Spring框架中有一个核心的概念,叫做AOP(面向切面编程)。而AOP的本质其实就是jdk动态代理。所以学习动态代理还是很有必要的。笔者对动态代理也只是研究了一点皮毛,如有写的不对的地方欢迎指点。
JDK动态代理有2个很重要的东西,一个是InvocationHandler接口,还有一个是Proxy类。
先来看一下InvaocationHandler接口的定义:
InvocationHandler is the interface implemented by the invocation handler of a proxy instance.
Each proxy instance has an associated invocation handler. When a method is invoked on a proxy instance, the method invocation is encoded and dispatched to the invoke method of its invocation handler.
1.我们写的每一个动态代理类都需要实现InvocationHandler接口。
2.每个代理类的实例都关联着一个Handler.当调用代理对象的方法时,其实调用的是InvocaionHandler的invoke()方法。
先来写一个类来实现InvocationHandler接口:
public class MyDataInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Service service;
//通过构造函数把Service传进来
public MyDataInvocationHandler(Service service) {
this.service= service;
}
/**
* proxy参数:真实对象
* method参数:真实对象的方法
* args参数:给真实对象的方法传入一些参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
before();//在调用真实对象的方法前加一些操作,比如事务开启等。
method.invoke(service, args);
after();//在调用真实对象的方法后加一些操作,比如事务关闭等。
return null;
}
public void before(){
System.out.println("通知类------before()");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("通知类------after()");
}
}
InvocationHandler先写到这,接下来看一下Proxy类
Proxy provides static methods for creating dynamic proxy classes and instances, and it is also the superclass of all dynamic proxy classes created by those methods.
Proxy类提供静态方法用来动态创建一个代理对象的类。
Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法算是最常用的一个静态方法了。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获得代理类对象的实例
/**
* 第一个参数:ClassLoader类型。一个ClassLoader对象,定义了由哪个ClassLoader对象来对生成的代理对象进行加载
* 第二个参数:一个Interface对象的数组,表示的是我将要给我需要代理的对象提供一组什么接口,如果我提供了一组接口给它,那么这个代理对象就宣称实现了该接口(多态),这样我就能调用这组接口中的方法了
* 第三个参数: 一个InvocationHandler对象,表示的是当我这个动态代理对象在调用方法的时候,会关联到哪一个InvocationHandler对象上
*/
Service proxyInstance = (Service) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Test.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { Service.class }, new MyDataInvocationHandler(new ServiceImpl()));
proxyInstance.update();
}
}
下面是我的Service接口和Service的实现类。
public interface Service {
void update();
}
public class ServiceImpl implements Service {
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("这是被代理Service的实现类----update");
}
}
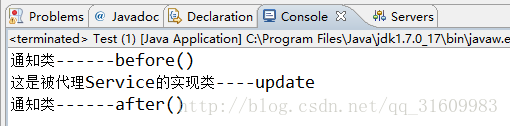
运行一下:
好了。效果出来了。但估计会有许多疑问吧。为什么他会自动的调用InvocationHandler的invoke()方法???待会再解释。。。
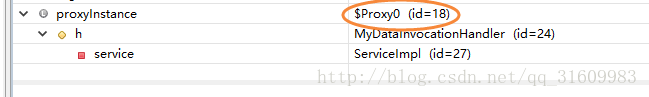
在上面Test测试类中通过Proxy.newProxyInstance生成的实例是属于哪一个类的呢?通过项目工程,没有找到该特殊的类。debug看一下。
我们看到,proxyInstance实例的类名叫做:"$Proxy0",默认动态代理类的类名取名方式是:"$"+Proxy关键字+一个数字的形式,我们也可以修改这个名字。
其实这个类是运行在内存中的。我们可以用流的形式将该类的二进制写到硬盘中的.class文件中,再通过反编译工具看一下源代码到底是什么!
在测试类中加这样一个方法
private static void createProxyClass() {
byte[] bs = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("MyProxy",new Class[] { Service.class }) ;
try {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d://a.class");
fileOutputStream.write(bs);
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
笔者刚开始用到ProxyGenerator的时候,始终报错,包倒不过来,这个百度自己查一下,有解决方案的。。。
ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass()方法的第一个参数就是修改了类名。
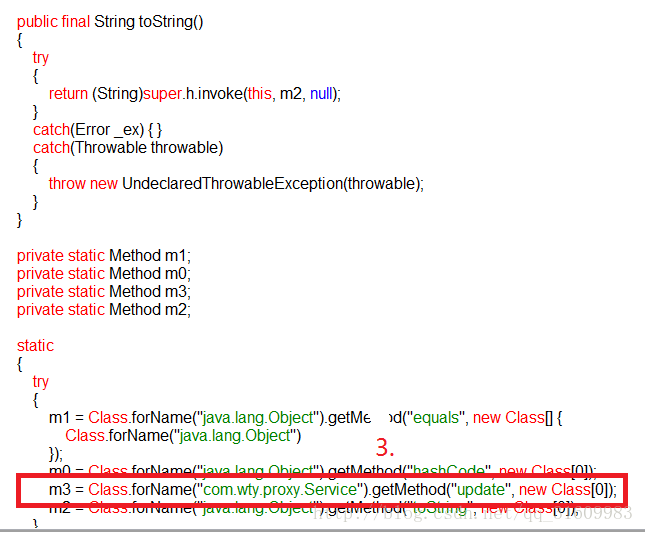
通过反编译工具终于看到了这个神秘的java代码
关键代码已经画了框框了。对于上面提的那个问题,在2中已经给了答案了。
声明:笔者还只是一个小小的菜鸟,目前还在读大三中,对于有些问题或许理解的还不够透彻,欢迎指正。