CentOS 7.8 配置 VNC 服务
文章目录
- 前言
- 环境说明
- 安装
- 安装桌面环境
- 安装 VNC Server
- 配置 VNC Server
- 配置单用户单界面
- 配置访问密码
- 开启服务
- 打开防火墙
- 客户端访问
前言
安装的 Centos 服务器需要进行 GUI 操作。
环境说明
CentOS 7.8(Desktop Install)
因为使用图形用户界面,本例使用 GNOME 桌面环境。
$ cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.8.2003 (Core)
系统用户有两个 root 和 user,VNC Viewer 使用 user 进行访问
安装
安装桌面环境
如果没有安装 Desktop 版本,需要先安装 X Windows
注意:
安装桌面环境,未测试
$ sudo yum check-update
$ sudo yum groupinstall "X Window System"
$ sudo yum install gnome-classic-session gnome-terminal nautilus-open-terminal control-center liberation-mono-fonts
设置默认启动图形界面:
$ sudo unlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target
$ sudo ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/graphical.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
重启服务器:
$ sudo reboot
重启之后,应该有 CentOS 7 的桌面环境
安装 VNC Server
yum 安装:
$ sudo yum install tigervnc-server
配置 VNC Server
VNC Server 支持多种配置,如:
- 单用户单界面配置(一个用户访问,使用一个界面)
- 多用户单界面配置(多个用户访问,使用同一个界面)
- 多用户多界面配置(多个用户访问,使用各自的界面)
本例比较简单,只介绍单用户单界面配置。其他类型的配置,可以参考 CHAPTER 12. TIGERVNC - RedHat Customer Portal
配置单用户单界面
拷贝模板:
$ sudo cp /usr/lib/systemd/system/[email protected] /etc/systemd/system/[email protected]
网上其他资料,拷贝的文件名为 vncserver@:1.service,没有必要,后续说明。
编辑配置文件:
$ sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/[email protected]
编辑完:
# The vncserver service unit file
#
# Quick HowTo:
# 1. Copy this file to /etc/systemd/system/[email protected]
# 2. Replace with the actual user name and edit vncserver
# parameters in the wrapper script located in /usr/bin/vncserver_wrapper
# 3. Run `systemctl daemon-reload`
# 4. Run `systemctl enable vncserver@:.service`
#
# DO NOT RUN THIS SERVICE if your local area network is
# untrusted! For a secure way of using VNC, you should
# limit connections to the local host and then tunnel from
# the machine you want to view VNC on (host A) to the machine
# whose VNC output you want to view (host B)
#
# [user@hostA ~]$ ssh -v -C -L 590N:localhost:590M hostB
#
# this will open a connection on port 590N of your hostA to hostB's port 590M
# (in fact, it ssh-connects to hostB and then connects to localhost (on hostB).
# See the ssh man page for details on port forwarding)
#
# You can then point a VNC client on hostA at vncdisplay N of localhost and with
# the help of ssh, you end up seeing what hostB makes available on port 590M
#
# Use "-nolisten tcp" to prevent X connections to your VNC server via TCP.
#
# Use "-localhost" to prevent remote VNC clients connecting except when
# doing so through a secure tunnel. See the "-via" option in the
# `man vncviewer' manual page.
[Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=root
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
#ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
#ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver_wrapper %i
#ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/runuser -l user -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1280x1024"
PIDFile=/home/user/.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
注意:
- 启动服务的用户为 root,添加
User=root,这样VNC Client访问时可以看到菜单栏 - 将
:wq保存配置之后,重启 systemd
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
配置访问密码
本例使用 user 用户的桌面环境,如果使用其他用户,请先切换到 user 用户
# su user
$ vncpasswd
Password:
Verify:
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n
开启服务
$ sudo systemctl start vncserver@:1
这样就开启了第一个界面
注意
服务的文件 /etc/systemd/system/[email protected]没有 :1
:1 使当参数启动服务器,表示启动第一个界面
打开防火墙
我们需要配置防火墙, 打开 VNC 服务
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service vnc-server
success
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
success
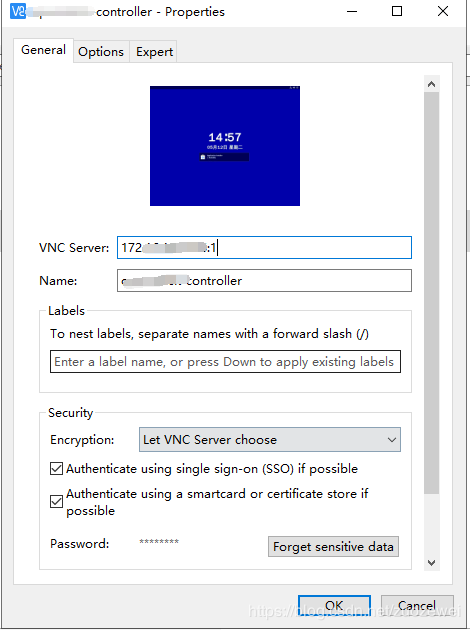
客户端访问
下载 VNC Viewer
设置如下:
VNC Server: YOUR_SERVER_IP:1
Name: YOUR_Display_1
连接之后,输入 user 的 passwd,既可看到界面了