分支限界法总结--例题(01背包,最大团,单源最短路径,装载问题,布线问题)
目录
- 分支限界法剪枝搜索策略(广度搜索)与算法框架
- 01背包问题
- 最大团
- 单源最短路径
- 装载问题
- 布线问题
分支限界法剪枝搜索策略(广度搜索)与算法框架
基本思想:
- 分支限界法与回溯法求解目标不同 : 回溯法的求解目标是找出解空间中满足约束条件的所有解,而分支限界法的求解目标是找出满足约束条件的一个解,或者是在满足约束条件的解中找出使某一个目标函数值达到极大或者极小的解,即某种意义下的最优解
- 搜索方式不同 : 回溯法以深度优先搜索的方式进行搜索,而分支限界法使用广度优先搜索或者最小耗费优先的方式进行搜索解空间,其策略是 : 在扩展结点处,先生成其所有的儿子结点(分支), 然后从当前的活结点表中选择下一个扩展结点。
- 计算一个函数值(限界) : 为了加速搜索的过程,在每一个活结点处,计算一个函数值,并根据函数值,从当前活结点表中选择一个最有利的结点作为扩展结点,使得搜索朝着解空间上最优解的分支进行推进,一遍尽快的找出一个最优解。
- 每个活结点只有一次机会成为扩展结点,一旦成为扩展结点,就一次性产生所有的儿子结点,在儿子结点中,导致不可行解或者导致非最优解的儿子结点被舍弃,其余的加入到活结点表中。
- 活结点表有两种框架:(1) 队列式分支限界法。(2) 优先队列式分支限界法 (主要是确定优先级的选取)
下面看几个例题:
01背包问题
解题思路:
- 对于
0-1背包问题中的每个活结点只有两个儿子 结点,分别表示对物品i的选取和对物品i的舍去;在判断儿子结点是否能加入到活结点表中,有两个 函数需要满足,第一个称为约束函数,判断能否满足背包容量约束,第二个称为限界函数,判断是否可能有最优解。 - 每次选取下一个活结点成为扩展结点的判断依据是当前情况下最有可能找到最优解的下一个结点。因此,每次选择扩展结点的方法:当前情况下,在活结点表中选择活结点的上界
uprofit(通过限界函数getBound求出)最大的活结点成为当前的扩展结点。 这一过程一直持续到找到所需的解或活结点表为空时为止。 - 为了在活结点表中选择拥有最大的上界
uprofit的活结点,在活结点表上实现优先队列。(堆按照uprofit排序) - 为了求出
0-1背包问题的最优解,对于每一个在活结点表中的活结点创建一个树结点,树节点需要反映该结点的父节点和是否有左孩子(有左孩子 表示物品i选取了,没有左孩子表示物品i舍去了)。因此,可以构造一颗子集树,最优解就是从树根到叶子结点的路径,子集树的第i层的所有结点就是在不同情况下对物品i的取舍结点。构造最优解的顺序是从叶子结点到根结点的过程。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 使用分支界限法解决01背包问题
*/
//子集树的结构
class Node {
public Node parent; //记录子集树的父节点
public boolean lChild; // 记录是左儿子还是右儿子
public Node(Node parent, boolean lChild) {
super();
this.parent = parent;
this.lChild = lChild;
}
}
//对背包按照单位重量价值排序的类
class UnitW implements Comparable<UnitW> {
public int id;
public double d; //
public UnitW(int id, double d) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.d = d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(UnitW o) { //按照d降序排列
// return -(d > o.d ? 1 :( d == o.d ? 0 : -1 ));
return -(Double.compare(d, o.d));
}
}
class HeapNode implements Comparable<HeapNode> {
public Node liveNode; //活结点
public int upProfit; //活结点的价值上界
public int profit; //结点所相应的价值
public int weight; //结点所相应的重量
public int level; //结点在子集树中的层数
public HeapNode(Node liveNode, int upProfit, int profit, int weight, int level) {
super();
this.liveNode = liveNode;
this.upProfit = upProfit;
this.profit = profit;
this.weight = weight;
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(HeapNode o) { //按照上界价值降序排列
// return -(upProfit > o.upProfit ? 1 : (upProfit == o.upProfit ? 0: -1));
return -(Integer.compare(upProfit, o.upProfit));
}
}
public class Main {
static int C;
static int n;
static int[] w;
static int[] v;
static int curW; //当前的重量
static int curVal; //当前的价值
static int[] bestX; //记录最优解
static PriorityQueue<HeapNode>heap;
//计算最优上界
static int getBound(int i) {
int cLeft = C - curW;
int b = curVal; //价值的上界
while (i < n && w[i] <= cLeft) { //以物品单位重量价值递减的顺序装填剩余容量
cLeft -= w[i];
b += v[i];
i++;
}
if (i < n) b += v[i] * 1.0 / w[i] * cLeft;
return b;
}
//生成一个活结点插入到子集树和最大堆中
static void addLiveNode(int up, int v, int w, int lev, Node par, boolean iCh) {
Node b = new Node(par, iCh);
HeapNode hN = new HeapNode(b, up, v, w, lev); //生成一个堆元素
heap.add(hN); //加入到堆中
}
//分支限界法求解
static int maxKnapsack() {
Node endNode = null;
int upProfit = getBound(0); //计算一开始的上界
int i = 0, bestV = 0;
while (i != n) {
if (curW + w[i] <= C) { //进入左子树
if (curVal + v[i] > bestV)
bestV = curVal + v[i];
addLiveNode(upProfit, curVal + v[i], curW + w[i], i + 1, endNode, true); //左子树插入到最大堆中
}
upProfit = getBound(i+1); //注意不是 (i) 计算下层的上界
if (upProfit >= bestV) //右子树可能含有最优解
addLiveNode(upProfit, curVal, curW, i + 1, endNode, false);
HeapNode top = heap.poll(); //把堆顶元素删掉
endNode = top.liveNode; //记录父亲结点
curW = top.weight;
curVal = top.profit;
upProfit = top.upProfit;
i = top.level;
}
//构造最优解
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
bestX[j] = endNode.lChild ? 1 : 0;
endNode = endNode.parent;
}
return curVal;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int T = cin.nextInt();
while(T-- > 0) {
int sumW = 0, sumV = 0;
n = cin.nextInt();
C = cin.nextInt();
int[] oriW = new int[n]; //体积
int[] oriV = new int[n]; //价值
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
oriW[i] = cin.nextInt();
sumW += oriW[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
oriV[i] = cin.nextInt();
sumV += oriV[i];
}
if (sumW <= C) {
System.out.println(sumV);
continue;
}
UnitW[] unitWS = new UnitW[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
unitWS[i] = new UnitW(i,oriV[i] * 1.0 / oriW[i]);
Arrays.sort(unitWS);
w = new int[n];
v = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
w[i] = oriW[unitWS[i].id];
v[i] = oriV[unitWS[i].id];
}
bestX = new int[n];
curW = 0;
curVal = 0;
heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
int maxValue = maxKnapsack();
System.out.println(maxValue);
int[] res = new int[n + 1]; //保存结果
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
res[unitWS[i].id] = bestX[i]; //获取最优解
System.out.println("---被选中物品的序号(从1开始)----");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (res[i] == 1)
System.out.print(i + 1 + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
最大团
最大团问题的解空间也是一颗子集树,结点的解空间树的结点类型是BNode,活结点优先队列中元素类型是CliqueHeapNode,cn是表示的该节点相应的团的顶点数,upn表示该结点为根的子树中最大顶点数的上界,level表示结点在子集空间树种所处的层次,lChild是左右儿子的标记 ,liveNode表示的是在子集树中的结点。
这里注意更新最优解以及右子树的剪枝:cn + n-i >= bestn。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 用分支限界法解决最大团问题
*/
//子集树的类
class BNode {
BNode parent; //记录子集树的父节点
boolean lChild; // 记录是左儿子还是右儿子
public BNode() {
}
public BNode(BNode parent, boolean lChild) {
super();
this.parent = parent;
this.lChild = lChild;
}
}
//优先队列的元素 -->按照
class CliqueHeapNode implements Comparable<CliqueHeapNode>{
BNode liveNode; //在子集树中的位置
public int upn;
public int cn;
public int level;
public CliqueHeapNode(BNode liveNode, int upn, int cn, int level) {
super();
this.liveNode = liveNode;
this.upn = upn;
this.cn = cn;
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(CliqueHeapNode o) { //按照upn降序排列
return -(upn > o.upn ? 1 : (upn == o.upn ? 0 : -1));
}
}
public class BBMaxClique {
private int[][] map;
private int n; //图的顶点个数
private LinkedList<CliqueHeapNode>heap;
private int[] bestx;
public BBMaxClique(int[][] map, int n, LinkedList<CliqueHeapNode> heap, int[] bestx) {
super();
this.map = map;
this.n = n;
this.heap = heap;
this.bestx = bestx;
}
public void AddLiveNode(int upn,int cn,int lev,BNode par,boolean iCh){
BNode b = new BNode(par,iCh);
CliqueHeapNode CH = new CliqueHeapNode(b, upn, cn, lev);
heap.add(CH);
Collections.sort(heap);
}
public int MaxClique(){
int i = 0;
BNode E = null;
int bestn = 0,cn = 0;
while( i != n){
boolean flag = true;
BNode B = E;
for(int j = i-1; j >= 0; B = B.parent, j--){ //注意起点是0
if(B.lChild == true && map[i][j] == 0){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
if(cn + 1 > bestn)bestn = cn+1;
AddLiveNode(cn + n-i+1,cn+1,i+1,E,true);//注意这里的上界是cn+n-i+1
}
if(cn + n-i >= bestn){
AddLiveNode(cn + n-i,cn,i+1,E,false);
}
CliqueHeapNode top = heap.poll();
E = top.liveNode;
cn = top.cn;
i = top.level;
}
for(int j = n-1; j >= 0; j--){
bestx[j] = (E.lChild == true) ? 1 : 0;
E = E.parent;
}
return bestn;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n,m; //顶点数,边数
n = cin.nextInt(); //顶点的序号是0~n-1
m = cin.nextInt();
int[] bestx = new int[n+1] ;// 记录每一个顶点
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) bestx[i] = 0; //一开始都不在团里面
int[][] map = new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)map[i][j] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
map[a-1][b-1] = map[b-1][a-1] = 1;
}
LinkedList<CliqueHeapNode>heap = new LinkedList<CliqueHeapNode>();
BBMaxClique mC = new BBMaxClique(map, n, heap, bestx);
System.out.println("-----最大团中点的个数-----");
System.out.println(mC.MaxClique());
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)System.out.print(bestx[i]+ " ");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---最大团中的点(序号从1开始)---");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if(bestx[i] == 1)
System.out.print(i+1 + " ");
System.out.println();
cin.close();
}
}
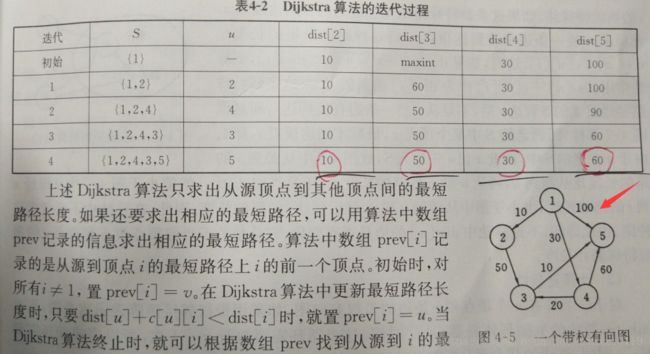
单源最短路径
活结点队列中使用极小堆存储,优先级是结点所对应的当前路径长。取出堆中的最小结点后,如果当前结点 i 到结点 j 有边可达,且从源点出发,途经顶点i再到顶点j的所相应的路径的长度小于当前最优路径长度,则将该结点加入到队列中。
然后就是利用控制关系进行剪枝,如果在解空间树种两条路径到达图中的一个顶点,而解空间树种A点所经过的长度小于B,则把B以及它的子树剪去。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 分支限界法解决单源最短路径
*/
public class BBShortestPath {
//最小堆中的元素类 id表示该活结点所表示的图中的相应的顶点号,length表示源点到该点的距离
private static class MinHeapNode implements Comparable<MinHeapNode>{
private int id;
private int length;
public MinHeapNode(int id, int length) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(MinHeapNode o) { //升序排列
return length > o.length ? 1: (length == o.length ? 0 : -1);
}
}
private static final int INF = 10000000;
private int n;
private int[][] map;
private int[] dist,pre; //记录最短距离的数组,以及保存前驱顶点的数组
public BBShortestPath(int n, int[][] map, int[] dist, int[] pre) {
super();
this.n = n;
this.map = map;
this.dist = dist;
this.pre = pre;
}
public void ShortestPath(int s){
LinkedList<MinHeapNode>heap = new LinkedList<MinHeapNode>();
MinHeapNode now = new MinHeapNode(s, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)dist[i] = INF;
dist[s] = 0;
while(true){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(map[now.id][j] != -1 && now.length + map[now.id][j] < dist[j]){
dist[j] = now.length + map[now.id][j];
pre[j] = now.id;
MinHeapNode next = new MinHeapNode(j, dist[j]) ;//加入活结点队列中
heap.add(next);
Collections.sort(heap);
}
}
if(heap.isEmpty())break;
else now = heap.poll();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = cin.nextInt();
int[] dist = new int[n+1];
int[] pre = new int[n+1];
int[][] map = new int[n+1][n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)map[i][j] = cin.nextInt();
}
BBShortestPath bbp = new BBShortestPath(n, map, dist, pre);
bbp.ShortestPath(1);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
System.out.println("源点到" + i + "结点的最短距离是 " + dist[i]);
System.out.println("这个结点的前驱结点是" + pre[i]);
}
}
}
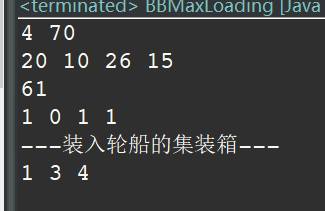
装载问题
使用优先队列式分支限界法解决装载问题,优先队列的优先级是从根节点到当前结点的相应载重量加上剩余集装箱的重量之和,进入左孩子之前,保证轮船的能装下当前的物品,进入右子树不需要检查。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 分支限界法结局解决最优装载问题
* @author 郑鑫
*/
class BMNode{
BMNode parent;
boolean iChild;
public BMNode() {
}
public BMNode(BMNode parent, boolean iChild) {
super();
this.parent = parent;
this.iChild = iChild;
}
}
class BMaxHeapNode implements Comparable<BMaxHeapNode>{
BMNode liveNode;
int upw;
int level;
public BMaxHeapNode(BMNode liveNode, int upw, int level) {
super();
this.liveNode = liveNode;
this.upw = upw;
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(BMaxHeapNode o) { //降序排列
return -(upw > o.upw ? 1 : ( upw == o.upw ? 0 : -1 ));
}
}
public class BBMaxLoading {
private int n,C;
private int[] w,bestx,r;
private LinkedList<BMaxHeapNode>heap;
public BBMaxLoading(int n, int c, int[] w, int[] bestx, int[] r, LinkedList<BMaxHeapNode> heap) {
super();
this.n = n;
C = c;
this.w = w;
this.bestx = bestx;
this.r = r;
this.heap = heap;
}
public void addLiveNode(int upw,int lev,BMNode par,boolean iCh){
BMNode bn = new BMNode(par,iCh);
BMaxHeapNode BH = new BMaxHeapNode(bn, upw, lev);
heap.add(BH);
Collections.sort(heap);
}
public int maxLoading(){ //返回最优值
int i = 1;
int cw = 0;
BMNode E = null;
while(i != n+1){
if(cw + w[i] <= C){
addLiveNode(cw+w[i]+r[i],i+1,E,true); //更新上界
}
addLiveNode(cw+r[i], i+1, E, false);
BMaxHeapNode top = heap.poll();
i = top.level;
E = top.liveNode;
cw = top.upw - r[i-1];
}
for(int j = n; j >= 1; j--){
bestx[j] = (E.iChild == true) ? 1 : 0;
E = E.parent;
}
return cw;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = cin.nextInt();
int C = cin.nextInt();
int[] w = new int[n+1];
int[] r = new int[n+1];
int[] bestx = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)w[i] = cin.nextInt();
for(int i = n-1; i >= 1; i--)r[i] = r[i+1] + w[i]; //定义剩余重量数组r
LinkedList<BMaxHeapNode>heap = new LinkedList<BMaxHeapNode>();
BBMaxLoading bbL = new BBMaxLoading(n, C, w, bestx, r, heap);
System.out.println(bbL.maxLoading());
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)System.out.print(bestx[i] + " ");
System.out.println("\n" + "---装入轮船的集装箱---");
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if(bestx[i] == 1) System.out.print(i + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
布线问题
这个问题和BFS寻找最短路没有很大的区别,注意一下四周填1的操作和记录路径的技巧就行。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 利用分支限界法解决布线问题 -->其实就是BFS加路径记录
*/
public class BBWireRouter {
private static class Point{
private int row;
private int col;
public Point(int row, int col) {
super();
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
}
private static final int[] dx = {0,1,0,-1};
private static final int[] dy = {1,0,-1,0};
private static int[][] map;//地图
private static int n,m,pathLen;
private static Point start,end;
private static LinkedList<Point> queue;
private static Point[] path; //记录路径
public static boolean FindPath(){
if(start.row == end.row && start.col == end.col ){
pathLen = 0;
return true;
}
map[start.row][start.col] = 2;
queue = new LinkedList<Point>();
queue.add(start);
Point now = new Point(start.row,start.col);
Point next = new Point(0,0);
boolean flag = false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
now = queue.poll();
if(now.row == end.row && now.col == end.col){
flag = true;
break;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
next = new Point(now.row + dx[i], now.col + dy[i]);
if(map[next.row][next.col] == 0){
map[next.row][next.col] = map[now.row][now.col] + 1;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
if(!flag)return false;
pathLen = map[end.row][end.col] - 2;
path = new Point[pathLen];
now = end;
for(int j = pathLen-1; j >= 0; j--){
path[j] = now;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
next = new Point(now.row + dx[i],now.col + dy[i]);
if(map[next.row][next.col] == j+2)break;
}
now = next;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
n = cin.nextInt(); m = cin.nextInt();
map = new int[n+2][m+2];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
map[i][j] = cin.nextInt();
}
}
for(int i = 0; i <= m+1; i++)map[0][i] = map[n+1][i] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= n+1; i++)map[i][0] = map[i][m+1] = 1;
start = new Point(0, 0);
end = new Point(0, 0);
start.row = cin.nextInt(); start.col = cin.nextInt();
end.row = cin.nextInt(); end.col = cin.nextInt();
FindPath();
System.out.println(pathLen);
for(int i = 0; i < pathLen-1; i++){
System.out.println("结点"+ (i+1) +"的位置" + (path[i].row) + "," + (path[i].col));
}
}
}