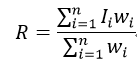Opencv2.4.9源码分析——Stitching(七)
7、融合
7.1 原理
在上一步中,虽然我们已经得到了接缝线,但如果只是简单的对接缝线的两侧选取不同的图像,那么对于重叠区域,在接缝线处的过度会出现不连贯的现象,在视觉上会显得有些突兀。因此我们还需要在接缝线两侧,对不同图像进行融合处理来克服上述不足之处。应用于图像拼接的融合算法有两种常用的方法:羽化和多频段融合。
羽化的原理是对边界进行平滑虚化,通过渐变的方法达到自然衔接的效果。在应用于图像拼接时,羽化是只对接缝线两侧的区域进行处理,它的公式为:
式中,R表示由n幅图像重叠后经过羽化处理后而得到的新图像,Ii表示第i幅图像在接缝线两侧区域内的部分,wi表示Ii的权值,它是当前像素到达第i幅图像最近边界的距离。从式92可以看出,羽化算法本质上就是加权平均的过程。另外羽化处理还可以通过设置锐度参数,来调整羽化平滑处理的虚化程度和羽化面积。
羽化算法虽然简单,但当重叠部分有细微的不重合的时候,图像的高频部分会出现较为明显的模糊情况。
为了能够保留图像的高频成分(即图像的细节部分),则需要应用多频段融合方法,它通过建立拉普拉斯(带通滤波器)金字塔,使各个频段上的信息都保留并融合在一起。
我们下面给出多频段融合方法的具体执行步骤:首先分别建立各个图像的拉普拉斯金字塔,然后针对重叠区域,把它们的金字塔的相同层应用式92进行合并,最后对该合并后的金字塔进行逆拉普拉斯变换,从而得到最终的融合图像。
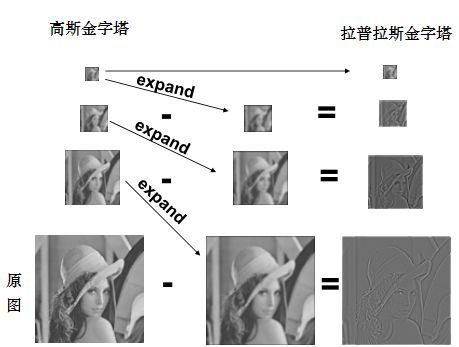
拉普拉斯金字塔是通过高斯金字塔得到。高斯金字塔的上一层图像是对下一层图像进行高斯模糊(卷积高斯内核)再降采样(隔点采样)得到的。而拉普拉斯金字塔的各层图像是由高斯金字塔的相同层减去它的上一层的扩展(即先升采样,再卷积高斯内核)得到的,即
式中,L和G分别表示拉普拉斯和高斯金字塔,拉普拉斯金字塔的顶层图像就是高斯金字塔的顶层图像,下标n表示的是金字塔的层数,底层为0,并且G0为图像原图,expand表示扩展运算。拉普拉斯金字塔是由底层向顶层逐层构建得到的。图14示意了拉普拉斯金字塔的建立方法。
图14 拉普拉斯金字塔
当得到了不同图像的拉普拉斯金字塔后,我们仍然可以应用式92对不同的区域的不同层进行合并,同样也得到了一个金字塔,我们称为合并金字塔。其中式92的权值,在这里就是掩码,而各层的掩码也是通过建立金字塔得到,也就是需要为掩码建立一个高斯金字塔,金字塔的底层就是该图的掩码。
逆拉普拉斯变换的计算公式为:
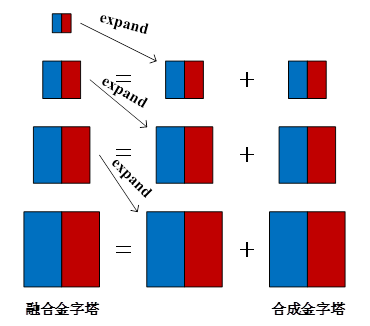
式中,R为由式92得到的合并金字塔,S为融合金字塔,其中,S的顶层为R的顶层,S是从顶层向底层计算得到的,最终得到的融合金字塔的底层图像就是我们想要的融合图像。图15和图16分别表示了合并金字塔和融合金字塔建立过程。
图15 合成金字塔创建示意图
图16融合金字塔创建示意图
7.2 源码
图像融合的基类Blender为:
class CV_EXPORTS Blender
{
public:
virtual ~Blender() {}
enum { NO, FEATHER, MULTI_BAND }; //表示融合算法的类别
//该函数的主要作用是根据不同的算法类别type,实例化并得到不同的子类
static Ptr createDefault(int type, bool try_gpu = false);
//prepare函数表示事先得到全景图像的Mat变量,就是为了像素赋值,先准备好全景图像的区域、尺寸
void prepare(const std::vector &corners, const std::vector &sizes);
virtual void prepare(Rect dst_roi);
virtual void feed(const Mat &img, const Mat &mask, Point tl); //预处理图像
virtual void blend(Mat &dst, Mat &dst_mask); //执行融合算法
protected:
//表示最终得到的全景图像和它的掩码
Mat dst_, dst_mask_;
Rect dst_roi_; //表示最终得到的全景图像的矩形变量
};
第一个prepare函数:
void Blender::prepare(const vector &corners, const vector &sizes)
//corners表示待拼接图像在全景图像中的左上角坐标
//sizes表示映射变换后待拼接图像的尺寸
{
//利用resultRoi函数得到最终的全景图像的尺寸
//调用另一个prepare函数,该函数的主要作用是初始化为dst_,dst_mask_和dst_roi_
prepare(resultRoi(corners, sizes));
}
为dst_和dst_mask_在img图像的区域内赋值,父类Blender类本质上没有进行任何融合,所以该类的feed函数就是简单赋值:
void Blender::feed(const Mat &img, const Mat &mask, Point tl)
//img表示待拼接的图像
//mask表示该图像的掩码
//tl表示该图像在全景图像的左上角坐标
{
CV_Assert(img.type() == CV_16SC3); //确保img类型正确
CV_Assert(mask.type() == CV_8U); //确保mask类型正确
int dx = tl.x - dst_roi_.x; //表示该图像在最终的全景图像的左上角的横坐标
int dy = tl.y - dst_roi_.y; //表示该图像在最终的全景图像的左上角的纵坐标
for (int y = 0; y < img.rows; ++y) //遍历图像的行
{
//得到各个变量的行首地址指针
const Point3_ *src_row = img.ptr >(y);
Point3_ *dst_row = dst_.ptr >(dy + y);
const uchar *mask_row = mask.ptr(y);
uchar *dst_mask_row = dst_mask_.ptr(dy + y);
for (int x = 0; x < img.cols; ++x) //遍历当前行的每个像素
{
if (mask_row[x]) //当前像素没有被掩码掉
dst_row[dx + x] = src_row[x]; //赋值
dst_mask_row[dx + x] |= mask_row[x]; //赋值
}
}
}
基类的blend并没有执行任何融合算法,只是简单的赋值,当融合类别为NO时,其实也就是调用的该基类:
void Blender::blend(Mat &dst, Mat &dst_mask)
//dst和dst_mask表示最终得到的全景图像和掩码
{
dst_.setTo(Scalar::all(0), dst_mask_ == 0); //为掩码部分赋0值
dst = dst_; //赋值
dst_mask = dst_mask_; //赋值
dst_.release(); //释放内存
dst_mask_.release(); //释放内容
}
下面介绍羽化融合算法FeatherBlender类的相关函数,它的父类为Blender类:
void FeatherBlender::prepare(Rect dst_roi)
{
Blender::prepare(dst_roi); //调用Blender::prepare函数
//全局变量dst_weight_map_表示最终得到的全景图像的权值映射图像,在这里初始化该变量
dst_weight_map_.create(dst_roi.size(), CV_32F);
dst_weight_map_.setTo(0);
}
void FeatherBlender::feed(const Mat &img, const Mat &mask, Point tl)
{
CV_Assert(img.type() == CV_16SC3); //确保img类型正确
CV_Assert(mask.type() == CV_8U); //确保mask类型正确
//该函数在后面给出介绍,全局变量sharpness_表示锐化系数,默认值为0.02,全局变量weight_map_表示图像img的权值映射图,也就是经过阈值处理后的距离图像
createWeightMap(mask, sharpness_, weight_map_);
int dx = tl.x - dst_roi_.x; //表示该图像在最终的全景图像的左上角的横坐标
int dy = tl.y - dst_roi_.y; //表示该图像在最终的全景图像的左上角的纵坐标
for (int y = 0; y < img.rows; ++y) //遍历图像的行
{
//得到各个变量的行首地址指针
const Point3_* src_row = img.ptr >(y);
Point3_* dst_row = dst_.ptr >(dy + y);
const float* weight_row = weight_map_.ptr(y);
float* dst_weight_row = dst_weight_map_.ptr(dy + y);
for (int x = 0; x < img.cols; ++x) //遍历当前行的每个像素,为相关变量赋值
{
//dst_为src_的加权结果,即式92的分子部分,如果不是重叠区域,则只有一幅图像,所以加号是不起作用的
dst_row[dx + x].x += static_cast(src_row[x].x * weight_row[x]);
dst_row[dx + x].y += static_cast(src_row[x].y * weight_row[x]);
dst_row[dx + x].z += static_cast(src_row[x].z * weight_row[x]);
dst_weight_row[dx + x] += weight_row[x]; //式92的分母部分
}
}
}
void FeatherBlender::blend(Mat &dst, Mat &dst_mask)
{
//该函数在后面给出介绍
normalizeUsingWeightMap(dst_weight_map_, dst_);
//WEIGHT_EPS = 1e-5f,表示很小的一个数
//dst_mask_为二值图像,权值很小为0,否则为1
dst_mask_ = dst_weight_map_ > WEIGHT_EPS;
Blender::blend(dst, dst_mask); //调用Blender:: blend函数,为dst和dst_mask赋值
}
生成权值映射图:
void createWeightMap(const Mat &mask, float sharpness, Mat &weight)
//mask表示掩码
//sharpness表示锐度,系统默认值为0.02
//weight表示返回的权值映射图,也就是经过阈值处理后的距离图像
{
CV_Assert(mask.type() == CV_8U); //再次确保mask类型正确
//在二值掩码图像mask内,得到每个像素到达最近的零值像素的距离,得到距离图像weight
distanceTransform(mask, weight, CV_DIST_L1, 3);
//调用threshold函数,首先把距离图像weight乘以锐度sharpness,此时如果距离图像像素值大于阈值1,则等于1,否则保留原值,即保留数值较小的那些像素,结果再次赋值给weight
threshold(weight * sharpness, weight, 1.f, 1.f, THRESH_TRUNC);
}
normalizeUsingWeightMap函数实现了式92:
void normalizeUsingWeightMap(const Mat& weight, Mat& src)
//weight表示权值映射图像
//src作为输入表示加权处理后的图像,作为输出表示归一化后的图像
{
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
if(tegra::normalizeUsingWeightMap(weight, src))
return;
#endif
CV_Assert(src.type() == CV_16SC3); //确保src类型符合要求
if(weight.type() == CV_32FC1) //weight类型为CV_32FC1
{
//遍历全景图像
for (int y = 0; y < src.rows; ++y)
{
//获取当前行的首地址指针
Point3_ *row = src.ptr >(y);
const float *weight_row = weight.ptr(y);
for (int x = 0; x < src.cols; ++x)
{
//对重叠区域,进行归一化处理,式92
//而对非重叠区域,还是原始像素值
row[x].x = static_cast(row[x].x / (weight_row[x] + WEIGHT_EPS));
row[x].y = static_cast(row[x].y / (weight_row[x] + WEIGHT_EPS));
row[x].z = static_cast(row[x].z / (weight_row[x] + WEIGHT_EPS));
}
}
}
else //weight类型为CV_16SC1
{
CV_Assert(weight.type() == CV_16SC1); //确保weight类型为CV_16SC1
//遍历全景图像
for (int y = 0; y < src.rows; ++y)
{
//获取当前行的首地址指针
const short *weight_row = weight.ptr(y);
Point3_ *row = src.ptr >(y);
for (int x = 0; x < src.cols; ++x)
{
int w = weight_row[x] + 1; //权值
//对重叠区域,进行归一化处理,式92
//而对非重叠区域,还是原始像素值
row[x].x = static_cast((row[x].x << 8) / w);
row[x].y = static_cast((row[x].y << 8) / w);
row[x].z = static_cast((row[x].z << 8) / w);
}
}
}
}
下面给出多频段融合算法MultiBandBlender类的相关函数,它的父类也是Blender类。我们首先给出它的构造函数:
MultiBandBlender::MultiBandBlender(int try_gpu, int num_bands, int weight_type)
//try_gpu表示是否应用图像处理器
//num_bands表示频段的数量,缺省值为5,即金字塔一共有5层
//weight_type表示权值的数据类型
{
//把num_bands赋值给全局变量actual_num_bands_
setNumBands(num_bands);
#if defined(HAVE_OPENCV_GPU) && !defined(DYNAMIC_CUDA_SUPPORT)
can_use_gpu_ = try_gpu && gpu::getCudaEnabledDeviceCount();
#else
(void)try_gpu;
can_use_gpu_ = false;
#endif
//确保权值的数据类型为CV_32F或CV_16S
CV_Assert(weight_type == CV_32F || weight_type == CV_16S);
weight_type_ = weight_type; //赋值
}
void MultiBandBlender::prepare(Rect dst_roi)
{
dst_roi_final_ = dst_roi; //赋值,表示最终的全景图像
// Crop unnecessary bands
//图像两边长的最大值
double max_len = static_cast(max(dst_roi.width, dst_roi.height));
//设置真正的频段数量
num_bands_ = min(actual_num_bands_, static_cast(ceil(log(max_len) / log(2.0))));
// Add border to the final image, to ensure sizes are divided by (1 << num_bands_)
//增加全景图像的边长,以确保能够完成num_bands_次的降采样
dst_roi.width += ((1 << num_bands_) - dst_roi.width % (1 << num_bands_)) % (1 << num_bands_);
dst_roi.height += ((1 << num_bands_) - dst_roi.height % (1 << num_bands_)) % (1 << num_bands_);
Blender::prepare(dst_roi); //调用Blender::prepare函数
//全局变量dst_pyr_laplace_表示拉普拉斯金字塔
dst_pyr_laplace_.resize(num_bands_ + 1); //金字塔的层数赋值
dst_pyr_laplace_[0] = dst_; //第0层(底层)为原图
//全局变量dst_band_weights_表示各个频段的权值,与拉普拉斯金字塔相对应
dst_band_weights_.resize(num_bands_ + 1);
dst_band_weights_[0].create(dst_roi.size(), weight_type_); //为底层大小类型赋值
dst_band_weights_[0].setTo(0); //初始化为0
//为除了底层以外的其他金字塔层赋值
for (int i = 1; i <= num_bands_; ++i) //遍历金字塔的层
{
//定义各个层的尺寸和数据类型
dst_pyr_laplace_[i].create((dst_pyr_laplace_[i - 1].rows + 1) / 2,
(dst_pyr_laplace_[i - 1].cols + 1) / 2, CV_16SC3);
dst_band_weights_[i].create((dst_band_weights_[i - 1].rows + 1) / 2,
(dst_band_weights_[i - 1].cols + 1) / 2, weight_type_);
dst_pyr_laplace_[i].setTo(Scalar::all(0)); //初始化为0
dst_band_weights_[i].setTo(0); //初始化为0
}
}
void MultiBandBlender::feed(const Mat &img, const Mat &mask, Point tl)
{
//确保图像和掩码的数据类型正确
CV_Assert(img.type() == CV_16SC3 || img.type() == CV_8UC3);
CV_Assert(mask.type() == CV_8U);
// Keep source image in memory with small border
//得到新的左上角和右下角坐标,新的矩形要比img大
int gap = 3 * (1 << num_bands_);
Point tl_new(max(dst_roi_.x, tl.x - gap),
max(dst_roi_.y, tl.y - gap));
Point br_new(min(dst_roi_.br().x, tl.x + img.cols + gap),
min(dst_roi_.br().y, tl.y + img.rows + gap));
// Ensure coordinates of top-left, bottom-right corners are divided by (1 << num_bands_).
// After that scale between layers is exactly 2.
//
// We do it to avoid interpolation problems when keeping sub-images only. There is no such problem when
// image is bordered to have size equal to the final image size, but this is too memory hungry approach.
//为了便于降采样,需要对左上角、右下角进行调整
tl_new.x = dst_roi_.x + (((tl_new.x - dst_roi_.x) >> num_bands_) << num_bands_);
tl_new.y = dst_roi_.y + (((tl_new.y - dst_roi_.y) >> num_bands_) << num_bands_);
int width = br_new.x - tl_new.x;
int height = br_new.y - tl_new.y;
width += ((1 << num_bands_) - width % (1 << num_bands_)) % (1 << num_bands_);
height += ((1 << num_bands_) - height % (1 << num_bands_)) % (1 << num_bands_);
br_new.x = tl_new.x + width;
br_new.y = tl_new.y + height;
int dy = max(br_new.y - dst_roi_.br().y, 0);
int dx = max(br_new.x - dst_roi_.br().x, 0);
tl_new.x -= dx; br_new.x -= dx;
tl_new.y -= dy; br_new.y -= dy;
//下面4个变量表示扩充的四边的长度
int top = tl.y - tl_new.y;
int left = tl.x - tl_new.x;
int bottom = br_new.y - tl.y - img.rows;
int right = br_new.x - tl.x - img.cols;
// Create the source image Laplacian pyramid
Mat img_with_border; //表示边界扩充后的图像
//对img通过边界反射的方式填充扩充了边界后的像素,得到img_with_border
copyMakeBorder(img, img_with_border, top, bottom, left, right,
BORDER_REFLECT);
vector src_pyr_laplace; //表示拉普拉斯金字塔
if (can_use_gpu_ && img_with_border.depth() == CV_16S)
createLaplacePyrGpu(img_with_border, num_bands_, src_pyr_laplace);
else
//创建拉普拉斯金字塔,该函数在后面给出介绍
createLaplacePyr(img_with_border, num_bands_, src_pyr_laplace);
// Create the weight map Gaussian pyramid
Mat weight_map; //表示权值映射图
//表示权值高斯金字塔
vector weight_pyr_gauss(num_bands_ + 1);
//把mask传递给weight_map
if(weight_type_ == CV_32F)
{
mask.convertTo(weight_map, CV_32F, 1./255.); //weight_map = mask / 255
}
else// weight_type_ == CV_16S
{
mask.convertTo(weight_map, CV_16S); //weight_map = mask
add(weight_map, 1, weight_map, mask != 0); //weight_map = weight_map + 1
}
//对weight_map通过赋予一个恒定常数的方式填充扩充了边界后的像素,得到weight_pyr_gauss[0]
copyMakeBorder(weight_map, weight_pyr_gauss[0], top, bottom, left, right, BORDER_CONSTANT);
//建立权值高斯金字塔
for (int i = 0; i < num_bands_; ++i)
pyrDown(weight_pyr_gauss[i], weight_pyr_gauss[i + 1]);
//得到金字塔底层图像的左上角和右下角坐标
int y_tl = tl_new.y - dst_roi_.y;
int y_br = br_new.y - dst_roi_.y;
int x_tl = tl_new.x - dst_roi_.x;
int x_br = br_new.x - dst_roi_.x;
// Add weighted layer of the source image to the final Laplacian pyramid layer
if(weight_type_ == CV_32F)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= num_bands_; ++i) //遍历金字塔各个层
{
for (int y = y_tl; y < y_br; ++y) //遍历当前层的各个行
{
int y_ = y - y_tl;
//得到各个图像的当前行的首地址指针
const Point3_* src_row = src_pyr_laplace[i].ptr >(y_);
Point3_* dst_row = dst_pyr_laplace_[i].ptr >(y);
const float* weight_row = weight_pyr_gauss[i].ptr(y_);
float* dst_weight_row = dst_band_weights_[i].ptr(y);
for (int x = x_tl; x < x_br; ++x) //遍历当前行的各个像素
{
int x_ = x - x_tl;
//式92的分子
dst_row[x].x += static_cast(src_row[x_].x * weight_row[x_]);
dst_row[x].y += static_cast(src_row[x_].y * weight_row[x_]);
dst_row[x].z += static_cast(src_row[x_].z * weight_row[x_]);
dst_weight_row[x] += weight_row[x_]; //式92的分母
}
}
//表示的含义是降采样的图像面积缩小了一倍
x_tl /= 2; y_tl /= 2;
x_br /= 2; y_br /= 2;
}
}
else // weight_type_ == CV_16S
{
for (int i = 0; i <= num_bands_; ++i) //遍历金字塔的各个层
{
for (int y = y_tl; y < y_br; ++y) //遍历当前层的各行
{
int y_ = y - y_tl;
//得到各个图像的当前行的首地址指针
const Point3_* src_row = src_pyr_laplace[i].ptr >(y_);
Point3_* dst_row = dst_pyr_laplace_[i].ptr >(y);
const short* weight_row = weight_pyr_gauss[i].ptr(y_);
short* dst_weight_row = dst_band_weights_[i].ptr(y);
for (int x = x_tl; x < x_br; ++x) //遍历当前行的各个像素
{
int x_ = x - x_tl;
//式92的分子
dst_row[x].x += short((src_row[x_].x * weight_row[x_]) >> 8);
dst_row[x].y += short((src_row[x_].y * weight_row[x_]) >> 8);
dst_row[x].z += short((src_row[x_].z * weight_row[x_]) >> 8);
dst_weight_row[x] += weight_row[x_]; //式92的分母
}
}
//表示的含义是降采样的图像面积缩小了一倍
x_tl /= 2; y_tl /= 2;
x_br /= 2; y_br /= 2;
}
}
}
void MultiBandBlender::blend(Mat &dst, Mat &dst_mask)
{
//遍历金字塔的各个层,得到归一化后的各个层的图像,计算式92
for (int i = 0; i <= num_bands_; ++i)
normalizeUsingWeightMap(dst_band_weights_[i], dst_pyr_laplace_[i]);
if (can_use_gpu_)
restoreImageFromLaplacePyrGpu(dst_pyr_laplace_);
else
restoreImageFromLaplacePyr(dst_pyr_laplace_); //得到融合金字塔
dst_ = dst_pyr_laplace_[0]; //得到融合金字塔的底层图像,即最终的多频段融合图像
//把融合图像还原回融合之前的图像尺寸
dst_ = dst_(Range(0, dst_roi_final_.height), Range(0, dst_roi_final_.width));
dst_mask_ = dst_band_weights_[0] > WEIGHT_EPS; //得到融合图像的掩码
//把掩码尺寸还原回融合之前的图像尺寸
dst_mask_ = dst_mask_(Range(0, dst_roi_final_.height), Range(0, dst_roi_final_.width));
dst_pyr_laplace_.clear(); //释放内存
dst_band_weights_.clear(); //释放内存
Blender::blend(dst, dst_mask); //调用Blender::blend函数
}
在多频段融合算法中,创建拉普拉斯金字塔函数:
void createLaplacePyr(const Mat &img, int num_levels, vector &pyr)
//img表示原图
//num_levels表示金字塔的层数,也就是多频段的频段数
//pyr表示最终得到的金字塔
{
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
if(tegra::createLaplacePyr(img, num_levels, pyr))
return;
#endif
pyr.resize(num_levels + 1); //建立金字塔
if(img.depth() == CV_8U) //图像像素为8位
{
if(num_levels == 0) //表示不需要建立拉普拉斯金字塔
{
img.convertTo(pyr[0], CV_16S); //原图赋予底层
return; //函数不再做任何处理,直接返回
}
Mat downNext; //表示降采样后的图像
Mat current = img; //表示当前层的图像
//调用pyrDown函数,对img图像进行高斯模糊和降采样,得到downNext
pyrDown(img, downNext);
for(int i = 1; i < num_levels; ++i) //遍历金字塔的各个层
{
Mat lvl_up; //表示对当前图像进行升采样得到的图像
Mat lvl_down; //表示对当前图像进行降采样得到的图像
//调用pyrDown函数,得到lvl_down
pyrDown(downNext, lvl_down);
//调用pyrUp函数,得到lvl_up
pyrUp(downNext, lvl_up, current.size()); //式93中的expand运算
//式93,pyr[i-1]= current - lvl_up
subtract(current, lvl_up, pyr[i-1], noArray(), CV_16S);
current = downNext; //更新current
downNext = lvl_down; //更新downNext
}
//得到金字塔的顶层图像
{
Mat lvl_up;
pyrUp(downNext, lvl_up, current.size());
subtract(current, lvl_up, pyr[num_levels-1], noArray(), CV_16S);
downNext.convertTo(pyr[num_levels], CV_16S);
}
}
else //图像像素的深度为其他情况
{
pyr[0] = img; //金字塔的底层图像
for (int i = 0; i < num_levels; ++i) //遍历金字塔的各个层
pyrDown(pyr[i], pyr[i + 1]); //得到各个层的图像
Mat tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < num_levels; ++i) //再次遍历金字塔的各个层
{
pyrUp(pyr[i + 1], tmp, pyr[i].size()); //式93中的expand运算
subtract(pyr[i], tmp, pyr[i]); //式93
}
}
}
得到融合金字塔:
void restoreImageFromLaplacePyr(vector &pyr)
//pyr作为输入表示拉普拉斯金字塔,作为输出表示融合金字塔
{
if (pyr.empty())
return;
Mat tmp;
for (size_t i = pyr.size() - 1; i > 0; --i) //遍历拉普拉斯金字塔的各层
{
pyrUp(pyr[i], tmp, pyr[i - 1].size()); //式94中的expand运算
add(tmp, pyr[i - 1], pyr[i - 1]); //式94
}
}
7.3 应用
下面给出融合的应用:
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "highgui.h"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp"
#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/autocalib.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/blenders.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/camera.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/exposure_compensate.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/matchers.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/motion_estimators.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/seam_finders.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/util.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/detail/warpers.hpp"
#include "opencv2/stitching/warpers.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
using namespace detail;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
vector imgs; //输入图像
Mat img = imread("1.jpg");
imgs.push_back(img);
img = imread("2.jpg");
imgs.push_back(img);
Ptr finder; //特征检测
finder = new SurfFeaturesFinder();
vector features(2);
(*finder)(imgs[0], features[0]);
(*finder)(imgs[1], features[1]);
vector pairwise_matches; //特征匹配
BestOf2NearestMatcher matcher(false, 0.3f, 6, 6);
matcher(features, pairwise_matches);
HomographyBasedEstimator estimator; //相机参数评估
vector cameras;
estimator(features, pairwise_matches, cameras);
for (size_t i = 0; i < cameras.size(); ++i)
{
Mat R;
cameras[i].R.convertTo(R, CV_32F);
cameras[i].R = R;
}
Ptr adjuster; //相机参数精确评估
adjuster = new detail::BundleAdjusterReproj();
adjuster->setConfThresh(1);
(*adjuster)(features, pairwise_matches, cameras);
vector rmats;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cameras.size(); ++i)
rmats.push_back(cameras[i].R.clone());
waveCorrect(rmats, WAVE_CORRECT_HORIZ); //波形校正
for (size_t i = 0; i < cameras.size(); ++i)
cameras[i].R = rmats[i];
//图像映射变换
vector corners(2);
vector masks_warped(2);
vector images_warped(2);
vector sizes(2);
vector masks(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
masks[i].create(imgs[i].size(), CV_8U);
masks[i].setTo(Scalar::all(255));
}
Ptr warper_creator;
warper_creator = new cv::PlaneWarper();
Ptr warper = warper_creator->create(static_cast(cameras[0].focal));
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
Mat_ K;
cameras[i].K().convertTo(K, CV_32F);
corners[i] = warper->warp(imgs[i], K, cameras[i].R, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_REFLECT, images_warped[i]);
sizes[i] = images_warped[i].size();
warper->warp(masks[i], K, cameras[i].R, INTER_NEAREST, BORDER_CONSTANT, masks_warped[i]);
}
//曝光补偿
Ptr compensator =
ExposureCompensator::createDefault(ExposureCompensator::GAIN);
compensator->feed(corners, images_warped, masks_warped);
for(int i=0;i<2;++i)
{
compensator->apply(i, corners[i], images_warped[i], masks_warped[i]);
}
//在后面,我们还需要用到映射变换图的掩码masks_warped,因此这里为该变量添加一个副本masks_seam
vector masks_seam(2);
for(int i = 0; i<2;i++)
masks_warped[i].copyTo(masks_seam[i]);
//寻找接缝线
Ptr seam_finder;
seam_finder = new GraphCutSeamFinder(GraphCutSeamFinder::COST_COLOR_GRAD);
vector images_warped_f(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
images_warped[i].convertTo(images_warped_f[i], CV_32F);
seam_finder->find(images_warped_f, corners, masks_seam);
//图像融合
Ptr blender; //定义图像融合器
//blender = Blender::createDefault(Blender::NO, false); //简单融合方法
/****羽化融合方法*********
blender = Blender::createDefault(Blender::FEATHER, false);
FeatherBlender* fb = dynamic_cast(static_cast(blender));
fb->setSharpness(0.005); //设置羽化锐度
**************/
blender = Blender::createDefault(Blender::MULTI_BAND, false); //多频段融合
MultiBandBlender* mb = dynamic_cast(static_cast(blender));
//设置频段数,即金字塔层数,原则上频段越多越好
mb->setNumBands(8);
blender->prepare(corners, sizes); //生成全景图像区域
//在融合的时候,最重要的是在接缝线两侧进行处理,而上一步在寻找接缝线后得到的掩码的边界就是接缝线处,因此我们还需要在接缝线两侧开辟一块区域用于融合处理,这一处理过程对羽化方法尤为关键
//应用膨胀算法缩小掩码面积
vector dilate_img(2);
Mat element = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(20, 20)); //定义结构元素
vector images_warped_s(2);
for(int k=0;k<2;k++) //遍历所有图像
{
images_warped_f[k].convertTo(images_warped_s[k], CV_16S); //改变数据类型
dilate(masks_seam[k], masks_seam[k], element); //膨胀运算
//映射变换图的掩码和膨胀后的掩码相“与”,从而使扩展的区域仅仅限于接缝线两侧,其他边界处不受影响
masks_seam[k] = masks_seam[k] & masks_warped[k];
blender->feed(images_warped_s[k], masks_seam [k], corners[k]); //初始化数据
}
Mat result, result_mask;
//完成融合操作,得到全景图像result和它的掩码result_mask
blender->blend(result, result_mask);
imwrite("pano.jpg", result); //存储全景图像
return 0;
}
最终的全景图像为:
图17 全景图像