ubuntu 安装MongoDB
后期备注1: ubuntu 18下安装 mongodb 3.6参考链接Install MongoDB On Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server
1. 安装 MongoDB 社区版
MongoDB 提供的包只支持 64 位长期支持版本的 Ubuntu 发行版。比如 Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (precise), 14.04 LTS (trusty), 16.04 LTS (xenial) 等等。这些包可能在其他发行版上也能工作,但是并未被支持。
1.1 导入包管理系统使用的公钥
Ubuntu 的软件包管理工具(即dpkg和APT)要求软件包的发布者通过GPG密钥签名来确保软件包的一致性和真实性。通过以下命令导入MongoDB公共GPG密钥:
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 0C49F3730359A14518585931BC711F9BA15703C6根据 Ubuntu 的版本使用适当的命令创建 list file: /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.4.list为 MongoDB 创建 list file
Ubuntu 12.04
echo "deb [ arch=amd64 ] http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu precise/mongodb-org/3.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.4.listUbuntu 14.04
echo "deb [ arch=amd64 ] http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu trusty/mongodb-org/3.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.4.listUbuntu 16.04
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu xenial/mongodb-org/3.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.4.list1.2. 重新下载本地包数据库索引
sudo apt-get update1.3. 通过以下命令安装最新的可靠版安装 MongoDB
sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org2. 运行 MongoDB 社区版
默认情况下, MongoDB 实例的数据文件位于 /var/lib/mongodb,日志文件位于 /var/log/mongodb,并且通过用户 mongodb 来运行。你可以在配置文件 /etc/mongod.conf指定不同的日志文件和数据文件目录,其对应的配置为:systemLog.path 和 storage.dbPath 。配置中的net.bindIp 默认是127.0.0.1,这样只能本地连接,可以指定成服务器的对外IP或者干脆设置为0.0.0.0。
如果你更改了运行 MongoDB 进程的用户,必须修改 /var/lib/mongodb 和 /var/log/mongodb 的访问权限来让用户能访问这些目录。
2.1 启动 MongoDB
按照官方文档,执行如下命令可以启动 mongod 进程
sudo service mongod start
# 或者
sudo systemctl start mongod实际上我操作过程中是没有成功使用以上命令启动成功的,我是通过手动添加系统服务来实现服务的启动的。
步骤如下:
- 进入 /etc/init.d
- 建立一个脚本mongodb文件,内容如下并赋予755权限
chmod 775 mongodb
#!/bin/bash
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: mongod
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $syslog
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $syslog
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: Start mongod at boot time
# Description: Enable service provided by mongod.
### END INIT INFO
start()
{
/usr/bin/mongod --config /etc/mongod.conf &
exit 0;
}
stop()
{
/usr/bin/mongod --config /etc/mongod.conf --shutdown
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
stop
start
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}"
exit 0
;;
esac
exit 0
- 加入到系统启动中
// 添加到系统启动
update-rc.d mongodb defaults
// 从系统启动中删除
update-rc.d mongodb remove- 启动命令
service mongodb start
service mongodb stop注意:
- 不要将脚本名称和已有的命令重名(刚开始使用的mongod,和mongodb server启动命令名称一样导致一直不成功)
- 启动方式和标准启动方式不一样,最后留下文档,方便其他人维护
3. MongoDB使用
MongoDB默认是没有设置鉴权的,业界大部分使用MongoDB的项目也没有设置访问权限。这就意味着只要知道MongoDB服务器的端口,任何能访问到这台服务器的人都可以查询和操作MongoDB数据库的内容。在一些项目当中,这种使用方式会被看成是一种安全漏洞。
3.1. 第一次进入mongodb
可以使用MongoDB shell 来连接 MongoDB 服务器。
标准 URI 连接语法:
mongodb://[username:password@]host1[:port1][,host2[:port2],...[,hostN[:portN]]][/[database][?options]]
mongodb:// 这是固定的格式,必须要指定。
username:password@ 可选项,如果设置,在连接数据库服务器之后,驱动都会尝试登陆这个数据库
host1 必须的指定至少一个host, host1 是这个URI唯一要填写的。它指定了要连接服务器的地址。如果要连接复制集,请指定多个主机地址。
portX 可选的指定端口,如果不填,默认为27017
/database 如果指定username:password@,连接并验证登陆指定数据库。若不指定,默认打开admin数据库。
?options 是连接选项。如果不使用/database,则前面需要加上/。所有连接选项都是键值对name=value,键值对之间通过&或;(分号)隔开使用shell的方式连接:
$ mongo
MongoDB shell version v3.4.2
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
MongoDB server version: 3.4.2
Server has startup warnings:
2016-08-31T22:13:06.344+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten]
2016-08-31T22:13:06.344+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Using the XFS filesystem is strongly recommended with the WiredTiger storage engine
2016-08-31T22:13:06.344+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten] ** See http://dochub.mongodb.org/core/prodnotes-filesystem
2016-08-31T22:13:06.571+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
2016-08-31T22:13:06.571+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Access control is not enabled for the database.
2016-08-31T22:13:06.571+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** Read and write access to data and configuration is unrestricted.
2016-08-31T22:13:06.571+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
> show databases;show databases; #查看数据库
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
>use admin #切换数据库
>switched to db admin
如下这种方式也可以
$ mongo mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
MongoDB shell version v3.4.2
connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017
MongoDB server version: 3.4.2
Server has startup warnings:
2016-09-02T21:07:29.630+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten]
2016-09-02T21:07:29.630+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Using the XFS filesystem is strongly recommended with the WiredTiger storage engine
2016-09-02T21:07:29.630+0800 I STORAGE [initandlisten] ** See http://dochub.mongodb.org/core/prodnotes-filesystem
2016-09-02T21:07:29.978+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
2016-09-02T21:07:29.978+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Access control is not enabled for the database.
2016-09-02T21:07:29.978+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** Read and write access to data and configuration is unrestricted.
2016-09-02T21:07:29.978+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
>
开启MongoDB的web界面访问
MongoDB自带一个微型的web管理信息界面,需要修改/etc/mongod.conf中的一个配置项:
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 10.0.90.24
http:
enabled: true #设置为true
RESTInterfaceEnabled: false #设置为false注:如果bindIp为127.0.0.1,只能在本机使用curl查看,无法再浏览器访问!
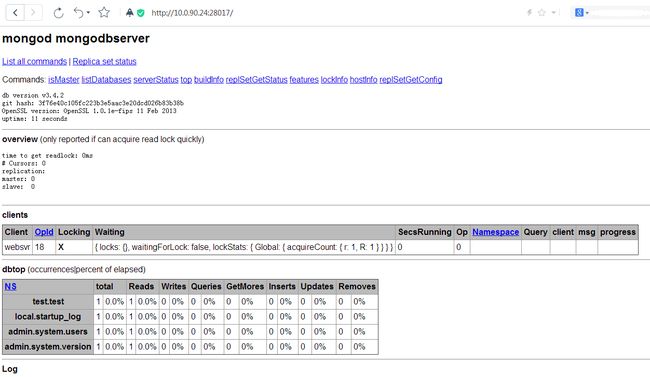
重启mongodb,会自动监听28017端口,然后访问,在浏览器输入:http://10.0.90.24:28017/,如下图:
其中mongodbserver为mongodb服务器的hostname,还有其他一些连接信息!不过web界面方式使用不多。
注:如果设置了net.http.enabled等于true,并且开启了security.authorization等于enabled,在浏览器访问http://10.0.90.24:28017/的时候,会提示输入用户名和密码,如下图:
3.2 为MongoDB创建用户管理员
MongoDB中,每个数据库的实例都可拥有多个用户,安全检查开启后,只要通过身份验证的用户才能够进行数据的读写操作。admin(管理员)和local(本地)是两个特殊的数据库,它们当中的用户可对任何数据库进行操作。这两个数据库中的用户可被看作是超级用户。经认证后,管理员用户可对任何数据库进行读写,同事能执行某些只有管理员才能执行的命令,如listDatabases和shutDown。
在默认情况下,mongod是监听在127.0.0.1之上的,任何客户端都可以直接连接27017,且没有认证。这样做的好处是,用户可以即时上手,不用担心被一堆配置弄的心烦意乱。然而坏处也是显而易见,如果直接在公网服务器上如此搭建MongoDB,那么所有人都可以直接访问并修改数据库数据了。
默认情况下,mongod也是没有管理员账户的。因此除非你在admin数据库中使用db.addUser()命令添加了管理员帐号,且使用--auth参数启动mongod,否则在数据库中任何人都可以无需认证执行所有命令,包括delete和shutdown。此外,mongod还会默认监听28017端口,同样是绑定所有ip。这是一个mongod自带的web监控界面。从中可以获取到数据库当前连接、log、状态、运行系统等信息。如果你开启了--rest参数,甚至可以直接通过web界面查询数据,执行mongod命令。
其实MongoDB本身有非常详细的安全配置准则,显然开发者也是想到了,然而他是将安全的任务推给用户去解决,这本身的策略就是偏向易用性的,对于安全性,则得靠边站了。
注:每个数据库都有自己的用户,创建用户的命令是db.createUser(),当你创建一个用户时,该用户就属于你当前所在的数据库。
MongoDB有一个比较奇怪的设置是,即便是一个admin用户,授权也必须在admin数据库下进行,而不能在其他数据库下进行。而授权之后admin用户就可以在任何数据库下进行任何操作了。当然数据库级别的用户在他自己的数据库下授权之后是不能到其他数据库进行操作的
每个用户包含三个要素:用户名、密码和角色列表。下面是一个例子:
{
user: "dbuser",
pwd : "dbpass",
roles: ["readWrite", "clusterAdmin"]
}这个例子表示一个名为dbuser的用户,它在当前的数据库中拥有readWrite和clusterAdmin两个角色。
注:MongoDB内置了很多角色,但要注意,不是每个数据库的内置角色都一样。其中admin数据库就包含了一些其他数据库所没有的角色。熟悉Oracle的朋友都知道,数据库用户有两种,一种是管理员,用来管理用户;一种是普通用户,用来访问数据。类似的,为MongoDB规划用户鉴权时,至少要规划两种角色:用户管理员和数据库用户。如果搭建了分片或主从,可能还会要规划数据库架构管理员的角色,它们专门用来调整数据库的分布式架构。
下面是一个创建用户管理员的操作例子:
> use admin
switched to db admin
> db.createUser({user:"root",pwd:"test123",roles:["userAdminAnyDatabase"]})
Successfully added user: { "user" : "root", "roles" : [ "userAdminAnyDatabase" ] }
然后登陆测试一下
> use admin
switched to db admin
> db.auth("root","test123")
1
注:db.auth()方法返回1表示登录成功。
查看用户
>show users;
{
"_id" : "admin.root",
"user" : "root",
"db" : "admin",
"roles" : [
{
"role" : "userAdminAnyDatabase",
"db" : "admin"
}
]
}
设置完后,MongoDB客户端必须用正确的用户名和密码登录,才能在指定的数据库中操作。下面是一个如何创建数据库用户的例子:
首先保证你已经以用户管理员的身份登录admin数据库。然后用use命令切换到目标数据库,同样用db.createUser()
命令来创建用户,其中角色名为“readWrite”,普通的数据库用户角色有两种,read和readWrite。顾名思义,
前者只能读取数据不能修改,后者可以读取和修改。
> use admin
switched to db admin
> db.auth("root","test123")
1
> show dbs;
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
test 0.000GB
> use test
switched to db test
> db
test
#创建一个名为testuser123的用户,密码设置为123456,如下:
> db.createUser({user:"testuser123",pwd:"123456,",roles:["readWrite"]})
Successfully added user: { "user" : "testuser123", "roles" : [ "readWrite" ] }
> db.auth("testuser123","123456,")
1 #认证通过
以上就实现了为test库创建了一个普通用户!!!
注意:普通用户就算认证db.auth()通过之后,也没有权限执行show dbs命令,只能用db命令查看当前数据库!3、在配置文件中开启mongodb连接认证功能,如果不开启认证功能,任何人只要可以ssh到mongodb的服务器,都可以进行增删改查等操作
在配置文件mongod.conf中开启,如下:
security:
authorization: enabled
然后重启mongodb就开启了认证功能,测试如下:
$ mongo --host 10.0.90.24 #如果是监听的127.0.0.1,就不需要加--host 参数了
MongoDB shell version v3.4.2
connecting to: mongodb://10.0.90.24:27017/
MongoDB server version: 3.4.2
> 可以看到增加了认证功能,就不会提示上面提到的第一个和第二个WARNING了。
然后直接执行show dbs 看看会不会列出所有的数据库
> show dbs
2017-02-13T11:54:45.562+0800 E QUERY [thread1] Error: listDatabases failed:{
"ok" : 0,
"errmsg" : "not authorized on admin to execute command { listDatabases: 1.0 }",
"code" : 13,
"codeName" : "Unauthorized"
} :
_getErrorWithCode@src/mongo/shell/utils.js:25:13
Mongo.prototype.getDBs@src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:62:1
shellHelper.show@src/mongo/shell/utils.js:755:19
shellHelper@src/mongo/shell/utils.js:645:15
@(shellhelp2):1:1
> 可以看到提示类似“not authorized on admin to execute command”说明如果不进行权限认证,就无
法进行其他操作,那么我们进行认证,如下:
> use admin
switched to db admin
> db.auth("root","test123")
1
> show dbs;
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
test 0.000GB说明认证通过,可以查看所有的数据库了!!!
一个例子:
$ mongo --host 10.0.90.24 #进入mongodb
MongoDB shell version v3.4.2
connecting to: mongodb://10.0.90.24:27017/
MongoDB server version: 3.4.2
> use web
switched to db web
> db.auth("xlg","123456,")db.auth("xlg","123456,")
1
> show dbs; #根据提示可以看出普通用户无法执行show dbs命令
2017-02-13T15:33:32.816+0800 E QUERY [thread1] Error: listDatabases failed:{
"ok" : 0,
"errmsg" : "not authorized on admin to execute command { listDatabases: 1.0 }",
"code" : 13,
"codeName" : "Unauthorized"
} :
_getErrorWithCode@src/mongo/shell/utils.js:25:13
Mongo.prototype.getDBs@src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:62:1
shellHelper.show@src/mongo/shell/utils.js:755:19
shellHelper@src/mongo/shell/utils.js:645:15
@(shellhelp2):1:1
> db
web
> db.web.findOne()db.web.findOne() #查看数据
{
"_id" : ObjectId("58a14e272fede9a9e553f929"),
"name" : "james",
"age" : "10"
}
> db.web.findOne({"name":"house"}) #查看name等于house的数据
{
"_id" : ObjectId("58a150492fede9a9e553f92a"),
"name" : "curry",
"age" : "9"
}
> use admin #切换到admin库
switched to db admin
> db.auth("root","test123") #用管理员root认证
1
> db
admin
> use web #切换到其他库
switched to db web
> db
web
> db.web.findOne()db.web.findOne() #查看数据
{
"_id" : ObjectId("58a14e272fede9a9e553f929"),
"name" : "james",
"age" : "10"
}
> db.web.findOne({"name":"house"})db.web.findOne({"name":"house"})
{
"_id" : ObjectId("58a150492fede9a9e553f92a"),
"name" : "curry",
"age" : "9"
}注意:如果想用admin超级用户查看除了admin之外的数据库,先用普通用户登录认证,然后切换到admin库,再进行认证后,才可以继续其他操作。
3.3 删除一个用户
>db.system.users.remove({"user" : "test_user"}); 删除一个test_user用户3.4. mongodb创建、删除、插入数据命令使用
> use test #创建一个test数据库
switched to db test
> db #列出当前db名称,为test
test
# 如果想列出所有数据库,使用show dbs命令
> show dbs;
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
# 但是并没有看到刚才我们创建的test数据库,那是因为test数据库是空的,我们插入一条数据
> use test
switched to db test
> db
test
> db.test.insert({"name":"ceshishuju"})db.test.insert({"name":"ceshishuju"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> show dbsshow dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
test 0.000GB #test 数据库就显示了
# 然后删除数据库
> use test
switched to db test
> db.dropDatabase();
{ "dropped" : "test", "ok" : 1 }
> show dbs;show dbs;
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB #可以看到test库删掉了
# 基本查看数据
> use test
switched to db test
> db.test.findOne()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("57c8206a8a704e1515c76e7b"), "name" : "ceshishuju" }
# 可以看到插入的数据这里可以查看到了!
# 多条件查询,一个例子:下面的示例等同于SQL语句的where name = "stephen" and age = 35
> db.test.find({"name":"stephen","age":35})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("4fd58ecbb9ac507e96276f1a"), "name" : "stephen", "age" : 35, "genda" : "male", "email" : "[email protected]" }
# 返回指定的文档键值对。下面的示例将只是返回name和age键值对。
> db.test.find({}, {"name":1,"age":1})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("4fd58ecbb9ac507e96276f1a"), "name" : "stephen", "age" : 35 }
#指定不返回的文档键值对。下面的示例将返回除name之外的所有键值对。
> db.test.find({}, {"name":0})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("4fd58ecbb9ac507e96276f1a"), "age" : 35, "genda" : "male", "email" : "[email protected]" }3.5. mongodb存储引擎介绍
存储引擎(Storage Engine)是MongoDB的核心组件,负责管理数据如何存储在硬盘(Disk)和内存(Memory)上。从MongoDB 3.2 版本开始,MongoDB 支持多数据存储引擎(Storage Engine),MongoDB支持的存储引擎有:WiredTiger,MMAPv1和In-Memory。
从MongoDB 3.2版本开始,WiredTiger成为MongDB默认的Storage Engine,用于将数据持久化存储到硬盘文件中,WiredTiger提供文档级别(Document-Level)的并发控制,检查点(CheckPoint),数据压缩和本地数据加密( Native Encryption)等功能。
MongoDB不仅能将数据持久化存储到硬盘文件中,而且还能将数据只保存到内存中;In-Memory存储引擎用于将数据只存储在内存中,只将少量的元数据和诊断日志(Diagnostic)存储到硬盘文件中,由于不需要Disk的IO操作,就能获取索取的数据,In-Memory存储引擎大幅度降低了数据查询的延迟(Latency)
查看MongoDB的默认存储引擎:
#echo "db.serverStatus()"| mongo|grep wiredTiger
"name" : "wiredTiger",
"wiredTiger" : {
在mongod.conf中设置:
storage:
dbPath: /var/lib/mongo
journal:
enabled: true
engine: wiredTiger #设置WiredTiger和MMAPv1都用于持久化存储数据,相对而言,WiredTiger比MMAPv1更新,功能更强大!
一篇很好地学习文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/ljhdo/archive/2016/10/30/4947357.html
4. MongoDB使用注意事项以及性能优化
1、Test every query in your application with explain().
使用explain()测试应用程序中的每个查询。
MongoDB provides the ability to view how a query will be evaluated in the system, including which indexes are used and whether the query is covered.
This capability is similar to the Explain Plan and similar features in relational databases. The feedback from explain() will help you understand
whether your query is performing optimally.
2、Avoid scatter-gather queries. 避免分散-聚集查询
In sharded systems, queries that cannot be routed to a single shard must be broadcast to multiple shards for evaluation. Because these queries
involve multiple shards for each request they do not scale well as more shards are added.
3、Your operational applications should only read from primaries.
你的操作应用程序只应从主节点读取 (待考证)
Updates are typically replicated to secondaries quickly, depending on network latency. However, reads on the secondaries will not be consistent
with reads on the primary. Note that the secondaries are not idle as they must process all writes replicated from the primary. To increase read
capacity in your operational system consider sharding. Secondary reads can be useful for analytics and ETL applications as this approach will
isolate traffic from operational workloads. You may choose to read from secondaries if your application can tolerate eventual consistency.
4、Use the most recent drivers from MongoDB. 使用MongoDB最新的驱动程序
MongoDB supports drivers for nearly a dozen languages. These drivers are engineered by the same team that maintains the database kernel.
Drivers are updated more frequently than the database, typically every two months. Always use the most recent version of the drivers when
possible. Install native extensions if available for your language. Join the MongoDB community mailing list to keep track of updates.
5、Store all data for a record in a single document. 将记录的所有数据存储在单个文档中
MongoDB provides ACID compliance at the document level. When data for a record is stored in a single document the entire record can
be retrieved in a single seek operation, which is very efficient. In some cases it may not be practical to store all data in a single
document, or it may negatively impact other operations. Make the trade-offs that are best for your application.
6、Avoid large documents. 避免使用大文档
The maximum size for documents in MongoDB is 16 MB. In practice most documents are a few kilobytes or less. Consider documents more
like rows in a table than the tables themselves. Rather than maintaining lists of records in a single document, instead make each
record a document. For large media items, such as video or images, consider using GridFS, a convention implemented by all the
drivers that automatically stores the binary data across many smaller documents.
7、Avoid large indexed arrays. 避免使用大型索引数组
Rather than storing a large array of items in an indexed field, store groups of values across multiple fields. Updates will be more efficient.
8、Avoid unnecessarily long field names. 避免不必要的长字段名称
Field names are repeated across documents and consume space. By using smaller field names your data will consume less space, which allows
for a larger number of documents to fit in RAM. Note that with WiredTiger's native compression, long field names have less of an impact
on the amount of disk space used but the impact on RAM is the same.
9、Use caution when considering indexes on low-cardinality fields.
在考虑低基数字段上的索引时,请谨慎
Queries on fields with low cardinality can return large result sets. Avoid returning large result sets when possible. Compound indexes
may include values with low cardinality, but the value of the combined fields should exhibit high cardinality.
10、Eliminate unnecessary indexes. 取消不必要的索引。
Indexes are resource-intensive: even with compression enabled they consume RAM, and as fields are updated their associated indexes
must be maintained, incurring additional disk I/O overhead.
11、Remove indexes that are prefixes of other indexes.
删除作为其他索引的前缀的索引。
Compound indexes can be used for queries on leading fields within an index. For example, a compound index on last name, first name
can be also used to filter queries that specify last name only. In this example an additional index on last name only is unnecessary;
the compound index is sufficient for queries on last name as well as last name and first name.
12、Use a compound index rather than index intersection.
使用复合索引而不是索引交集
For best performance when querying via multiple predicates, compound indexes will generally be a better option.
13、Avoid regular expressions that are not left anchored or rooted.
避免没有留下锚定或生根的正则表达式。
Indexes are ordered by value. Leading wildcards are inefficient and may result in full index scans. Trailing wildcards can be efficient
if there are sufficient case-sensitive leading characters in the expression.
14、Use index optimizations available in the WiredTiger storage engine.
使用WiredTiger存储引擎中提供的索引优化(3.0版本之后默认是WiredTiger引擎)
As discussed earlier, the WiredTiger engine compresses indexes by default. In addition, administrators have the flexibility to place
indexes on their own separate volume, allowing for faster disk paging and lower contention.
15、Use RAID10. 使用raid10
Most MongoDB deployments should use RAID-10. RAID-5 and RAID-6 have limitations and may not provide sufficient performance.
RAID-0 provides good read and write performance, but insufficient fault tolerance. MongoDB's replica sets allow deployments
to provide stronger availability for data, and should be considered with RAID and other factors to meet the desired availability SLA.
16、Use multiple devices for different databases – WiredTiger.
对不同的数据库使用多个设备 - WiredTiger。
Set directoryForIndexes so that indexes are stored in separate directories from collections and directoryPerDB to use a different
directory for each database. The various directories can then be mapped to different storage devices, thus increasing overall
throughput. Note that using different storage devices will affect your ability to create snapshot-style backups of your data,
since the files will be on different devices and volumes.
17、Use EXT4 or XFS file systems; avoid EXT3.
避免使用ext3文件系统,使用ext4或者xfs文件系统
EXT3 is quite old and is not optimal for most database workloads. For example, MMAPv1 preallocates space for data.
In EXT3 preallocation will actually write 0s to the disk to allocate the space, which is time consuming. In EXT4 and XFS
preallocation is performed as a logical operation, which is much more efficient. With the WiredTiger storage engine, use
of XFS is strongly recommended to avoid performance issues that have been observed when using EXT4 with WiredTiger.5. MongonDB 3.4.2版本配置文件参数详解
官网链接地址:
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/configuration-options/
注:配置参数是分级式的,比如net.http.RESTInterfaceEnabled其实在mongodb.conf中配置为:
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 127.0.0.1
http:
enabled: true
RESTInterfaceEnabled: false
所有下面都以net.http.RESTInterfaceEnabled这种方式介绍
参数类型一共三种:
string 字符串
boolean 布尔型 false/true
integer 整形
1、systemLog 选项如下:
systemLog.verbosity --用法:verbosity:
日志文件输出的级别,越大级别越低,默认是0
systemLog.quiet --用法: quite: boolean
在quite模式下会限制输出信息:
数据库命令输出,副本集活动,连接接受事件,连接关闭事件。
systemLog.traceAllExceptions --用法:traceAllExceptions: boolean
打印用于调试的详细信息。 用于其他日志记录以进行支持相关的故障排除。
systemLog.syslogFacility --用法:syslogFacility: string,默认为user
指定syslog日志信息的设备级别,需要指定--syslog来使用这个选项。
systemLog.logAppend --用法:logAppend: boolean
是否启用追加日志
systemLog.destination --用法:destination:string ,默认为file
指定一个文件或syslog。如果指定为文件,必须同时指定systemLog.path
systemLog.path --用法:path: string 比如:/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
日志路径
systemLog.logRotate --用法:logRotate: string ,默认值为rename,另一个是reopen
可以实现rotage日志,实现日志切割
systemLog.timeStampFormat --用法:timeStampFormat: string 默认值为 iso8601-local
日志消息中时间戳的时间格式。还有ctime、iso8601-utc格式
2、storage 选项用法:
范例:
storage:
dbPath:
indexBuildRetry:
repairPath:
journal:
enabled:
commitIntervalMs:
directoryPerDB:
syncPeriodSecs:
engine:
mmapv1:
preallocDataFiles:
nsSize:
quota:
enforced:
maxFilesPerDB:
smallFiles:
journal:
debugFlags:
commitIntervalMs:
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB:
journalCompressor:
directoryForIndexes:
collectionConfig:
blockCompressor:
indexConfig:
prefixCompression:
inMemory:
engineConfig:
inMemorySizeGB:
具体参数的解释:
storage.dbPath --用法:dbPath: string 默认是/data/db(linux) ;\data\db (windows)
注意:如果是yum安装的mongodb,默认是/var/lib/mongo
mongodb数据存储的路径
storage.indexBuildRetry --用法:indexBuildRetry: boolean 默认值是true
指定数据库在索引建立过程中停止,重启后是否重新建立索引。
storage.repairPath --用法:repairPath: string 默认值是:A _tmp_repairDatabase_ ( directory under the dbPath. )
在--repair操作期间MongoDB将使用的工作目录。当--repair结束后,storage.repairPath 目录变为空
注:storage.repairPath设置仅可用于mongod。
storage.journal.enabled --用法:journal.enabled: boolean
64bit操作系统默认为true,32bit操作系统默认为false
启用或禁用持久性日志以确保数据文件保持有效和可恢复,此选项仅在您指定--dbpath选项时适用。
storage.journal.commitIntervalMs --用法:journal.commitIntervalMs: number
mongod进程在日志操作之间允许的最大时间(以毫秒为单位),较低的值会增加日志的持久性,但会降低磁盘性能。
范围是1-500,默认值是100 毫秒。
storage.directoryPerDB --用法:directoryPerDB: boolean 默认值时false
当为true时,MongoDB使用单独的目录来存储每个数据库的数据,目录位于storage.dbPath目录下,每个子目录名称对应于数据库名称。
storage.syncPeriodSecs --用法:syncPeriodSecs: number 默认为60,不要设置为0
MongoDB通过fsync操作将数据刷新到数据文件之前可以经过的时间量。
特别注意:不要在生产系统上设置此值
storage.engine --用法: engine: wiredTiger 默认值为wiredTiger
设置mongodb的存储引擎。还有mmapv1和inMemory
storage.wiredTiger.engineConfig.cacheSizeGB --用法:cacheSizeGB: float
WiredTiger将用于所有数据的内部缓存的最大大小。值的范围可以从256MB到10TB,可以是浮点数。 此外,默认值也已更改。
从3.4开始,WiredTiger内部缓存默认使用以下两者中较大的一个:
50% of RAM minus 1 GB(50%的RAM减去1 GB), or 256 MB.
3、net 选项用法:
net:
port:
bindIp:
maxIncomingConnections:
wireObjectCheck:
ipv6:
unixDomainSocket:
enabled:
pathPrefix:
filePermissions:
http:
enabled:
JSONPEnabled:
RESTInterfaceEnabled:
ssl:
sslOnNormalPorts: # deprecated since 2.6
mode:
PEMKeyFile:
PEMKeyPassword:
clusterFile:
clusterPassword:
CAFile:
CRLFile:
allowConnectionsWithoutCertificates:
allowInvalidCertificates:
allowInvalidHostnames:
disabledProtocols:
FIPSMode:
net.port --用法 port: integer 默认值是27017
mongodb监听的端口
net.bindIp --用法 bindIp: string 默认值是127.0.0.1
mongodb监听的ip地址,也可以自定义
net.maxIncomingConnections --用法:maxIncomingConnections: integer 默认值是65536
mongos或mongod将接受的最大并发连接数,如果此设置高于操作系统配置的最大连接跟踪阈值,则此设置不起作用。
net.wireObjectCheck --用法:wireObjectCheck: boolean 默认值是true
为true时,mongod或mongos实例验证客户端收到的所有请求,以防止客户端将错误格式或无效的BSON插入到MongoDB数据库中。
注意:对于具有高度子文档嵌套的对象,net.wireObjectCheck对性能有轻微影响。
net.http.enabled --用法:enabled: boolean 默认值是false
启用或禁用HTTP接口。 启用接口可能会增加网络暴露。
net.http.RESTInterfaceEnabled --用法:RESTInterfaceEnabled: boolean,默认为false
即使http接口选项关闭,打开也会暴露http接口,会导致更多的不安全因素。不过开启为true可以在
mongodb的web页面访问List all commands 页面!
net.unixDomainSocket.enabled --用法 unixDomainSocket.enabled: boolean 默认值是true
在UNIX域套接字上启用或禁用侦听。 net.unixDomainSocket.enabled仅适用于基于Unix的系统。
4、security 选项
security:
keyFile:
clusterAuthMode:
authorization:
transitionToAuth:
javascriptEnabled:
redactClientLogData:
sasl:
hostName:
serviceName:
saslauthdSocketPath:
enableEncryption:
encryptionCipherMode:
encryptionKeyFile:
kmip:
keyIdentifier:
rotateMasterKey:
serverName:
port:
clientCertificateFile:
clientCertificatePassword:
serverCAFile:
ldap:
servers:
bind:
method:
saslMechanism:
queryUser:
queryPassword:
useOSDefaults:
transportSecurity:
timeoutMS:
userToDNMapping:
authz:
queryTemplate:
security.keyFile --用法:keyFile: string
密钥文件的路径,该文件存储MongoDB实例用于在分片集群或副本集中彼此进行身份验证的共享密钥
keyFile意味着security.authorization!
security.clusterAuthMode --用法: clusterAuthMode: string 默认值是keyFile
用于集群身份验证的身份验证模式
security.authorization --用法:authorization: string 默认值是disabled
启用或禁用基于角色的访问控制(RBAC)以管理每个用户对数据库资源和操作的访问。
enabled: 用户只能访问已为其授予了权限的数据库资源和操作。
diabled: 用户可以访问任何数据库并执行任何操作
security.transitionToAuth --用法:transitionToAuth: boolean 默认值是false
3.4版本新的功能,允许mongod或mongos接受和创建到部署中的其他mongod和mongos实例的已验证和未验证的连接
security.javascriptEnabled --用法:javascriptEnabled: boolean 默认值是true
启用或禁用服务器端JavaScript执行,禁用时,不能使用执行服务器端执行JavaScript代码的操作,例如$ where查询运算符,mapReduce命令和db.collection.mapReduce()方法,group命令和db.collection.group()方法 。
5、setParameter 选项
设置MongoDB服务器参数中描述的MongoDB参数或参数
要在YAML配置文件中设置参数,请使用以下格式:
setParameter:
:
:
例如,要在配置文件中指定enableLocalhostAuthBypass
setParameter:
enableLocalhostAuthBypass: false
6、operationProfiling 选项
operationProfiling:
slowOpThresholdMs:
mode:
operationProfiling.slowOpThresholdMs --用法:slowOpThresholdMs: integer 默认值是100
数据库概要分析器认为查询速度缓慢的阈值(以毫秒为单位),MongoDB将所有慢查询记录到日志中,即使数据库分析器关闭
当分析器打开时,它将写入system.profile集合
operationProfiling.mode --用法:mode: string 默认值是 off
数据库概要分析的级别,它将有关操作性能的信息插入到system.profile集合中。它的值有off、slowOp、all
注意:数据库分析可能会影响数据库性能。 仅在仔细考虑后才启用此选项
7、replication 选项
replication:
oplogSizeMB:
replSetName:
secondaryIndexPrefetch:
enableMajorityReadConcern:
replication.oplogSizeMB --用法:oplogSizeMB: integer
复制操作日志的最大大小(以兆字节为单位),例如:oplog。mongod进程基于可用的最大空间量创建oplog
对64bit系统而言,oplog通常是可用磁盘空间的5%,一旦mongod第一次创建oplog,更改replication.oplogSizeMB选项将不会影响oplog的大小
replication.replSetName --用法: replSetName: string
mongod所属的副本集的名称。 副本集中的所有主机必须具有相同的集名称。如果应用程序连接到多个副本集,则每个副本集应具有不同的名称。 某些驱动程序按副本集名称对副本集连接进行分组。
replication.secondaryIndexPrefetch --用法:secondaryIndexPrefetch: string 默认值是all
存储引擎特定功能:
replication.secondaryIndexPrefetch仅适用于mmapv1存储引擎。
replication.enableMajorityReadConcern --用法: enableMajorityReadConcern: boolean 默认是false
启用“多数”的读取关注级别。
8、sharding 选项
sharding:
clusterRole:
archiveMovedChunks:
sharding.clusterRole --用法:clusterRole: string
mongodb实例在分片集群中具有的角色。有2个值,如下:
configsvr:将此实例作为配置服务器启动。 默认情况下,实例在端口27019上启动。
shardsvr: 将此实例作为分片启动。 默认情况下,实例在端口27018上启动。
sharding.archiveMovedChunks --用法: archiveMovedChunks:boolean
在块迁移期间,分片不保存从分片迁移的文档。
9、auditLog 选项
仅在MongoDB Enterprise中可用
auditLog:
destination:
format:
path:
filter:
还有很多其他参数,这里不一一介绍了! 参考网址:
http://blog.51cto.com/linuxg/1895805
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhoujinyi/p/4610050.html
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/method/db.updateUser/
http://www.runoob.com/mongodb/mongodb-tutorial.html