWEIURYTASBKJDFHG < 13 < JZQAWSXCDERFVBGTYHNUMKILOP <'
m = 'NFQKSEVOQOFNP'
# 将sss转化为列表形式
content=re.findall(r'< (.*?) <',sss,re.S)
# re.S:DOTALL,此模式下,"."的匹配不受限制,可匹配任何字符,包括换行符
iv=[2,3,7,5,13,12,9,1,8,10,4,11,6]
print(content)
vvv=[]
for i in range(13):
index=content[iv[i]-1].index(m[i])
vvv.append(index)
print(vvv)
for i in range(0,26):
flag=""
for j in range(13):
flag += content[iv[j]-1][(vvv[j]+i)%26]
print(flag.lower())Fire开头的就是了,直接提交即可
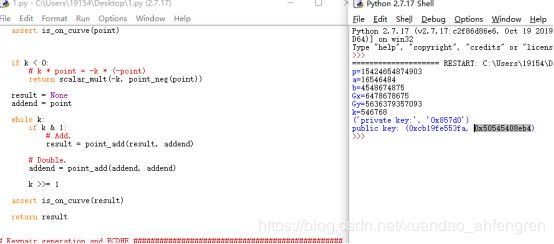
easy_ECC
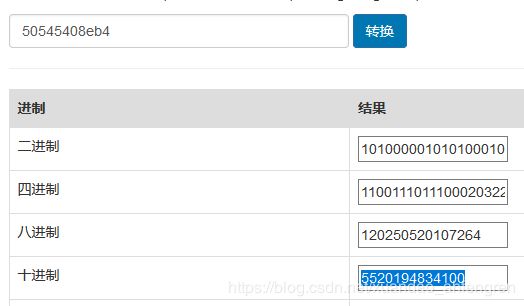
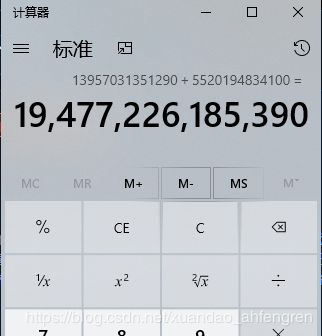
运行代码,然后把公匙的十六进制转换成十进制再相加即可
import collections
import random
EllipticCurve = collections.namedtuple('EllipticCurve', 'name p a b g n h')
curve = EllipticCurve(
'secp256k1',
# Field characteristic.
p=int(input('p=')),
# Curve coefficients.
a=int(input('a=')),
b=int(input('b=')),
# Base point.
g=(int(input('Gx=')),
int(input('Gy='))),
# Subgroup order.
n=int(input('k=')),
# Subgroup cofactor.
h=1,
)
# Modular arithmetic ##########################################################
def inverse_mod(k, p):
"""Returns the inverse of k modulo p.
This function returns the only integer x such that (x * k) % p == 1.
k must be non-zero and p must be a prime.
"""
if k == 0:
raise ZeroDivisionError('division by zero')
if k < 0:
# k ** -1 = p - (-k) ** -1 (mod p)
return p - inverse_mod(-k, p)
# Extended Euclidean algorithm.
s, old_s = 0, 1
t, old_t = 1, 0
r, old_r = p, k
while r != 0:
quotient = old_r // r
old_r, r = r, old_r - quotient * r
old_s, s = s, old_s - quotient * s
old_t, t = t, old_t - quotient * t
gcd, x, y = old_r, old_s, old_t
assert gcd == 1
assert (k * x) % p == 1
return x % p
# Functions that work on curve points #########################################
def is_on_curve(point):
"""Returns True if the given point lies on the elliptic curve."""
if point is None:
# None represents the point at infinity.
return True
x, y = point
return (y * y - x * x * x - curve.a * x - curve.b) % curve.p == 0
def point_neg(point):
"""Returns -point."""
assert is_on_curve(point)
if point is None:
# -0 = 0
return None
x, y = point
result = (x, -y % curve.p)
assert is_on_curve(result)
return result
def point_add(point1, point2):
"""Returns the result of point1 + point2 according to the group law."""
assert is_on_curve(point1)
assert is_on_curve(point2)
if point1 is None:
# 0 + point2 = point2
return point2
if point2 is None:
# point1 + 0 = point1
return point1
x1, y1 = point1
x2, y2 = point2
if x1 == x2 and y1 != y2:
# point1 + (-point1) = 0
return None
if x1 == x2:
# This is the case point1 == point2.
m = (3 * x1 * x1 + curve.a) * inverse_mod(2 * y1, curve.p)
else:
# This is the case point1 != point2.
m = (y1 - y2) * inverse_mod(x1 - x2, curve.p)
x3 = m * m - x1 - x2
y3 = y1 + m * (x3 - x1)
result = (x3 % curve.p,
-y3 % curve.p)
assert is_on_curve(result)
return result
def scalar_mult(k, point):
"""Returns k * point computed using the double and point_add algorithm."""
assert is_on_curve(point)
if k < 0:
# k * point = -k * (-point)
return scalar_mult(-k, point_neg(point))
result = None
addend = point
while k:
if k & 1:
# Add.
result = point_add(result, addend)
# Double.
addend = point_add(addend, addend)
k >>= 1
assert is_on_curve(result)
return result
# Keypair generation and ECDHE ################################################
def make_keypair():
"""Generates a random private-public key pair."""
private_key = curve.n
public_key = scalar_mult(private_key, curve.g)
return private_key, public_key
private_key, public_key = make_keypair()
print("private key:", hex(private_key))
print("public key: (0x{:x}, 0x{:x})".format(*public_key))