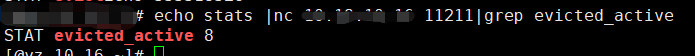Memcached LRU淘汰策略,以及数据丢失问题
0x01 问题说明:
有两个服务,一个服务A会先通过get操作到memcached中拿图片c,如果返回为空会去对象存储系统中拿图片c然后缓存在memcached中,超时时间设置为一周,然后返回mc_key信息,另外一个服务B会拿这个mc_key信息去memcached中获取保存的图片。这个是个异步的过程。
然后线上出现一个诡异的问题,A服务已经在memcached中get到了这个图片(日志中打印:picture already in memcached),但是B服务拿着mc_key去取这个图片的时候却找不到这个图了,看日志相隔时间不超过50ms左右
memcached memcached -m 16384M -p 11211 -c 8096 -I 20M
memcached版本是1.5.4
内存足够大不至于50ms就把一个位于LRU头部的数据给淘汰了。以前用的是1.4.x的版本,最近升级到1.5.x发现有这个问题。
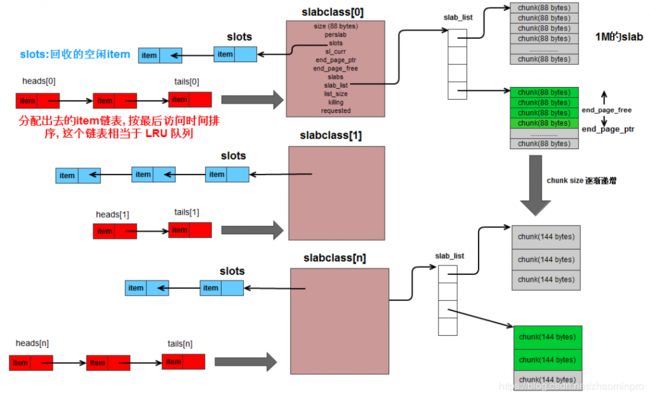
0x02 memcached内存模型
然后我们就来看看memcached的LRU吧。
首先要知道的概念:
slab: memcached中会有多个,是内存分级用的。不同层级的slab归做一类,叫做:slabclass,结构体如下:
typedef struct {
unsigned int size; /* sizes of items */
unsigned int perslab; /* how many items per slab */
//这个是用来保存空闲item的
void *slots; /* list of item ptrs */
unsigned int sl_curr; /* total free items in list */
void *end_page_ptr; /* pointer to next free item at end of page, or 0 */
unsigned int end_page_free; /* number of items remaining at end of last alloced page */
unsigned int slabs; /* how many slabs were allocated for this class */
void **slab_list; /* array of slab pointers */
unsigned int list_size; /* size of prev array */
unsigned int killing; /* index+1 of dying slab, or zero if none */
size_t requested; /* The number of requested bytes */
} slabclass_t;
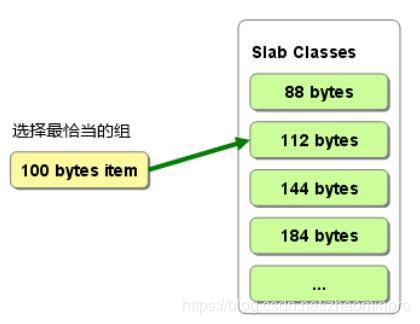
chunk:slab中的一个内存空间。slab就是按照不同大小的chunk来分级的。从下图中可以看到chunk的size是逐渐增大,这个增大的量级是由增长因子决定的,默认1.25。
可以用如下命令查看:

之间的关系就是这样的:
slabclass是由chunk size确定的, 同一个slabclass内的chunk大小都一样, 每一个slabclass 要负责管理一些内存, 初始时, 系统为每个 slabclass 分配一个 slab, 一个 slab 就是一个内存块, 其大小等于1M(这个可通过-I指定). 然后每个slabclass 再把 slab 切分成一个个 chunk, 算一下, 一个 slab 可以切分得到 1M/chunk_size 个chunk.
item: memcached中保存数据的结构体,也是LRU链表中的node,数据也就是保存在item中的,结构如下:
/**
* Structure for storing items within memcached.
*/
typedef struct _stritem {
struct _stritem *next;
struct _stritem *prev;
struct _stritem *h_next; /* hash chain next */
rel_time_t time; /* least recent access */
rel_time_t exptime; /* expire time */
int nbytes; /* size of data */
unsigned short refcount;
uint8_t nsuffix; /* length of flags-and-length string */
uint8_t it_flags; /* ITEM_* above */
uint8_t slabs_clsid;/* which slab class we're in */
uint8_t nkey; /* key length, w/terminating null and padding */
/* this odd type prevents type-punning issues when we do
* the little shuffle to save space when not using CAS. */
union {
uint64_t cas;
char end;
} data[];
/* if it_flags & ITEM_CAS we have 8 bytes CAS */
/* then null-terminated key */
/* then " flags length\r\n" (no terminating null) */
/* then data with terminating \r\n (no terminating null; it's binary!) */
} item;
大体是这个样子的:
memcached的LRU就是靠item连接成的双向链表。
添加一个item的方法:(可以看到新节点都是之间添加到链表头部的)
static void do_item_link_q(item *it) { /* item is the new head */
item **head, **tail;
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0);
head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid];
tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid];
assert(it != *head);
assert((*head && *tail) || (*head == 0 && *tail == 0));
it->prev = 0;
it->next = *head;
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it;
*head = it;
if (*tail == 0) *tail = it;
sizes[it->slabs_clsid]++;
return;
}
移除一个item:
static void do_item_unlink_q(item *it) {
item **head, **tail;
head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid];
tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid];
if (*head == it) {
assert(it->prev == 0);
*head = it->next;
}
if (*tail == it) {
assert(it->next == 0);
*tail = it->prev;
}
assert(it->next != it);
assert(it->prev != it);
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it->prev;
if (it->prev) it->prev->next = it->next;
sizes[it->slabs_clsid]--;
return;
}
0x03 新版本的分段LRU
基本知识了解这些差不多够了。在老版本中memcached的LRU是一个很典型的实现了,最近访问的应该bump到head位置,但是新版本做了一些改变,将LRU分段了(Segmented LRU)。这也就是导致我开篇就说的问题的原因,具体我慢慢分析。
我们先看看memcached的官方文档,将LRU分成了:HOT WARM COLD TEMP
为什么要分段?主要是为了降低锁竞争,提升效率。
每个 item 有一个 flag,存储在其元数据中,标识其活跃程度:
- FETCHED:如果一个 item 有请求操作,其 flag 等于 FETCHED。
- ACTIVE:如果一个 item 第二次被请求则会标记为 ACTIVE;当一个 item 发生 bump 或被删除了,flag 会被清空。
- INACTIVE:不活跃状态。
item在他们之间的变化规则是这样的:
- 新来的item都加到HOT中
- 一个item被访问两次就标记为active状态
- (随着新item不断的加入),如果item移动到了链表的bottom。
- 如果是在HOT LRU中且为active状态,则把这个item直接移入WARM,否则加入COLD;
- 如果是在WARM中,且是active状态那么把这个item提到WARM链表的开头,否则移动到COLD中;
- COLD中的item是最惨的,他们都是inactive状态。当内存满了的时候就要开始淘汰他们中的一些
- COLD中的item如果变成了active状态后,会被放入队列,然后异步(注意是异步的哦)移动到WARM中
- HOT和WARM的大小是受限的,占该slab class内存量的N%, COLD 大小是不受限的
具体状态图如下:
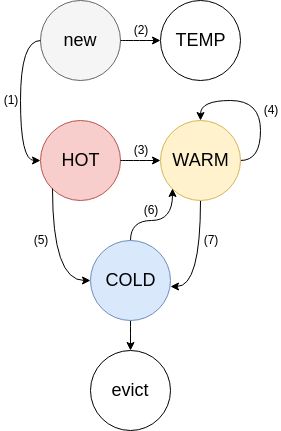
上面第5点要关注哦。是异步,并不是立马就移动到WARM中,所以,在COLD中的item变成active后还是可能被淘汰。
引用下别人的,当新来一个item时候的流程:
1.do_item_alloc进入新增item的内存申请流程。
2.do_item_alloc_pull进入item申请的逻辑处理,最多处理10次。
3.do_item_alloc_pull内部逻辑是尝试通过slabs_alloc申请内存,失败则尝试通过lru_pull_tail方法释放LRU队列中的item变成可用item。
4.lru_pull_tail执行释放LRU队列中item的过程,内部包括各种过期item的回收
5.在lru_pull_tail当中调用do_item_unlink_nolock进行item回收
6.在do_item_unlink_nolock当中调用do_item_unlink_q释放LRU链表,调用do_item_remove回收item为可用item。
下面这两段代码是一个新的item来的时候如何处理:
item *do_item_alloc(char *key, const size_t nkey, const unsigned int flags,
const rel_time_t exptime, const int nbytes) {
uint8_t nsuffix;
item *it = NULL;
char suffix[40];
size_t ntotal = item_make_header(nkey + 1, flags, nbytes, suffix, &nsuffix);
unsigned int id = slabs_clsid(ntotal);
unsigned int hdr_id = 0;
if (ntotal > settings.slab_chunk_size_max) {
int htotal = nkey + 1 + nsuffix + sizeof(item) + sizeof(item_chunk);
if (settings.use_cas) {
htotal += sizeof(uint64_t);
}
hdr_id = slabs_clsid(htotal);
it = do_item_alloc_pull(htotal, hdr_id);
if (it != NULL)
it->it_flags |= ITEM_CHUNKED;
} else {
it = do_item_alloc_pull(ntotal, id);
}
// 省略一堆代码
return it;
}
item *do_item_alloc_pull(const size_t ntotal, const unsigned int id) {
item *it = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
uint64_t total_bytes;
if (!settings.lru_segmented) {
lru_pull_tail(id, COLD_LRU, 0, 0, 0, NULL);
}
// 先尝试申请新的内存
it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id, &total_bytes, 0);
if (settings.temp_lru)
total_bytes -= temp_lru_size(id);
if (it == NULL) {
//这里要尤其注意哦,待会我会提到。这里的意思就是如果内存满了,就要从LRU尾部开始淘汰数据了,注意传入了LRU_PULL_EVICT。这个表示直接剔除,而不是报错。
// 再尝试lru_pull_tail执行COLD_LRU当中释放item
if (lru_pull_tail(id, COLD_LRU, total_bytes, LRU_PULL_EVICT, 0, NULL) <= 0) {
if (settings.lru_segmented) {
// 最后尝试lru_pull_tail执行HOT_LRU当中释放item
lru_pull_tail(id, HOT_LRU, total_bytes, 0, 0, NULL);
} else {
break;
}
}
} else {
break;
}
}
return it;
}
可以看到会先申请内存,如果申请失败的话,就会调用lru_pull_tail(id, COLD_LRU, total_bytes, LRU_PULL_EVICT, 0, NULL)这个函数就是淘汰COLD LRU尾部节点
int lru_pull_tail(const int orig_id, const int cur_lru,
const uint64_t total_bytes, const uint8_t flags, const rel_time_t max_age,
struct lru_pull_tail_return *ret_it) {
item *it = NULL;
int id = orig_id;
int removed = 0;
int tries = 5;
item *search;
item *next_it;
void *hold_lock = NULL;
unsigned int move_to_lru = 0;
uint64_t limit = 0;
id |= cur_lru;
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[id]);
// 获取slabclass对应id的LRU队列的队尾元素
search = tails[id];
for (; tries > 0 && search != NULL; tries--, search=next_it) {
next_it = search->prev;
// 如果item内容为空,则继续往LRU列表尾部搜索。
if (search->nbytes == 0 && search->nkey == 0 && search->it_flags == 1) {
if (flags & LRU_PULL_CRAWL_BLOCKS) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[id]);
return 0;
}
tries++;
continue;
}
// 如果item被其它worker引用锁定等情况,则继续往LRU列表尾部搜索。
uint32_t hv = hash(ITEM_key(search), search->nkey);
if ((hold_lock = item_trylock(hv)) == NULL)
continue;
if (refcount_incr(search) != 2) {
itemstats[id].lrutail_reflocked++;
if (settings.tail_repair_time &&
search->time + settings.tail_repair_time < current_time) {
itemstats[id].tailrepairs++;
search->refcount = 1;
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
continue;
}
}
if ((search->exptime != 0 && search->exptime < current_time)
|| item_is_flushed(search)) {
itemstats[id].reclaimed++;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) {
itemstats[id].expired_unfetched++;
}
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
STORAGE_delete(ext_storage, search);
do_item_remove(search);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
removed++;
continue;
}
/* If we're HOT_LRU or WARM_LRU and over size limit, send to COLD_LRU.
* If we're COLD_LRU, send to WARM_LRU unless we need to evict
*/
switch (cur_lru) {
case HOT_LRU:
limit = total_bytes * settings.hot_lru_pct / 100;
case WARM_LRU:
if (limit == 0)
limit = total_bytes * settings.warm_lru_pct / 100;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_ACTIVE) != 0) {
search->it_flags &= ~ITEM_ACTIVE;
removed++;
if (cur_lru == WARM_LRU) {
itemstats[id].moves_within_lru++;
do_item_update_nolock(search);
do_item_remove(search);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
} else {
itemstats[id].moves_to_warm++;
move_to_lru = WARM_LRU;
do_item_unlink_q(search);
it = search;
}
} else if (sizes_bytes[id] > limit ||
current_time - search->time > max_age) {
itemstats[id].moves_to_cold++;
move_to_lru = COLD_LRU;
do_item_unlink_q(search);
it = search;
removed++;
break;
} else {
/* Don't want to move to COLD, not active, bail out */
it = search;
}
break;
case COLD_LRU:
//重点就直接看这里吧
it = search; /* No matter what, we're stopping */
if (flags & LRU_PULL_EVICT) {
if (settings.evict_to_free == 0) {
/* Don't think we need a counter for this. It'll OOM. */
break;
}
itemstats[id].evicted++;
itemstats[id].evicted_time = current_time - search->time;
if (search->exptime != 0)
itemstats[id].evicted_nonzero++;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) {
itemstats[id].evicted_unfetched++;
}
//可以看到如果是EVICT的话,就算你是active状态也会把你移除
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_ACTIVE)) {
//可以通过stats|grep evicted_active命令查看
itemstats[id].evicted_active++;
}
LOGGER_LOG(NULL, LOG_EVICTIONS, LOGGER_EVICTION, search);
STORAGE_delete(ext_storage, search);
//强制移除
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
removed++;
if (settings.slab_automove == 2) {
slabs_reassign(-1, orig_id);
}
} else if (flags & LRU_PULL_RETURN_ITEM) {
/* Keep a reference to this item and return it. */
ret_it->it = it;
ret_it->hv = hv;
} else if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_ACTIVE) != 0
&& settings.lru_segmented) {
itemstats[id].moves_to_warm++;
search->it_flags &= ~ITEM_ACTIVE;
move_to_lru = WARM_LRU;
do_item_unlink_q(search);
removed++;
}
break;
case TEMP_LRU:
it = search; /* Kill the loop. Parent only interested in reclaims */
break;
}
if (it != NULL)
break;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[id]);
if (it != NULL) {
if (move_to_lru) {
it->slabs_clsid = ITEM_clsid(it);
it->slabs_clsid |= move_to_lru;
item_link_q(it);
}
if ((flags & LRU_PULL_RETURN_ITEM) == 0) {
do_item_remove(it);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
}
}
return removed;
}
void do_item_unlink_nolock(item *it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_UNLINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
if ((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) != 0) {
it->it_flags &= ~ITEM_LINKED;
STATS_LOCK();
stats_state.curr_bytes -= ITEM_ntotal(it);
stats_state.curr_items -= 1;
STATS_UNLOCK();
item_stats_sizes_remove(it);
assoc_delete(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, hv);
// 从LRU的链表中删除
do_item_unlink_q(it);
// 回收到可用的item列表当中
do_item_remove(it);
}
}
通过上面代码注释的地方可以看到,要是item进入了COLD里面,还是evict的话,那就算你是active的话也会直接强制移除。
可以通过如下命令查看
默认在1.4.X中的版本中是没有开启分段LRU的,但是1.5里面是默认开启的。如果你用的是1.5而且还是evict模式的话就要注意你的信息可能被删了。而且就是你设置的是永不过期也会删。
可以使用-M 参数( 内存耗尽时返回错误,而不是删除项)。
(图中部分图片来自于一下参考)
参考:
官网关于分段锁的解释:https://memcached.org/blog/modern-lru/
一篇讲源码分析的https://www.jianshu.com/p/bbd24ba0ad62
https://toutiao.io/posts/5ivota/preview
https://github.com/memcached/memcached/blob/3b11d16b3f92c51bfedbb092147e1c2b225945ff/doc/new_lru.txt
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhoujinyi/p/5554083.html
https://blog.csdn.net/yxnyxnyxnyxnyxn/article/details/7869900
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a99ecc052756