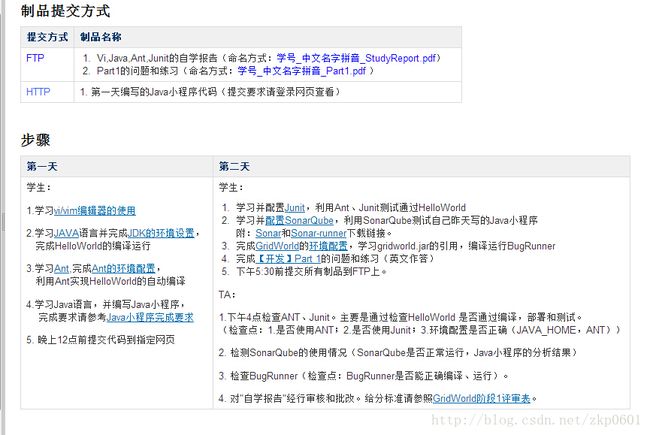
中山大学软件学院中级实训-GridWorld
为期两周的实训总算是快结束了,虽然还有一天,但是这两天去实验室基本上不是为了赶任务而是为了能按时签到签退。这次实训总体来说还是挺简单的( 凭良心说,而不是自己很厉害 ),至少比起大一的Agenda简直是轻松许多。原因一方面可能是因为这次实训用 JAVA,要让大家在短期内熟悉一门语言的使用,另一方面,也可能是因为比起11级的确实删减了一些内容 。话说回来,虽然这是一门刚接触的语言,但是相信大家都不会陌生,因为它的使用跟C++很相像,或者说比C++容易上手多了。实训前两个阶段重点是为了让我们熟悉整个项目即gridworld,目的是让我们通过了解这个项目来掌握JAVA语言的使用,同时也让我们多了解一些编程工具等的使用,比如 Eclipse, Junit, sonar, ant 等。其中Eclipse软件我们不一定需要学会使用,但是我想说,如果你会Eclipse, 你在完成一些任务的时候真的是方便不少,至少比起ubuntu的终端要好多了!
废话不说太多,下面就大概讲下这次实训的情况吧。因为平时在完成一些任务的时候,深刻感受到前人经验带给自己的便利,在此我也分享下自己的东西,希望能给后人乘荫吧~!
第一阶段是让我们学会基本的工具,方便接下来的两个阶段能让我们用这些工具检测之类的。下面是这一阶段需要掌握的东西 :
关于 Ant:
使用 Ant 是为了实现项目的自动部署与构建,简单点说就是不用我们在终端输入javac XXX.java编译然后又要用java XXX去运行,它可以一步实现这些步骤。此外我们还能利用它来打包一些文件,包括.class类等。具体使用方法就是要事先创建 build.xml文件并置于代码根目录中,然后在终端进入到 build.xml 所在目录并运行 ant。或者利用eclipse 运行 build.xml 文件,运行时可选择 Run as Ant_Build。使用 Ant 过程中,最重要的就是 build.xml 文件的编写了。不过每次在利用 Ant 进行编译的时候,经常会提示一个警告 warning: 'includeantruntime' was not set, defaulting tobuild.sysclasspath=last; set to false for repeatable build。虽然这对运行结果没影响,但 是 自 己 还 是 去 查 了 。 最 后 发 现 只 要 在 编 译 时 < j a v a c s r c d i r = " s r c "destdir="build/classes"/>的最后加上 includeAntRuntime="flase" 便可解决。
关于 Junit:
元数据是描述数据的数据一样来修饰类名,作用是描述这个数据是做什么的。Junit 是为了检测代码中所定义的各类函数是否有 bug。在利用 Junit 进行测试时有如下说明:①、JUnit3 要求单元测试类必须继承自 TestCase 且测试的方法必须以 test 开头
②、JUnit4 不要求必须继承自 TestCase,而且测试方法不必以 test 开头,只要@Test元数据来描述即可;
③、元数据:
使用了@Before 元数据时在每个测试执行之前都要一次。
使用了@After 元数据时在每个测试执行之后要一次。
使用了@ignore 元数据时,被标记的测试方法会被忽略。
使用了@BeforeClass 元数据时,在所有测试开始时运行一次
使用了@AfterClass 元数据时,在所有测试结束后运行一次
限时测试: 在@Test 后面加(timeout = ..) 如果在规定的时间内没有完成测试就报错
我个人是在 Eclipse 下进行 Junit 测试的,首先是对需要测试的类右键,之后便可按提示自动创建 Test 类文件,最后完善所要检测的各函数便可查看结果。而在终端输 入命令进行测试时, 首先把要测试的类、 进行测试的 Test.java 文件和 junit 的 jar 包放在同个文件夹,否则可能会因为找不到 jar 包而出现各类错误等。
关于 Sonar:
Sonar 是一款用于检测代码质量的工具,可通过代码的测试覆盖率、代码复杂度、重复性检查等各方面对代码进行一个量化。
利用 Sonar 进行代码质量测试时,我们首先需要创建一个 sonar-project.properties配置文件并置于需检测的代码根目录中,进入 SONAR_HOME 运行 ./sonar.sh start 开启Sonar服务, 然后进入包含sonar-project.properties配置文件的目录中运行sonar-runner命令,最后上 localhost:9000 查看。Sonar 检测时会逐条列出我们代码需要完善的地方,比 如 一 个 函 数 太 多 行 、 magic number 、 用 空 格 代 替 Tab 、 catch 中 不 能 使 用printStackTrace()函数而应该使用 log 等, 虽然评分时很严格, 但确实是让我们的代码质量有了很大提升。(其实我好像说Sonar好傻,什么都报!!!不过习惯就好,还好sonar 评分上60%就达到要求了)
而关于阶段二,目的就是让我们深入地去了解gridworld,进一步掌握里面各种 Actor 的属性行为等。写代码的那些实话说挺简单的,而繁琐一点的就是那些文档 —— 即各个Part 的练习什么的,重点是要用英文作答。不过,我们还是有神器的。
http://apcentral.collegeboard.com/apc/members/repository/ap07_gridworld_solutions_doc_v2.pdf
最后重点还是第三个阶段。虽然本阶段名义上属于 gridworld 范畴,但其实它跟 gridworld 还是没有什么关联的。
阶段三分为三部分,第一部分是ImageReader,要我们实现一个关于图片读取的软件,且要求我们不能直接使用 JAVA 自带的API进行读取。除了一个Runner ,我们需要实现两个接口 IImageIO 和 IImageProcessor. 在做本任务前,我们要再重新学习下关于位运算的知识:
1、& 表示两个字节做与运算;2、 | 表示两个字接做或运算; 3、<< 表示向左移动多少位;4、>> 表示向右移动多少位;
实验要求
1. 利用二进制流读取bitmap位图文件。注意,这里要求不能使用java提供的api直接读取图像,根据二进制数据创建image时可以使用api;
2. 把读取彩色图像转换成灰度图像;
3. 提取并且显示彩色图像各个色彩通道;
4. 把处理完的图像保存为bmp格式图像。注意,这里可以使用java提供的api完成,但本文档不提供,希望各位同学自行上网查找资料自学。如果学有余力的同学,可以实现按照二进制流输出保存bmp图像;
5. 编写junit测试程序,测试输出的图片是否与goal文件夹下的图片一致。(比较位图宽度、位图高度以及像素值);
实现IImageIO代码如下:
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.ImageProducer;
import java.awt.image.MemoryImageSource;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import imagereader.IImageIO;
public class MyImageIO implements IImageIO{
Image img;
public Image myRead(String filePath){
File file = new File(filePath);
try{
//创建FileInputStream类对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//创建byte对象,分别存储位图头及位图信息
byte bmpHead[] = new byte[14];
byte bmpInfo[] = new byte[40];
fis.read(bmpHead, 0, 14);
fis.read(bmpInfo, 0, 40);
//读取位图头#2-5字节,保存位图文件大小
int sizeOfbmpHead = (int)( (bmpHead[5] & 0xff) << 24 | (bmpHead[5] & 0xff) << 16
| (bmpHead[3] & 0xff) << 8 | (bmpHead[2] & 0xff) );
//读取位图信息,保存位图大小,每一个像素为3个字节
int sizeOfbmpInfo = (int)( (bmpInfo[23] & 0xff) << 24 | (bmpInfo[22] & 0xff) << 16
| (bmpInfo[21] & 0xff) << 8 | (bmpInfo[20] & 0xff) );
//读取位图宽度,单位为像素
int widthOfbmpInfo = (int)( (bmpInfo[7] & 0xff) << 24 | (bmpInfo[6] & 0xff) << 16
| (bmpInfo[5] & 0xff) << 8 | (bmpInfo[4] & 0xff) );
//读取位图高度,单位为像素
int heightOfbmpInfo = (int)( (bmpInfo[11] & 0xff) << 24 | (bmpInfo[10] & 0xff) << 16
| (bmpInfo[9] & 0xff) << 8 | (bmpInfo[8] & 0xff) );
//读取位图信息#28-29位,即bmpInfo#14-15位,判断位图是否为24位
int byteNumOfbmp = (int)( (bmpInfo[15] & 0xff) << 8 | (bmpInfo[14] & 0xff) );
if (byteNumOfbmp == 24){
//由于像素使用的字节若不是4的倍数,则会自动扩大,由此产生空白。因此我们需要在一开始计算出空白的大小
int numOfEmptyByte = sizeOfbmpInfo / heightOfbmpInfo - 3*widthOfbmpInfo;
if(numOfEmptyByte == 4) {
numOfEmptyByte = 0;
}
//定义数组从左到右,从下到上存储每个像素
int temp = 0;
int pixelArray[] = new int [widthOfbmpInfo * heightOfbmpInfo];
byte bmpTotalByte[] = new byte[sizeOfbmpInfo];
fis.read(bmpTotalByte, 0, sizeOfbmpInfo);
for(int i = heightOfbmpInfo-1; i >= 0; i-- ){
for( int j = 0; j < widthOfbmpInfo; j++ ){
//第一个0xff << 24表示透明度
pixelArray[ widthOfbmpInfo * i + j ] = 0xff << 24
| (bmpTotalByte[temp+2] & 0xff) << 16
| (bmpTotalByte[temp+1] & 0xff) << 8
| (bmpTotalByte[temp] & 0xff) ;
temp += 3;
}
temp += numOfEmptyByte;
}
img = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().createImage((ImageProducer) new MemoryImageSource(
widthOfbmpInfo, heightOfbmpInfo, pixelArray, 0, widthOfbmpInfo));
}
fis.close();
return img;
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return (Image) null;
}
//根据二进制数据创建Image时可以使用API public Image myWrite (Image img, String filepath){
try{
File imgFile = new File(filepath + "bmp");
BufferedImage buffer = new BufferedImage(img.getWidth(null), img.getHeight(null), BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics2D graph = buffer.createGraphics();
graph.drawImage(img, 0, 0, null);
graph.dispose();
ImageIO.write(buffer, "bmp", imgFile );
return img;
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return img;
}
}
import imagereader.IImageProcessor;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.image.FilteredImageSource;
import java.awt.image.RGBImageFilter;
public class MyImageProcessor implements IImageProcessor{
public Image showChanelR(Image sourceImage){
ColorFilter redFilter = new ColorFilter(1);
Toolkit toolKit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Image img = toolKit.createImage(new FilteredImageSource(sourceImage.getSource(), redFilter));
return img;
}
public Image showChanelG(Image sourceImage){
ColorFilter greenFilter = new ColorFilter(2);
Toolkit toolKit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Image img = toolKit.createImage(new FilteredImageSource(sourceImage.getSource(), greenFilter));
return img;
}
public Image showChanelB(Image sourceImage){
ColorFilter blueFilter = new ColorFilter(3);
Toolkit toolKit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Image img = toolKit.createImage(new FilteredImageSource(sourceImage.getSource(), blueFilter));
return img;
}
public Image showGray(Image sourceImage){
ColorFilter grayFilter = new ColorFilter(4);
Toolkit toolKit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Image img = toolKit.createImage(new FilteredImageSource(sourceImage.getSource(), grayFilter));
return img;
}
}
class ColorFilter extends RGBImageFilter{
private int colorNum;
public ColorFilter(int c){
colorNum = c;
canFilterIndexColorModel = true;
}
public int filterRGB(int x, int y, int rgb){
if(colorNum==1){
return ( rgb & 0xffff0000 );
}else if(colorNum==2){
return ( rgb & 0xff00ff00 );
}else if(colorNum==3){
return ( rgb & 0xff0000ff );
}else{
int g = (int)( ((rgb & 0x00ff0000) >> 16)*0.299 + ((rgb & 0x0000ff00) >> 8 )*0.587
+ ((rgb & 0x000000ff))*0.114 );
return (rgb & 0xff000000) + (g << 16) + (g << 8) + g;
}
}
}
Runner 代码:
import imagereader.Runner;
public class Run {
public static void main(String args[]){
MyImageIO myImageIO = new MyImageIO();
MyImageProcessor myImageProcessor = new MyImageProcessor();
Runner.run(myImageIO, myImageProcessor);
}
}
第二部分是关于迷宫的问题,就是利用DFS找到迷宫的正确路径。做这道题需要标记地图上哪些位置走过哪些没走过。由于Bug走的时候会在身后留下一朵花,因此有个小窍门就是有花的地方我们就不再找。
刚开始一直纠结为何是stack
0: (0, 0) //栈的初始状态
1: (0, 0), (0, 1) | (0,1) //走到(0,1)是的栈状态,我用|分割不同arraylist
2: (0, 0), (0, 1) | (0, 1), (0, 2) | (0, 2) //走到(0,2)是的栈状态
3: (0, 0), (0, 1) | (0, 1), (0, 2) //假如不能再走,则pop一下
4: (0, 0), (0, 1) | (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 1) | (1, 1) //取出(0, 1)即栈顶链表的第一个元素,找到可以走的点(1, 1),为何不是(0, 2)了呢?因为已经在链表中,证明已经走过了。这样就对为何使用arraylist有所理解了。
import info.gridworld.actor.Actor;
import info.gridworld.actor.Bug;
import info.gridworld.actor.Flower;
import info.gridworld.actor.Rock;
import info.gridworld.grid.*;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Stack;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
/**
* A MazeBug can find its way in a maze.
* The implementation of this class is testable on the AP CS A and AB exams.
*/
public class MazeBug extends Bug {
public Location next;
public boolean isEnd = false;
public Stack> crossLocation = new Stack>();
public Integer stepCount = 0;
public Stack trueWay = new Stack();
boolean hasShown = false;//final message has been shown
private int[] probility = {1, 1, 1, 1};
/**
* Constructs a box bug that traces a square of a given side length
*
* @param length
* the side length
*/
public MazeBug() {
setColor(Color.GREEN);
}
/**
* Moves to the next location of the square.
*/
public void act() {
//add the initial location to the first array list
if(stepCount==0){
Location local = this.getLocation();
directionPredic();
ArrayList first = new ArrayList();
first.add(local);
trueWay.push(local);
crossLocation.add(first);
}
if(stepCount==341){
directionPredic();
}
boolean willMove = canMove();
if (isEnd == true) {
setRightWay(trueWay);
//to show step count when reach the goal
if (hasShown == false) {
String msg = stepCount.toString() + " steps";
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, msg);
hasShown = true;
}
} else if (willMove) {
move();
//increase step count when move
stepCount++;
} else {
//If can't move, return to last location
goBack();
}
}
/**
* Find all positions that can be move to.
*
* @param loc
* the location to detect.
* @return List of positions.
*/
public ArrayList getValid(Location loc) {
Grid g = getGrid();
if (g == null)
return null;
ArrayList valid = new ArrayList();
//get the valid location of the determined four direction
int[] dir = {Location.NORTH, Location.EAST, Location.SOUTH, Location.WEST};
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ ){
Location location = loc.getAdjacentLocation(dir[i]);
if(g.isValid(location)){
Actor actor = g.get(location);
//if the goal is around, return the location of the goal
if(( actor instanceof Rock) && actor.getColor().equals(Color.RED) ){
next = location;
ArrayList tar = new ArrayList();
tar.add(next);
return tar;
}else if(actor == null){
valid.add(location);
}
}
}
return valid;
}
/**
* Tests whether this bug can move forward into a location that is empty or
* contains a flower.
*
* @return true if this bug can move.
*/
public boolean canMove() {
ArrayList validLocation = new ArrayList();
Location current = this.getLocation();
validLocation = getValid(current);
if (validLocation.size() == 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Moves the bug forward, putting a flower into the location it previously
* occupied.
*/
public void move() {
Grid g = getGrid();
if (g == null)
return;
Location loc = this.getLocation();
ArrayList chooseLocation = getValid(loc);
//根据当前每个方向走了多少次来分配概率。某一方向走的步数最多,则往该方向概率最大
int max = 0;
int j = 0;
int total = 0;
int whichOne = 0;
for( Location got : chooseLocation ){
int direc = loc.getDirectionToward(got);
if( probility[direc/90] > max ){
max = probility[direc/90];
j = (int) direc/90;
whichOne = total;
}
total++;
}
if(chooseLocation.size() == 1){
next = chooseLocation.get(whichOne);
probility[j]++;
}else {
int randomNumber = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
if(randomNumber >= 0 && randomNumber < 7){
next = chooseLocation.get(whichOne);
probility[j]++;
}else {
next = chooseLocation.get(randomNumber % chooseLocation.size());
int dire = loc.getDirectionToward(next);
j = dire / 90;
probility[j]++;
}
}
for( Location l : chooseLocation ){
if( this.getDirection() == this.getLocation().getDirectionToward(l) ){
next = l;
int dire = loc.getDirectionToward(next);
j = dire / 90;
probility[j]++;
break;
}
}
if (g.isValid(next)) {
Actor actor = (Actor)g.get(next);
if( actor instanceof Rock && actor.getColor().equals(Color.RED) ){
isEnd = true;
setRightWay(trueWay);
}
moveTo(next);
trueWay.push(next);
int facing = loc.getDirectionToward(next);
this.setDirection(facing);
ArrayList temp = crossLocation.pop();
temp.add(next);
crossLocation.push(temp);
ArrayList latest = new ArrayList();
latest.add(next);
crossLocation.push(latest);
} else {
removeSelfFromGrid();
}
System.out.println(stepCount);
Flower flower = new Flower(getColor());
flower.putSelfInGrid(g, loc);
}
//回溯
public void goBack(){
if (crossLocation.size() > 0) {
crossLocation.pop();
trueWay.pop();
if(crossLocation.size() > 0){
Grid g = getGrid();
if( g == null )
return;
ArrayList back = crossLocation.peek();
Location returnLocation = back.get(0);
Location current = this.getLocation();
//set the direction when the bug return
int dire = current.getDirectionToward(returnLocation);
if (g.isValid(returnLocation)) {
this.setDirection(dire);
moveTo(returnLocation);
stepCount++;
}else {
removeSelfFromGrid();
}
if ( (int)(dire/90) == 0 ) {
probility[2]--;
}else if ( (int)(dire/90) == 1 ) {
probility[3]--;
}else if ( (int)(dire/90) == 2 ) {
probility[0]--;
}else if ( (int)(dire/90) == 3 ) {
probility[1]--;
}
Flower flower = new Flower(getColor());
flower.putSelfInGrid(g, current);
}
}
}
//关于方向估计的函数,先判断终点大概位于虫子的哪个方向,然后选择位置的时候优先选择距离终点近的位置
public void directionPredic(){
Grid g = getGrid();
ArrayList array = g.getOccupiedLocations();
for( Location a : array ){
Actor act = (Actor) g.get(a);
if ( act instanceof Rock && act.getColor().equals(Color.RED)){
Location loc = this.getLocation();
if( loc.getRow() < a.getRow() ){
probility[2] = 6;
probility[0] = 1;
}else {
probility[0] = 6;
probility[2] = 1;
}
if( loc.getCol() < a.getCol() ){
probility[1] = 6;
probility[3] = 1;
}else {
probility[3] = 6;
probility[1] = 1;
}
break;
}
}
}
//此函数是为了在虫子到达终点后把正确路径标记出来
public void setRightWay(Stack way){
for( Location w : way ){
Grid g = getGrid();
Actor act = (Actor) g.get(w);
act.setColor(Color.GREEN);
}
}
}
第三部分是要我们利用广搜和启发式搜索来实现拼图问题,代码看起来多,但其实很多都是源码就已经给出的了。我们需要完成的只是一个关于BFSearch的小任务和一个估价函数。估价函数的实现其实就是要我们找到合适的估价方法和它们的权重。实训网站给出的可参考的估价方法有:
(1)所有 放错位的数码 个数; (2) 所有 放错位的数码与其正确位置的距离 之和(曼哈顿距离); (3) 后续节点不正确的数码个数;
在此基础上我自己增加了(4)几何距离,即直角三角形的斜边。在设置权重时,第1个方法我没用,感觉用了跑出来的效果没那么好,用了后三种且比例按顺序为2:1:1,平均次数为5500左右吧,然后在规定步数内跑不出来的也算是比较少。注意在比较拼图上的数据是否应该在它应该在的位置上时,一定要排除数据为0的情况,不然结果基本上是跑不出来的。好多同学因为这个被坑了很久!!
下面是相关代码:
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Vector;
/** 在此类中填充算法,完成重拼图游戏(N-数码问题)
* @author zhengkaipei
*
*/
public class Jigsaw {
JigsawNode beginJNode; // 拼图的起始状态节点
JigsawNode endJNode; // 拼图的目标状态节点
JigsawNode currentJNode; // 拼图的当前状态节点
private Vector openList; // open表 :用以保存已发现但未访问的节点
private Vector closeList; // close表:用以保存已访问的节点
private Vector solutionPath;// 解路径 :用以保存从起始状态到达目标状态的移动路径中的每一个状态节点
private boolean isCompleted; // 完成标记:初始为false;当求解成功时,将该标记至为true
private int searchedNodesNum; // 已访问节点数: 用以记录所有访问过的节点的数量
/**拼图构造函数
* @param bNode - 初始状态节点
* @param eNode - 目标状态节点
*/
public Jigsaw(JigsawNode bNode, JigsawNode eNode) {
this.beginJNode = new JigsawNode(bNode);
this.endJNode = new JigsawNode(eNode);
this.currentJNode = new JigsawNode(bNode);
this.openList = new Vector();
this.closeList = new Vector();
this.solutionPath = null;
this.isCompleted = false;
this.searchedNodesNum = 0;
}
/**此函数用于打散拼图:将输入的初始状态节点jNode随机移动len步,返回其打散后的状态节点
* @param jNode - 初始状态节点
* @param len - 随机移动的步数
* @return 打散后的状态节点
*/
public static JigsawNode scatter(JigsawNode jNode, int len) {
int randomDirection;
len += (int) (Math.random() * 2);
JigsawNode jigsawNode = new JigsawNode(jNode);
for (int t = 0; t < len; t++) {
int[] movable = jigsawNode.canMove();
do{randomDirection = (int) (Math.random() * 4);}
while(0 == movable[randomDirection]);
jigsawNode.move(randomDirection);
}
jigsawNode.setInitial();
return jigsawNode;
}
/**获取拼图的当前状态节点
* @return currentJNode - 拼图的当前状态节点
*/
public JigsawNode getCurrentJNode() {
return currentJNode;
}
/**设置拼图的初始状态节点
* @param jNode - 拼图的初始状态节点
*/
public void setBeginJNode(JigsawNode jNode) {
beginJNode = jNode;
}
/**获取拼图的初始状态节点
* @return beginJNode - 拼图的初始状态节点
*/
public JigsawNode getBeginJNode() {
return beginJNode;
}
/**设置拼图的目标状态节点
* @param jNode - 拼图的目标状态节点
*/
public void setEndJNode(JigsawNode jNode) {
this.endJNode = jNode;
}
/**获取拼图的目标状态节点
* @return endJNode - 拼图的目标状态节点
*/
public JigsawNode getEndJNode() {
return endJNode;
}
/**获取拼图的求解状态
* @return isCompleted - 拼图已解为true;拼图未解为false
*/
public boolean isCompleted() {
return isCompleted;
}
/**计算解的路劲
* @return 若有解,则将结果保存在solutionPath中,返回true; 若无解,则返回false
*/
private boolean calSolutionPath() {
if (!this.isCompleted()) {
return false;
} else {
JigsawNode jNode = this.currentJNode;
solutionPath = new Vector();
while (jNode != null) {
solutionPath.addElement(jNode);
jNode = jNode.getParent();
}
return true;
}
}
/**获取解路径文本
* @return 解路径solutionPath的字符串,若有解,则分行记录从初始状态到达目标状态的移动路径中的每一个状态节点;
* 若未解或无解,则返回提示信息。
*/
public String getSolutionPath() {
String str = new String();
str += "Begin->";
if (this.isCompleted) {
for (int i = solutionPath.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
str += solutionPath.elementAt(i).toString() + "->";
}
str+="End";
} else
str = "Jigsaw Not Completed.";
return str;
}
/**获取访问过的节点数searchedNodesNum
* @return 返回所有已访问过的节点总数
*/
public int getSearchedNodesNum() {
return searchedNodesNum;
}
/**将搜索结果写入文件中,同时显示在控制台
* 若搜索失败,则提示问题无解,输出已访问节点数;
* 若搜索成功,则输出初始状态beginJnode,目标状态endJNode,已访问节点数searchedNodesNum,路径深度nodeDepth和解路径solutionPath。
* @param pw - 文件输出PrintWriter类对象,如果pw为null,则写入到D://Result.txt
* @throws IOException
*/
public void printResult(PrintWriter pw) throws IOException{
boolean flag = false;
if(pw == null){
pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("Result.txt"));// 将搜索过程写入D://BFSearchDialog.txt
flag = true;
}
if (this.isCompleted == true) {
// 写入文件
pw.println("Jigsaw Completed");
pw.println("Begin state:" + this.getBeginJNode().toString());
pw.println("End state:" + this.getEndJNode().toString());
pw.println("Solution Path: ");
pw.println(this.getSolutionPath());
pw.println("Total number of searched nodes:" + this.getSearchedNodesNum());
pw.println("Length of the solution path is:" + this.getCurrentJNode().getNodeDepth());
// 输出到控制台
System.out.println("Jigsaw Completed");
System.out.println("Begin state:" + this.getBeginJNode().toString());
System.out.println("End state:" + this.getEndJNode().toString());
System.out.println("Solution Path: ");
System.out.println(this.getSolutionPath());
System.out.println("Total number of searched nodes:" + this.getSearchedNodesNum());
System.out.println("Length of the solution path is:" + this.getCurrentJNode().getNodeDepth());
}
else {
// 写入文件
pw.println("No solution. Jigsaw Not Completed");
pw.println("Begin state:" + this.getBeginJNode().toString());
pw.println("End state:" + this.getEndJNode().toString());
pw.println("Total number of searched nodes:"
+ this.getSearchedNodesNum());
// 输出到控制台
System.out.println("No solution. Jigsaw Not Completed");
System.out.println("Begin state:" + this.getBeginJNode().toString());
System.out.println("End state:" + this.getEndJNode().toString());
System.out.println("Total number of searched nodes:"
+ this.getSearchedNodesNum());
}
if(flag)
pw.close();
}
/**探索所有与jNode邻接(上、下、左、右)且未曾被访问的节点
* @param jNode - 要探索的节点
* @return 包含所有与jNode邻接且未曾被访问的节点的Vector对象
*/
private Vector findFollowJNodes(JigsawNode jNode) {
Vector followJNodes = new Vector();
JigsawNode tempJNode;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
tempJNode = new JigsawNode(jNode);
if(tempJNode.move(i) && !this.closeList.contains(tempJNode) && !this.openList.contains(tempJNode))
followJNodes.addElement(tempJNode);
}
return followJNodes;
}
/**排序插入openList:按照节点的代价估值(estimatedValue)将节点插入openList中,估值小的靠前。
* @param jNode - 要插入的状态节点
*/
private void sortedInsertOpenList(JigsawNode jNode) {
this.estimateValue(jNode);
for (int i = 0; i < this.openList.size(); i++) {
if (jNode.getEstimatedValue() < this.openList.elementAt(i)
.getEstimatedValue()) {
this.openList.insertElementAt(jNode, i);
return;
}
}
this.openList.addElement(jNode);
}
// ****************************************************************
// *************************实验任务************************
/**实验任务一:广度优先搜索算法,求指定3*3拼图(8-数码问题)的最优解
* 要求:填充广度优先搜索算法BFSearch(),执行测试脚本RunnerPart1
* 主要涉及函数:BFSearch()
*/
/**实验任务二:启发式搜索算法,求解随机5*5拼图(24-数码问题)
* 要求:1.修改启发式搜索算法ASearch()和代价估计函数estimateValue(),执行测试脚本RunnerPart2
* 2.访问节点总数不超过25000个
* 主要涉及函数:ASearch(),estimateValue()
*/
// ****************************************************************
/**(实验一)广度优先搜索算法,求解指定3*3拼图(8-数码问题)的最优解。
* 要求函数结束后:1,isCompleted记录了求解完成状态;
* 2,closeList记录了所有访问过的节点;
* 3,searchedNodesNum记录了访问过的节点数;
* 4,solutionPath记录了解路径。
* @return isCompleted, 搜索成功时为true,失败为false
* @throws IOException
*/
public boolean BFSearch() throws IOException {
// 将搜索过程写入D://BFSearchDialog.txt
String filePath = "BFSearchDialog.txt";
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(filePath));
// *************************************
// Write your code here.
openList.addElement(beginJNode);
currentJNode = beginJNode;
while(!openList.isEmpty()){
if (openList.firstElement().equals(endJNode)) {
isCompleted = true;
calSolutionPath();
break;
}else {
closeList.addElement(openList.firstElement());
Vector findAdjacent = findFollowJNodes(openList.firstElement());
for( JigsawNode node : findAdjacent ){
openList.addElement(node);
}
openList.remove(0);
currentJNode = openList.firstElement();
closeList.addElement(currentJNode);
searchedNodesNum++;
}
}
// *************************************
this.printResult(pw);
pw.close();
System.out.println("Record into " + filePath);
return isCompleted;
}
/**(Demo+实验二)启发式搜索。访问节点数大于30000个则认为搜索失败。
* 函数结束后:isCompleted记录了求解完成状态;
* closeList记录了所有访问过的节点;
* searchedNodesNum记录了访问过的节点数;
* solutionPath记录了解路径。
* 搜索过程和结果会记录在D://DemoASearchDialog.txt中。
* @return 搜索成功返回true,失败返回false
* @throws IOException
*/
public boolean ASearch() throws IOException{
// 将搜索过程写入ASearchDialog.txt
String filePath = "ASearchDialog.txt";
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(filePath));
// 访问节点数大于30000个则认为搜索失败
int maxNodesNum = 25000;
// 用以存放某一节点的邻接节点
Vector followJNodes = new Vector();
// 重置求解完成标记为false
isCompleted = false;
// (1)将起始节点放入openList中
this.sortedInsertOpenList(this.beginJNode);
// (2) 如果openList为空,或者访问节点数大于maxNodesNum个,则搜索失败,问题无解;否则循环直到求解成功
while (this.openList.isEmpty() != true && searchedNodesNum <= maxNodesNum) {
// (2-1)访问openList的第一个节点N,置为当前节点currentJNode
// 若currentJNode为目标节点,则搜索成功,设置完成标记isCompleted为true,计算解路径,退出。
this.currentJNode = this.openList.elementAt(0);
if (this.currentJNode.equals(this.endJNode)){
isCompleted = true;
this.calSolutionPath();
break;
}
// (2-2)从openList中删除节点N,并将其放入closeList中,表示以访问节点
this.openList.removeElementAt(0);
this.closeList.addElement(this.currentJNode);
searchedNodesNum++;
// 记录并显示搜索过程
pw.println("Searching.....Number of searched nodes:" + this.closeList.size() + " Current state:" + this.currentJNode.toString());
System.out.println("Searching.....Number of searched nodes:" + this.closeList.size() + " Current state:" + this.currentJNode.toString());
// (2-3)寻找所有与currentJNode邻接且未曾被访问的节点,将它们按代价估值从小到大排序插入openList中
followJNodes = this.findFollowJNodes(this.currentJNode);
while (!followJNodes.isEmpty()) {
this.sortedInsertOpenList(followJNodes.elementAt(0));
followJNodes.removeElementAt(0);
}
if( openList.size() > 2000 ){
int init = openList.size();
for (int i = init-1; i >= init - 100 ; i-- ) {
openList.removeElementAt(i);
}
}
}
this.printResult(pw); // 记录搜索结果
pw.close(); // 关闭输出文件
System.out.println("Record into " + filePath);
return isCompleted;
}
/**(Demo+实验二)计算并修改状态节点jNode的代价估计值:f(n)=s(n)。
* s(n)代表后续节点不正确的数码个数
* @param jNode - 要计算代价估计值的节点;此函数会改变该节点的estimatedValue属性值。
*/
private void estimateValue(JigsawNode jNode) {
int s = 0; // 后续节点不正确的数码个数
int dimension = JigsawNode.getDimension();
for(int index =1 ; index= x2 ? x1-x2 : x2-x1 );
int yManhaton = ( y1 >= y2 ? y1-y2 : y2-y1 );
distance += ( xManhaton + yManhaton );
geometry += Math.sqrt( xManhaton*xManhaton + yManhaton*yManhaton);
break;
}
}
}
int aver = (int) (s*1 + distance*2 + geometry*1);
jNode.setEstimatedValue(aver);
}
} 本次实训情况大概是这样,不难!相信大家只要认真对待,应该都能拿到很高的分数。然后,尽量按照自己的能力完成,遇到问题先独立思考,不要一味的拷贝复制。。
2014.08.14
ZKP.
注:由于上述内容在显示的时候有些问题,我把个人阶段一的自学报告也附上。见 http://download.csdn.net/detail/zkp0601/8473359