决策树分类算法-ID3
实现的功能:
1、对数值型数据和标称型数据 进行分类
2、可将决策树pickle于txt文件中
但是本人在scikit_learn包中 暂时没成功处理标称型数据
trees.py
'''
Created on 2018年7月27日
@author: hcl
'''
from math import log
import operator
import numpy as np
def createDataSet():
'''
产生测试数据
数据特征:[x1,x2,y] 两个特征 一个输出
那么label 代表的是特征的名字
'''
dataSet = [[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no']]
feature_names = ['no surfacing','flippers']
return dataSet, feature_names
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
'''
计算给定数据集的香农熵
'''
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
#统计每个类别出现的次数,保存在字典labelCounts中
for featVec in dataSet:
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #如果当前键值不存在,则扩展字典并将当前键值加入字典
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
#使用所有类标签的发生频率计算类别出现的概率
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
#用这个概率计算香农熵
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) #取2为底的对数
return shannonEnt
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
'''
按照给定特征划分数据集
dataSet:待划分的数据集
axis: 划分数据集的第axis个特征
value: 特征的返回值(比较值)
'''
retDataSet = []
#遍历数据集中的每个元素,一旦发现符合要求的值,则将其添加到新创建的列表中
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
#下面两句代表去除了featVec[axis]
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
#再将去除后的值进行追加至新数据集
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
#返回去除 第axis特征值 = value 以后的数据集
return retDataSet
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
'''
选择最好的数据集划分方式
输入:数据集
输出:最优分类的特征的index
'''
#计算特征数量
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures):
#创建唯一的分类标签列表 取出第i列的特征集合 并做去重处理
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
#计算每种划分方式的信息熵
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
#计算最好的信息增益,即infoGain越大划分效果越好
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain):
bestInfoGain = infoGain
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature
def majorityCnt(classList):
'''
投票表决函数
输入classList:标签集合,本例为:['yes', 'yes', 'no', 'no', 'no']
输出:得票数最多的分类名称
'''
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys(): classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
#把分类结果进行排序,然后返回得票数最多的分类结果
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def createTree(dataSet,labels):
'''
创建树
输入:数据集和标签列表 ;要对首次传入labels值时进行copy 因为后面出现了del(label)的操作,对原始数据有影响
输出:树的所有信息
'''
# classList为数据集的所有类标签
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
# 停止条件1:所有类标签完全相同,直接返回该类标签 如果 第一个标签长的长度 == 总标签的长度 --》 标签完全相同
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]
# 停止条件2:遍历完所有特征时仍不能将数据集划分成仅包含唯一类别的分组,则返回出现次数最多的类标签
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1:
return majorityCnt(classList)
# 选择最优分类特征
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatName = labels[bestFeat]
# myTree存储树的所有信息
myTree = {bestFeatName:{}}
# 以下得到列表包含的所有属性值
del(labels[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
#遍历当前选择特征包含的所有属性值
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:]
myTree[bestFeatName][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels)
return myTree
def classify(inputTree,feature_names,testVec):
'''
决策树的分类函数
inputTree:训练好的树信息
feature_names:标签列表
testVec:测试向量
'''
# 在2.7中,找到key所对应的第一个元素为:firstStr = myTree.keys()[0],
# 这在3.4中运行会报错:‘dict_keys‘ object does not support indexing,这是因为python3改变了dict.keys,
# 返回的是dict_keys对象,支持iterable 但不支持indexable,
# 我们可以将其明确的转化成list,则此项功能在3中应这样实现:
firstSides = list(inputTree.keys()) #['no surfacing'] ; ['flippers']
firstStr = firstSides[0] #no surfacing ; flippers
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr] #{0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}} ; {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}
# 将标签字符串转换成索引
featIndex = feature_names.index(firstStr) # 0; 1
key = testVec[featIndex] # 1; 0
valueOfFeat = secondDict[key] # {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}};no
# 递归遍历整棵树,比较testVec变量中的值与树节点的值,如果到达叶子节点,则返回当前节点的分类标签
# isinstance用于判断对象的类型
if isinstance(valueOfFeat, dict):
classLabel = classify(valueOfFeat, feature_names, testVec)
else:
classLabel = valueOfFeat
return classLabel
def storeTree(inputTree,filename):
'''
使用pickle模块存储决策树
'''
import pickle
fw = open(filename,'wb+')
pickle.dump(inputTree,fw)
fw.close()
def grabTree(filename):
'''
导入决策树模型
'''
import pickle
fr = open(filename,'rb')
return pickle.load(fr)
if __name__== "__main__":
dataSet,feature_names = createDataSet()
myTree = createTree(dataSet, feature_names.copy())
ans = classify(myTree,feature_names,[1,0])
print(ans)
# storeTree(myTree,'mt.txt')
# myTree2 = grabTree('mt.txt')
# print(myTree2)
通过matlibplot 绘制决策树
trees_plot.py
'''
Created on 2018年7月27日
@author: hcl
'''
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义文本框和箭头格式
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
# 绘制带箭头的注释
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args )
def createPlot(inTree):
'''
绘树主函数
'''
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
# 设置坐标轴数据
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
# 无坐标轴
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
# 带坐标轴
# createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
# 两个全局变量plotTree.xOff和plotTree.yOff追踪已经绘制的节点位置,
# 以及放置下一个节点的恰当位置
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0;
plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '')
plt.show()
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
'''
获取叶节点的数目
'''
numLeafs = 0
firstSides = list(myTree.keys())
firstStr = firstSides[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
# 判断节点是否为字典来以此判断是否为叶子节点
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else: numLeafs +=1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
'''
获取树的层数
'''
maxDepth = 0
firstSides = list(myTree.keys())
firstStr = firstSides[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else: thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
'''
计算父节点和子节点的中间位置,并在此处添加简单的文本标签信息
'''
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):#if the first key tells you what feat was split on
# 计算宽与高
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #this determines the x width of this tree
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstSides = list(myTree.keys())
firstStr = firstSides[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
# 标记子节点属性值
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
# 减少y偏移
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key)) #recursion
else: #it's a leaf node print the leaf node
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD
def retrieveTree(i):
'''
保存了树的测试数据
'''
listOfTrees =[{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}},
{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: {'head': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'no'}}}}
]
return listOfTrees[i]
if __name__== "__main__":
'''
绘制树
'''
createPlot(retrieveTree(0))输出:
预测隐形眼睛分类
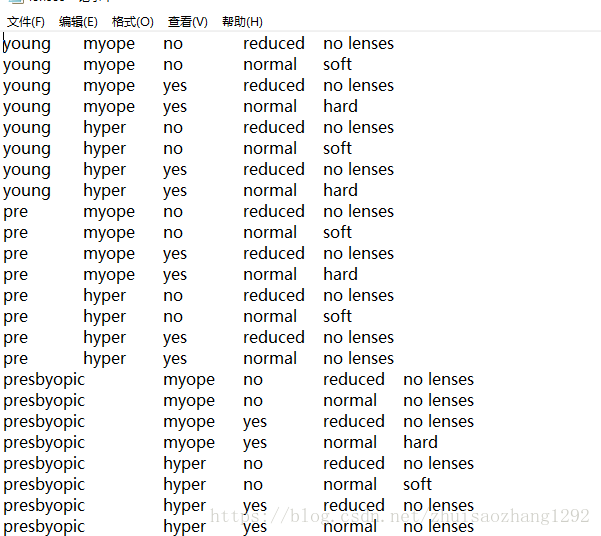
数据集:
输入 test.py
'''
Created on 2018年7月26日
@author: hcl
'''
import trees
import trees_plot
fr = open('lenses.txt')
lenses = [inst.strip().split('\t') for inst in fr.readlines()]
lensesLabels=['age','prescript','astigmatic','tearRate']
lensesTree = trees.createTree(lenses,lensesLabels)
trees_plot.createPlot(lensesTree)输出: