android RTMP直播流媒体支持
软硬件环境
- ubuntu 16.04
- Android Studio 2.1.3
- OTT BOx with android 5.1.1
- nginx 1.11.3
- nginx-rtmp-module
- vitamio
前言
当下,直播已经成为网络热词,它不单单是指传统广播电视的实时播放,更是更为广泛的音视频实时分享的延伸。早先,直播数据源只可能来自于电视台及节目制作中心,但是放眼现在,基于计算机技术的高速发展,任何人都可以独自完成内容的制作,再利用身边的终端设备完成分享,你不仅仅是受众,同样可以成为主角。可以说,时下流行的”网红”文化,直播技术立下了汗马功劳。本文旨在搭建一个最简单的视频直播系统,包括服务器端及Android客户端,采用了nginx、nginx-rtmp、vitamio及ffmpeg。
rtmp协议
RTMP是Real Time Messaging Protocol的缩写,是被设计用来进行实时数据通信的网络协议。它是一个协议族,包括rtmpe、rtmpt、rtmps等,是直播技术中常用的协议
服务端配置
nginx添加rtmp支持
从http://nginx.org/en/download.html下载最新版1.11.3,然后从https://github.com/arut/nginx-rtmp-module下载nginx的rtmp补丁,下载的文件都放在目录/home/djstava(请根据实际情况自行修改)下,重新编译nginx
tar xvf nginx-1.11.3.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.11.3
mkdir build
./configure --prefix=/home/djstava/nginx-1.11.3/build --add-module=/home/djstava/nginx-rtmp-module
make
make install
修改配置文件nginx.conf
编辑/home/djstava/nginx-1.11.3/build/conf/nginx.conf,在文件末尾添加如下内容
rtmp {
server {
listen 1935;
ping 30s;
notify_method get;
application myapp {
live on;
# sample play/publish handlers
#on_play http://localhost:8080/on_play;
#on_publish http://localhost:8080/on_publish;
# sample recorder
#recorder rec1 {
# record all;
# record_interval 30s;
# record_path /tmp;
# record_unique on;
#}
# sample HLS
#hls on;
#hls_path /tmp/hls;
#hls_sync 100ms;
}
# Video on demand
#application vod {
# play /var/Videos;
#}
# Video on demand over HTTP
#application vod_http {
# play http://localhost:8080/vod/;
#}
}
}
启动nginx服务
/home/djstava/nginx-1.11.3/build/sbin/nginx
ffmpeg推送rtmp
找一个本地的视频文件进行推送,命令为
ffmpeg -re -i 大话西游之月光宝盒.BD1280超清国粤双语中英双字.mp4 -c copy -f flv rtmp://localhost/myapp/mystream
ffplay播放测试
如果没有安装ffplay的话,也可以用vlc
ffplay rtsmp://localhost/myapp/mystream
后记
前面的步骤都是在本机中进行的。可是在实际应用中,情况会复杂的多,nginx可能是一台服务器,ffmpeg推流的可能就是另一台服务器,这样的话,可将localhost换成对应的IP地址。如果数据源来自摄像头,同样可以通过ffmpeg进行推送,命令如下
ffmpeg -f dshow -i video="Integrated Camera" -vcodec libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency -f flv rtmp://10.10.10.84/myapp/mystream1
Android客户端播放
之前已经写过一个基于vitamio的视频播放器,地址是https://github.com/djstava/DJMediaPlayer,我们就在它的基础上进行修改,找到MainActivity.Java
private String[] files = {"rtmp demo","apple demo"};
在listview的item被点击后发送包含播放地址的intent
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, VitamioVideoViewActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("movieUrl", "rtmp://10.10.10.84/myapp/mystream");
startActivity(intent);
HLS
前言
之前的一篇博文http://www.xugaoxiang.com/2016/08/20/android-rtmp%E7%9B%B4%E6%92%AD/已经简单的介绍了如何利用nginx、nginx-rtmp-module和ffmpeg实现基于rtmp协议的直播.今天这篇继续直播这个话题,聊聊hls的应用.
HLS
HLS(Http Live Streaming)是由Apple公司定义的用于实时流传输的协议,HLS基于HTTP协议实现,传输内容包括两部分,一是M3U8描述文件,二是TS媒体文件。
m3u8文件
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
如上,m3u8文件是一个描述文件,必须以#EXTM3U开头,之后是切片TS文件的序列.对于直播来讲,m3u8文件需要进行实时的更新,只保留若干个TS切片序列,防止本地存储撑爆硬盘.
多码率支持
针对应用网络多变及不稳定的情况,多数直播都会提供多码率支持,播放器会根据用户当前的网络状况,自动切换到对应的码率上,大大提升用户体验.在服务器端.为了提供多码率的支持,就需要多级m3u8文件.在主m3u8文件不再有TS序列,而是二级m3u8文件,如下所示
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
nginx-rtmp对HLS的支持
nginx-rtmp-module本身对rtmp和hls都有很好的支持,只需要在nginx.conf配置下就ok了
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
在rtmp标签下,指定hls application的根路径/opt/www/live,所有的TS切片文件都存放在这里
ffmpeg推流
推送本地文件
- 1
- 1
推送成功后,你可以通过如下2个url播放对应的模拟实时流,请确保nginx服务已启动.
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
另外http://192.168.1.88:8081/stat页面可以显示当前服务的一些信息,如接入的客户端数量,音频 视频的信息等等,见下图
![]()
推送UDP组播数据
- 1
- 1
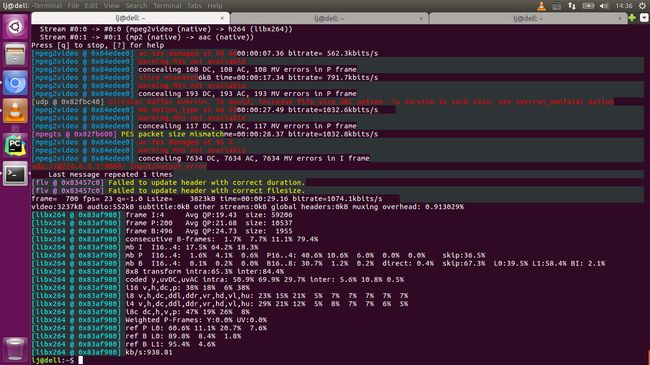
在以UDP数据为输入源时,ffmpeg会报如下图中的错误信息
这时只需要重新修改下ffmpeg的推流命令就可以,如下
- 1
- 1
fifo_size的单位是字节,自己酌情增减.
前言
Android RTMP直播(续)介绍了HLS协议相关的基础内容,本文将继续深入学习HLS的其它高级特性.
服务端多码率支持
nginx.conf
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
主要看看application hls的内容
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
这里设定当带宽分别为800k 1200k 2000k的时候,终端都播放相对应的m3u8索引文件
ffmpeg推流
这里需要利用ffmpeg推送3路不同的流,对应上面提到的低 中 高
- 1
- 1
- 1
- 1
- 1
- 1
推送开始后,hls的root目录下就会生成相应的文件内容,如下图所示
![]()
此时livestream.m3u8文件内容为
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
相应的,播放链接为 http://10.10.10.59:8081/live/livestream.m3u8,播放器需要做的就是根据自身的网络状况,切换到其它的索引文件.
直播节目的录制
直播进行的同时一般都会有本地录制的需求,nginx-rtmp-module提供了这个功能,接下来实践一下.还是看nginx.conf配置文件
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
record all录制所有内容,也可以只录音频或者视频.
推流后/opt/www/record路径下就会自动生成带对应时间戳的flv文件,用vlc测试播放OK.
时移电视
要想实现时移电视(这里指的是服务器端)的话,首先需要在服务器上保留足够的切片文件,比如说你提供1小时的时移,就意味着要有1小时的切片文件,而且索引文件中包含前1小时的切片序列.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
hls_fragment指的是切片文件的长度,这里是10秒,hls_playlist_length指的是索引文件的长度,我这里设的是5分钟.推流开始后,你到切片生成的目录,会发现*.m3u8文件包含了30个ts序列.所以,在上面这种情况下,就只能进行5分钟的时移,当播放进度到达当前直播点时则继续回到直播状态.
执行外部shell脚本
比如有个脚本test.sh,内容如下
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
我这里把它放在hls application中执行,则nginx.conf应如下
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
当hls服务正常启动时(如上面写过的ffmpeg推流动作),外部脚本test.sh也被执行了.脚本中捕捉了退出的中断信号,也就说,如果ffmpeg推流动作中断了,那么test.sh脚本也就不再执行了.
制作RAMDISK
为了提高HLS的读写效率,可以把切片和索引文件操作放在内存中进行.
- 1
- 1