Linux kernel打印栈信息方法
在kernel代码的任意位置直接调用dump_stack方法即可。dump_stack已经包含在内核符号表中,并在include/linux/kernel.h中被声明。获取栈信息的原理是使用ebp逐层回溯。dump_stack函数在arch/x86/kernel/traps_32.c中定义(kernel 2.6.24)如下:
/*
* The architecture-independent dump_stack generator
*/
void dump_stack(void)
{
unsigned long stack;
printk("Pid: %d, comm: %.20s %s %s %.*s\n",
current->pid, current->comm, print_tainted(),
init_utsname()->release,
(int)strcspn(init_utsname()->version, " "),
init_utsname()->version);
show_trace(current, NULL, &stack);
}
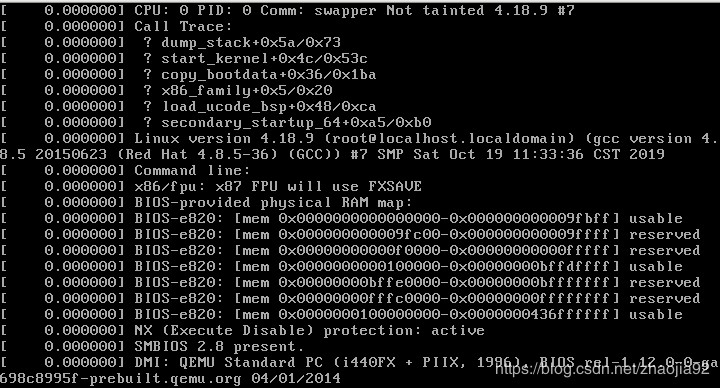
EXPORT_SYMBOL(dump_stack);在start_kernel函数开头加入dump_stack打印的栈信息如上图所示。
asmlinkage void __init start_kernel(void)
{
char * command_line;
extern struct kernel_param __start___param[], __stop___param[];
smp_setup_processor_id();
dump_stack();
/* Need to run as early as possible, to initialize the lockdep hash: */
unwind_init();
lockdep_init();
cgroup_init_early();
local_irq_disable();
early_boot_irqs_off();
early_init_irq_lock_class();
......
/*
* HACK ALERT! This is early. We're enabling the console before
* we've done PCI setups etc, and console_init() must be aware of
* this. But we do want output early, in case something goes wrong.
*/
console_init();
if (panic_later)
panic(panic_later, panic_param);
lockdep_info();
/* Need to run this when irqs are enabled, because it wants
* to self-test [hard/soft]-irqs on/off lock inversion bugs
* too: */
locking_selftest();
......
}
dump_stack借助printk将栈信息写入kernel的ring buffer中,当start_kernel调用到console_init后,会将ring buffer的信息全部输出到每个console中显示。在kernel启动完成后,使用dmesg也可将ring buffer中的启动信息输出。因此,无论dump_stack在何处调用,即使当时无法立即在屏幕上显示,都存在于ring buffer中,一旦kernel调用console_init完成,即把ring buffer的全部内容打印到屏幕,并且,后续只要缓冲区不覆盖即可从中导出栈信息。
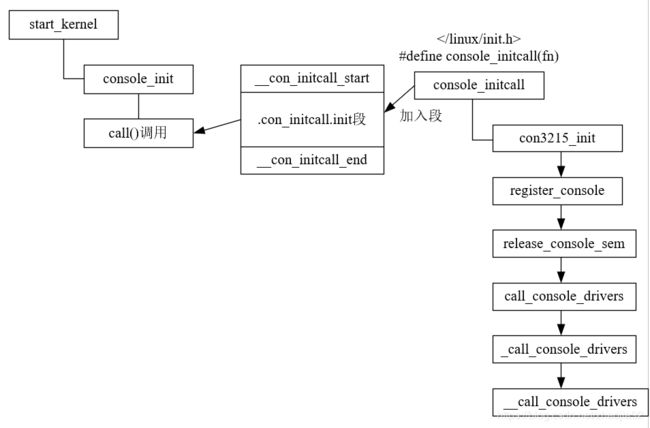
kernel调用console_init时,读取.con_initcall.init段的每个条目依次对各console初始化。console_init函数实现如下:
/drivers/char/tty_io.c
/*
* Initialize the console device. This is called *early*, so
* we can't necessarily depend on lots of kernel help here.
* Just do some early initializations, and do the complex setup
* later.
*/
void __init console_init(void)
{
initcall_t *call;
/* Setup the default TTY line discipline. */
(void) tty_register_ldisc(N_TTY, &tty_ldisc_N_TTY);
/*
* set up the console device so that later boot sequences can
* inform about problems etc..
*/
call = __con_initcall_start;
while (call < __con_initcall_end) {
(*call)();
call++;
}
}.con_initcall.init段在/arch/x86/kernel/vmlinux_32.lds.S中定义:
.initcall.init : AT(ADDR(.initcall.init) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__initcall_start = .;
INITCALLS
__initcall_end = .;
}
.con_initcall.init : AT(ADDR(.con_initcall.init) - LOAD_OFFSET) {
__con_initcall_start = .;
*(.con_initcall.init)
__con_initcall_end = .;
}.con_initcall.init段中的每个条目都是函数指针,指针使用console_initcall宏注册。console_initcall宏定义如下:
#define console_initcall(fn) \
static initcall_t __initcall_##fn \
__attribute_used__ __attribute__((__section__(".con_initcall.init")))=fn 例如kernel中console设备注册要使用console_initcall宏将init函数写入.con_initcall.init段中。
/drivers/s390/char/con3215.c
/*
* 3215 console initialization code called from console_init().
* NOTE: This is called before kmalloc is available.
*/
static int __init
con3215_init(void)
{
struct ccw_device *cdev;
struct raw3215_info *raw;
struct raw3215_req *req;
int i;
/* Check if 3215 is to be the console */
if (!CONSOLE_IS_3215)
return -ENODEV;
/* Set the console mode for VM */
if (MACHINE_IS_VM) {
cpcmd("TERM CONMODE 3215", NULL, 0, NULL);
cpcmd("TERM AUTOCR OFF", NULL, 0, NULL);
}
/* allocate 3215 request structures */
raw3215_freelist = NULL;
spin_lock_init(&raw3215_freelist_lock);
for (i = 0; i < NR_3215_REQ; i++) {
req = (struct raw3215_req *) alloc_bootmem_low(sizeof(struct raw3215_req));
req->next = raw3215_freelist;
raw3215_freelist = req;
}
cdev = ccw_device_probe_console();
if (IS_ERR(cdev))
return -ENODEV;
raw3215[0] = raw = (struct raw3215_info *)
alloc_bootmem_low(sizeof(struct raw3215_info));
memset(raw, 0, sizeof(struct raw3215_info));
raw->buffer = (char *) alloc_bootmem_low(RAW3215_BUFFER_SIZE);
raw->inbuf = (char *) alloc_bootmem_low(RAW3215_INBUF_SIZE);
raw->cdev = cdev;
cdev->dev.driver_data = raw;
cdev->handler = raw3215_irq;
raw->flags |= RAW3215_FIXED;
tasklet_init(&raw->tasklet,
(void (*)(unsigned long)) raw3215_tasklet,
(unsigned long) raw);
init_waitqueue_head(&raw->empty_wait);
/* Request the console irq */
if (raw3215_startup(raw) != 0) {
free_bootmem((unsigned long) raw->inbuf, RAW3215_INBUF_SIZE);
free_bootmem((unsigned long) raw->buffer, RAW3215_BUFFER_SIZE);
free_bootmem((unsigned long) raw, sizeof(struct raw3215_info));
raw3215[0] = NULL;
printk("Couldn't find a 3215 console device\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
register_console(&con3215);
return 0;
}
console_initcall(con3215_init);con3215_init函数中调用register_console函数,该函数定义如下:
/kernel/printk.c
/*
* The console driver calls this routine during kernel initialization
* to register the console printing procedure with printk() and to
* print any messages that were printed by the kernel before the
* console driver was initialized.
*/
void register_console(struct console *console)
{
int i;
unsigned long flags;
struct console *bootconsole = NULL;
if (console_drivers) {
if (console->flags & CON_BOOT)
return;
if (console_drivers->flags & CON_BOOT)
bootconsole = console_drivers;
}
if (!(console->flags & CON_ENABLED))
return;
if (bootconsole && (console->flags & CON_CONSDEV)) {
printk(KERN_INFO "console handover: boot [%s%d] -> real [%s%d]\n",
bootconsole->name, bootconsole->index,
console->name, console->index);
unregister_console(bootconsole);
console->flags &= ~CON_PRINTBUFFER;
} else {
printk(KERN_INFO "console [%s%d] enabled\n",
console->name, console->index);
}
/*
* Put this console in the list - keep the
* preferred driver at the head of the list.
*/
acquire_console_sem();
......
release_console_sem();
}其中调用了release_console_sem函数:
/kernel/printk.c
/**
* release_console_sem - unlock the console system
* Releases the semaphore which the caller holds on the console system
* and the console driver list.
* While the semaphore was held, console output may have been buffered
* by printk(). If this is the case, release_console_sem() emits
* the output prior to releasing the semaphore.
* If there is output waiting for klogd, we wake it up.
* release_console_sem() may be called from any context.
*/
void release_console_sem(void)
{
unsigned long flags;
unsigned long _con_start, _log_end;
unsigned long wake_klogd = 0;
if (console_suspended) {
up(&secondary_console_sem);
return;
}
console_may_schedule = 0;
for ( ; ; ) {
spin_lock_irqsave(&logbuf_lock, flags);
wake_klogd |= log_start - log_end;
if (con_start == log_end)
break; /* Nothing to print */
_con_start = con_start;
_log_end = log_end;
con_start = log_end; /* Flush */
spin_unlock(&logbuf_lock);
call_console_drivers(_con_start, _log_end);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
console_locked = 0;
up(&console_sem);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&logbuf_lock, flags);
if (wake_klogd)
wake_up_klogd();
}该函数内调用call_console_drivers函数将ring buffer中的信息写入设备中完成显示。
/kernel/printk.c
/*
* Call the console drivers, asking them to write out
* log_buf[start] to log_buf[end - 1].
* The console_sem must be held.
*/
static void call_console_drivers(unsigned long start, unsigned long end)
{
unsigned long cur_index, start_print;
static int msg_level = -1;
BUG_ON(((long)(start - end)) > 0);
cur_index = start;
start_print = start;
while (cur_index != end) {
if (msg_level < 0 && ((end - cur_index) > 2) &&
LOG_BUF(cur_index + 0) == '<' &&
LOG_BUF(cur_index + 1) >= '0' &&
LOG_BUF(cur_index + 1) <= '7' &&
LOG_BUF(cur_index + 2) == '>') {
msg_level = LOG_BUF(cur_index + 1) - '0';
cur_index += 3;
start_print = cur_index;
}
while (cur_index != end) {
char c = LOG_BUF(cur_index);
cur_index++;
if (c == '\n') {
if (msg_level < 0) {
/* printk() has already given us loglevel tags in
* the buffer. This code is here in case the
* log buffer has wrapped right round and scribbled
* on those tags
*/
msg_level = default_message_loglevel;
}
_call_console_drivers(start_print, cur_index, msg_level);
msg_level = -1;
start_print = cur_index;
break;
}
}
}
_call_console_drivers(start_print, end, msg_level);
}/*
* Write out chars from start to end - 1 inclusive
*/
static void _call_console_drivers(unsigned long start,
unsigned long end, int msg_log_level)
{
if ((msg_log_level < console_loglevel || ignore_loglevel) &&
console_drivers && start != end) {
if ((start & LOG_BUF_MASK) > (end & LOG_BUF_MASK)) {
/* wrapped write */
__call_console_drivers(start & LOG_BUF_MASK,
log_buf_len);
__call_console_drivers(0, end & LOG_BUF_MASK);
} else {
__call_console_drivers(start, end);
}
}
}/*
* Call the console drivers on a range of log_buf
*/
static void __call_console_drivers(unsigned long start, unsigned long end)
{
struct console *con;
for (con = console_drivers; con; con = con->next) {
if ((con->flags & CON_ENABLED) && con->write &&
(cpu_online(smp_processor_id()) ||
(con->flags & CON_ANYTIME)))
con->write(con, &LOG_BUF(start), end - start);
}
}可见其中遍历了console_drivers链表,对每个console驱动调用write接口写入字符串。在console_init函数调用前,各驱动已经完成加载,并将console设备信息存储在对应结构体内。当write调用时直接从这些结构体内取出设备信息。
上述函数调用关系图如下:
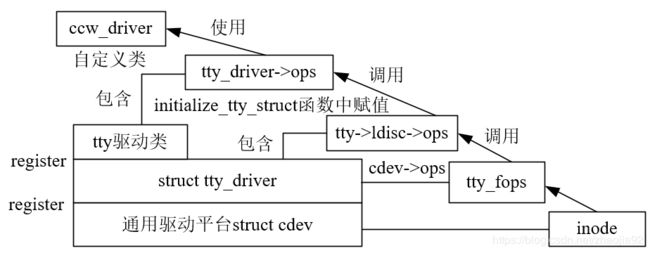
tty驱动类和cdev的关系图如下,该关系方便分析serial console、console的驱动组织结构:
同样在module内的任何位置也可以使用dump_stack函数,在函数运行到dump_stack后打印栈信息到ring buffer。
arm架构下,在include/asm-arm/system.h下声明了extern asmlinkage void __backtrace(void)函数,其采用汇编实现,同样可以获取栈信息(x86下没有这个同名函数)。汇编实现位于arch/arm/lib/backtrace.S中:
@ fp is 0 or stack frame
#define frame r4
#define sv_fp r5
#define sv_pc r6
#define mask r7
#define offset r8
ENTRY(__backtrace)
mov r1, #0x10
mov r0, fp
ENTRY(c_backtrace)
#if !defined(CONFIG_FRAME_POINTER) || !defined(CONFIG_PRINTK)
mov pc, lr
#else
stmfd sp!, {r4 - r8, lr} @ Save an extra register so we have a location...
movs frame, r0 @ if frame pointer is zero
beq no_frame @ we have no stack frames
......