剑指offer刷题笔记-Java实现
1.找出数组中重复的数字
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums,数组中所有的数字都在 0∼n−1 的范围内。
数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字重复了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次。
请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
注意:如果某些数字不在 0∼n−1 的范围内,或数组中不包含重复数字,则返回 -1;
样例
给定 nums = [2, 3, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6, 7]。
返回 2 或 3。
解:将对应的值放在对应的框内
class Solution {
public int duplicateInArray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for(int x : nums) {
if(x < 0 || x > n)
return -1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n ;i++) {
while(i != nums[i]) {
if(nums[nums[i]] == nums[i])
return nums[i];
else{
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[tmp];
nums[tmp] = tmp;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
2.不修改数组找出重复的数字
给定一个长度为 n+1 的数组nums,数组中所有的数均在 1∼n 的范围内,其中 n≥1。
请找出数组中任意一个重复的数,但不能修改输入的数组。
样例
给定 nums = [2, 3, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6, 7]。
返回 2 或 3。
思考题:如果只能使用 O(1) 的额外空间,该怎么做呢?
解:
class Solution {
public int duplicateInArray(int[] nums) {
int l = 1, r = nums.length - 1;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1; // 划分区间[l,mid] [mid+1,r] mid = (l+r)/2;
int s = 0;
for(int x : nums) {
if(x >= l && x <=mid) {
s++;
}
}
if(s > mid - l + 1) {
r = mid;
}
else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return r;
}
}
3.二维数组中的查找
在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。
请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
样例
输入数组:
[
[1,2,8,9],
[2,4,9,12],
[4,7,10,13],
[6,8,11,15]
]
如果输入查找数值为7,则返回true,
如果输入查找数值为5,则返回false。
解:
算法
(单调性扫描) O(n+m)
核心在于发现每个子矩阵右上角的数的性质:
x左边的数都小于等于x,x下边的数都大于等于x。
因此我们可以从整个矩阵的右上角开始枚举,假设当前枚举的数是 x:
如果 x 等于target,则说明我们找到了目标值,返回true;
如果 x 小于target,则 x 左边的数一定都小于target,我们可以直接排除当前一整行的数;
如果 x 大于target,则 x 下边的数一定都大于target,我们可以直接排序当前一整列的数;
排除一整行就是让枚举的点的横坐标加一,排除一整列就是让纵坐标减一。
当我们排除完整个矩阵后仍没有找到目标值时,就说明目标值不存在,返回false。
时间复杂度分析
每一步会排除一行或者一列,矩阵一共有 n 行,m 列,所以最多会进行 n+m 步。所以时间复杂度是 O(n+m)。
class Solution {
public boolean searchArray(int[][] array, int target) {
if((array == null || array.length == 0) || (array.length == 1 && array[0].length == 0))
return false;
int i = 0, j = array[0].length - 1;
while(i < array.length && j >=0) {
if(array[i][j] == target)
return true;
if(array[i][j] > target) {
j--;
}
else {
i++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
4.替换空格
请实现一个函数,把字符串中的每个空格替换成"%20"。
你可以假定输入字符串的长度最大是1000。
注意输出字符串的长度可能大于1000。
样例
输入:“We are happy.”
输出:“We%20are%20happy.”
解法1:时间复杂度O(n) 不推荐使用,面试官不喜欢,使用了额外的空间。
class Solution {
public String replaceSpaces(StringBuffer str) {
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(str.charAt(i) != ' ') {
ans.append(str.charAt(i));
}
else {
ans.append("%20");
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
解法2: 双指针法 从后往前,相比从前往后遍历节省时间 时间复杂度O(n);
class Solution {
public String replaceSpaces(StringBuffer str) {
int len = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < str.length();i++) {
if(str.charAt(i) == ' ') len += 3;
else len++;
}
int i = str.length() - 1, j = len - 1;
str.setLength(len);
while(i >= 0) {
if(str.charAt(i) == ' ') {
str.setCharAt(j--, '0');
str.setCharAt(j--, '2');
str.setCharAt(j--, '%');
}
else {
str.setCharAt(j--, str.charAt(i));
}
i--;
}
return str.toString();
}
}
5.从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头结点,按照 从尾到头 的顺序返回节点的值。
返回的结果用数组存储。
样例
输入:[2, 3, 5]
返回:[5, 3, 2]
解法1:使用栈
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] printListReversingly(ListNode head) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
int count = 0;
for(ListNode node = head; node != null; node = node.next) {
stack.add(node.val);
count++;
}
int i = 0;
int[] res = new int[count];
while(!stack.empty()) {
res[i] = stack.pop();
i++;
}
return res;
}
}
解法2:利用三个指针将链表反转后,将其值返回
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] printListReversingly(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
if(head.next == null)
return new int[]{head.val};
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode nextTemp;
int count = 0;
while(head != null) {
nextTemp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = nextTemp;
count++;
}
int[] ans = new int[count];
for(int i = 0; i < count && pre != null; i++,pre = pre.next) {
ans[i] = pre.val;
}
return ans;
}
}
扩展:反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
// ListNode cur = head;
ListNode nextTemp;
while(head != null) {
nextTemp = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = nextTemp;
}
return pre;
}
}
6.重建二叉树
输入一棵二叉树前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建该二叉树。
注意:
二叉树中每个节点的值都互不相同;
输入的前序遍历和中序遍历一定合法;
样例
给定:
前序遍历是:[3, 9, 20, 15, 7]
中序遍历是:[9, 3, 15, 20, 7]
返回:[3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7, null, null, null, null]
返回的二叉树如下所示:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null)
return null;
if(preorder.length == 0 || inorder.length == 0)
return null;
if(preorder.length != inorder.length)
return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
if(preorder[0] == inorder[i]) {
//pre的0往后数i个是左子树的,copyofrange包含前面的下标,不包含后面的下标
//in的i往前数i个是左子树的。
root.left = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, 1, i+1), Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 0, i));
//注意in是从i+1开始,因为i是现在的根,i+1开始才是右子树
root.right = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, i+1, preorder.length), Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, i+1, inorder.length));
}
}
return root;
}
}
7.二叉树的下一个节点
给定一棵二叉树的其中一个节点,请找出中序遍历序列的下一个节点。
注意:
如果给定的节点是中序遍历序列的最后一个,则返回空节点;
二叉树一定不为空,且给定的节点一定不是空节点;
样例
假定二叉树是:[2, 1, 3, null, null, null, null], 给出的是值等于2的节点。
则应返回值等于3的节点。
解释:该二叉树的结构如下,2的后继节点是3。
2
/ \
1 3
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode father;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode p) {
if(p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
while(p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
}
return p;
}
while(p.father != null && p == p.father.right) {
p = p.father;
}
return p.father;
}
}
8.用两个栈实现一个队列
请用栈实现一个队列,支持如下四种操作:
push(x) – 将元素x插到队尾;
pop() – 将队首的元素弹出,并返回该元素;
peek() – 返回队首元素;
empty() – 返回队列是否为空;
注意:
你只能使用栈的标准操作:push to top,peek/pop from top, size 和 is empty;
如果你选择的编程语言没有栈的标准库,你可以使用list或者deque等模拟栈的操作;
输入数据保证合法,例如,在队列为空时,不会进行pop或者peek等操作;
样例:
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.peek(); // returns 1
queue.pop(); // returns 1
queue.empty(); // returns false
解:
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
class MyQueue {
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Stack stk = new Stack();
Stack cache = new Stack();
public MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stk.push(x);
}
public static void copy(Stack a, Stack b) {
while(a.size() != 0) {
b.push(a.peek());
a.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
copy(stk, cache);
int res = cache.peek();
cache.pop();
copy(cache, stk);
return res;
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
copy(stk, cache);
int res = cache.peek();
copy(cache, stk);
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stk.isEmpty();
}
}
9.斐波那契数列
输入一个整数 n ,求斐波那契数列的第 n 项。
假定从0开始,第0项为0。(n<=39)
样例
输入整数 n=5
返回 5
解法1:
class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
final int MOD = 1000000007; // 防止整数溢出,用an%MOD
int x = 0, y = 1, z = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
z = ( x + y)% MOD;
x = y;
y = z;
}
return z;
}
}
解法2:递归
class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
final int MOD = 1000000007; // 防止整数溢出,用an%MOD
if(n == 0)
return 0;
if(n == 1 || n == 2)
return 1;
return (Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2)) % MOD;
}
}
10.旋转数组的最小数字
输入一个升序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。
例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
数组可能包含重复项。
注意:数组内所含元素非负,若数组大小为0,请返回-1。
样例
输入:nums=[2,2,2,0,1]
输出:0
解: 利用选组数组的特性 使用二分查找法
class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length -1;
if(n < 0)
return -1;
while(n > 0 && nums[n] == nums[0]) {
n--;
}
if(nums[n] >= nums[0])
return nums[0];
int l = 0, r = n;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(nums[mid] < nums[0]) {
r = mid;
}
else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return nums[r];
}
}
11.矩阵中的路径
请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。
路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。
如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则之后不能再次进入这个格子。
注意:
输入的路径不为空;
所有出现的字符均为大写英文字母;
样例
matrix=
[
["A","B","C","E"],
["S","F","C","S"],
["A","D","E","E"]
]
str=“BCCE” , return “true”
str=“ASAE” , return “false”
解法1 :acwing解法
class Solution {
public boolean hasPath(char[][] matrix, String str) {
for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {
if(dfs(matrix, str, 0, i, j))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static boolean dfs(char[][] matrix, String str, int u, int x, int y) {
if(matrix[x][y] != str.charAt(u))
return false;
if(u == str.length() - 1)
return true;
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
char t = matrix[x][y];
matrix[x][y] = '*';
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a >= 0 && a < matrix.length && b >= 0 && b < matrix[a].length) {
if(dfs(matrix, str, u+1, a, b))
return true;
}
}
matrix[x][y] = t;
return false;
}
}
解法2:比较清楚直观的回溯法
class Solution {
public boolean hasPath(char[][] matrix, String str) {
if (matrix.length <= 0 || matrix[0].length <= 0)
return false;
int rows = matrix.length, cols = matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] flag = new boolean[rows][cols]; //为true表示当前节点已经被访问过
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(hasPathCore(matrix, str, rows, cols, i, j, 0,flag))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static boolean hasPathCore(char[][] matrix, String str, int rows, int cols, int row, int col,int index, boolean[][] flag) {
if (row < 0 || row >= rows || col < 0 || col >= cols || matrix[row][col] != str.charAt(index) || flag[row][col])
return false;
flag[row][col] = true;
if (index == str.length() - 1)
return true;
index++;
if (hasPathCore(matrix, str, rows, cols, row + 1, col, index, flag) ||
hasPathCore(matrix, str, rows, cols, row - 1, col, index, flag) ||
hasPathCore(matrix, str, rows, cols, row, col + 1, index, flag) ||
hasPathCore(matrix, str, rows, cols, row, col - 1 , index, flag)
)
return true;
flag[row][col] = false;
return false;
}
}
12.机器人的运动范围
地上有一个 m 行和 n 列的方格,横纵坐标范围分别是 0∼m−1 和 0∼n−1。
一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格。
但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。
请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
样例1
输入:k=7, m=4, n=5
输出:20
样例2
输入:k=18, m=40, n=40
输出:1484
解释:当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。
但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。
解:
class Solution {
public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols)
{
if (threshold < 0 || rows <= 0|| cols <= 0)
return 0;
// 默认为false, 为真时表示已经访问过了
boolean[][] flag = new boolean[rows][cols];
return helper(threshold, rows, cols, 0, 0, flag);
}
private int helper(int threshold, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, boolean[][] flag){
if (row < 0 || row >= rows || col < 0 || col >= cols || numSum(row) + numSum(col) > threshold || flag[row][col])
return 0;
flag[row][col] = true;
return helper(threshold, rows, cols, row - 1, col, flag) +
helper(threshold, rows, cols, row + 1, col, flag) +
helper(threshold, rows, cols, row , col - 1, flag) +
helper(threshold, rows, cols, row , col + 1, flag) + 1;
}
private int numSum(int i) {
int sum = 0;
while (i > 0) {
sum += i % 10;
i = i / 10;
}
return sum;
}
}
13.剪绳子
给你一根长度为 n 绳子,请把绳子剪成 m 段(m、n 都是整数,2≤n≤58 并且 m≥2)。
每段的绳子的长度记为k[0]、k[1]、……、k[m]。k[0]k[1] … k[m] 可能的最大乘积是多少?
例如当绳子的长度是8时,我们把它剪成长度分别为2、3、3的三段,此时得到最大的乘积18。
样例
输入:8
输出:18
解法1:这道题目是数学中一个很经典的问题。
下面我们给出证明:
首先把一个正整数 N 拆分成若干正整数只有有限种拆法,所以存在最大乘积。
假设 N=n1+n2+…+nk,并且 n1×n2×…×nk是最大乘积。
显然1不会出现在其中;
如果对于某 i 有 ni≥5,那么把 ni 拆分成 3+(ni−3),我们有 3(ni−3)=3ni−9>ni;
如果 ni=4,拆成 2+2乘积不变,所以不妨假设没有4;
如果有三个以上的2,那么 3×3>2×2×2,所以替换成3乘积更大;
综上,选用尽量多的3,直到剩下2或者4时,用2。
时间复杂度分析:当 n 比较大时,n 会被拆分成 ⌈n/3⌉⌈n/3⌉ 个数,我们需要计算这么多次减法和乘法,所以时间复杂度是 O(n)。
class Solution {
public int maxProductAfterCutting(int length)
{
if(length <= 3)
return 1 * (length - 1);
int res = 1;
if(length % 3 == 1) {
res = 4;
length -= 4;
}
else if(length % 3 == 2) {
res = 2;
length -= 2;
}
while(length != 0) {
res *= 3;
length -= 3;
}
return res;
}
}
14.二进制中 1 的个数
输入一个32位整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。
注意:
负数在计算机中用其绝对值的补码来表示。
样例1
输入:9
输出:2
解释:9的二进制表示是1001,一共有2个1。
样例2
输入:-2
输出:31
解释:-2在计算机里会被表示成11111111111111111111111111111110,
一共有31个1。
解: n&(n-1)
class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n)
{
int res = 0;
while(n != 0) {
n &= (n - 1);
res++;
}
return res;
}
}
15.数值的整数次方
实现函数double Power(double base, int exponent),求base的 exponent次方。
不得使用库函数,同时不需要考虑大数问题。
注意:
不会出现底数和指数同为0的情况
样例1
输入:10 ,2
输出:100
样例2
输入:10 ,-2
输出:0.01
解:
class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
double minus = 1;
if(exponent < 0) {
minus = -1;
exponent = -exponent;
}
double res = 1;
while(exponent != 0) {
res *= base;
exponent--;
}
if(minus == -1) {
res = 1 / res;
}
return res;
}
}
16. 在O(1)时间删除链表结点
给定单向链表的一个节点指针,定义一个函数在O(1)时间删除该结点。
假设链表一定存在,并且该节点一定不是尾节点。
样例
输入:链表 1->4->6->8
删掉节点:第2个节点即6(头节点为第0个节点)
输出:新链表 1->4->8
解:将下一个节点的复制到当前节点,删除下一个节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
**/
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
拓展:如果考虑是尾节点的情况
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
if(node.next == null) {
ListNode tmp = head;
while(tmp.next.next != null) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = null;
}
else {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
}
}
17.删除链表中重复的节点
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留。
样例1
输入:1->2->3->3->4->4->5
输出:1->2->5
样例2
输入:1->1->1->2->3
输出:2->3
解:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode head) {
if(head == null)
return null;
//新建一个节点,防止头结点被删除
ListNode firstNode = new ListNode(-1);
firstNode.next = head;
ListNode p = head;
//指向前一个节点
ListNode preNode = firstNode;
while(p != null && p.next != null) {
if(p.val == p.next.val) {
int val = p.val;
//向后重复查找
while(p != null && p.val ==val) {
p = p.next;
}
//上个非重复值指向下一个非重复值:即删除重复值
preNode.next = p;
}
else
{
//如果当前节点和下一个节点值不等,则向后移动一位
preNode = p;
p = p.next;
}
}
return firstNode.next;
}
}
18.表示数值的字符串
请实现一个函数用来判断字符串是否表示数值(包括整数和小数)。
例如,字符串"+100",“5e2”,"-123",“3.1416"和”-1E-16"都表示数值。
但是"12e",“1a3.14”,“1.2.3”,"±5"和"12e+4.3"都不是。
注意:
小数可以没有整数部分,例如.123等于0.123;
小数点后面可以没有数字,例如233.等于233.0;
小数点前面和后面可以有数字,例如233.666;
当e或E前面没有数字时,整个字符串不能表示数字,例如.e1、e1;
当e或E后面没有整数时,整个字符串不能表示数字,例如12e、12e+5.4;
样例:
输入: “0”
输出: true
解:
- 1.先去除行首和行尾空格;
- 2.行首如果有一个正负号,直接忽略;
- 3.如果字符串为空或只有一个’.’,则不是一个合法数;
- 4.循环整个字符串,去掉以下几种情况:
- (1) '.'或’e’多于1个;
- (2) '.'在’e’后面出现;
- (3) ‘e’后面或前面为空,或者’e’前面紧跟着’.’;
- (4) 'e’后面紧跟着正负号,但正负号后面为空;
- 剩下的情况都合法;
时间复杂度分析:整个字符串只遍历一遍,所以时间复杂度是 O(n)。
class Solution {
public boolean isNumber(String s) {
s = s.trim(); //去除首尾空格
if(s.length() == 0 || s.charAt(0) == '.' && s.length() == 1)
return false;
int index = 0; //记录索引位置
int dot = 0; //记录.的数量
int eNum = 0; // 记录e的数量
//判断是否有正负号
if(s.charAt(0) == '-' || s.charAt(0) == '+')
s = s.substring(1);
for(;index < s.length();index++) {
if(s.charAt(index) >= '0' && s.charAt(index) <= '9') //同时满足才行
continue;
else if(s.charAt(index) == '.') {
dot++;
if( eNum != 0 || dot > 1 || s.length() == 1)
return false;
}
else if(s.charAt(index) == 'e' || s.charAt(index) == 'E') {
eNum++;
if(index + 1 == s.length() || index == 0 || eNum > 1 || s.charAt(index - 1) == '.')
return false;
if(s.charAt(index + 1) == '-' || s.charAt(index + 1) == '+') {
if(index + 2 == s.length())
return false;
index++;
}
}
else
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
19.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序。
使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分。
样例
输入:[1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [1,3,5,2,4]
解:
class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
int l = 0;
int r = array.length - 1;
while(l < r) {
while(l < r && array[l] % 2 == 1)
l++;
while(l < r && array[r] % 2 == 0)
r--;
if(l < r) {
array[l] ^= array[r];
array[r] ^= array[l];
array[l] ^= array[r];
}
}
}
}
20.链表中倒数第K个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
注意:
- k >= 0;
- 如果k大于链表长度,则返回 NULL;
样例
输入:链表:1->2->3->4->5 ,k=2
输出:4
解:主要注意代码鲁棒性,考虑到各种情况
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode findKthToTail(ListNode pListHead, int k) {
if(pListHead == null || k == 0)
return null;
ListNode fast = pListHead;
for(int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
if(fast.next != null) { //考虑当链表长度小于k的情况
fast = fast.next;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
ListNode slow = pListHead;
while(fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
21.链表中环的入口节点
给定一个链表,若其中包含环,则输出环的入口节点。
若其中不包含环,则输出null。
样例
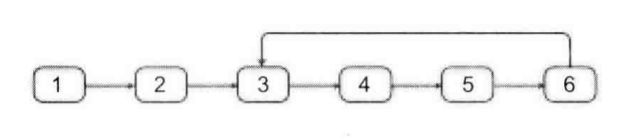
给定如上所示的链表:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
2
注意,这里的2表示编号是2的节点,节点编号从0开始。所以编号是2的节点就是val等于3的节点。
则输出环的入口节点3.
解:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null)
return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
//因为fast每次要走两步,所有需要判断fast的下一个是否为空
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
//一个走一步 一个走两步
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
//先找环,后找节点
if(slow == fast) {
slow = head;
while(slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
22.反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头结点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头结点。
样例
输入:1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出:5->4->3->2->1->NULL
解:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode reverse = null;
ListNode node = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while(node != null) {
ListNode pNext = node.next;
if(pNext == null)
reverse = node;
node.next = pre;
pre = node;
node = pNext;
}
return reverse;
}
}
23.合并两个排序的链表
输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的结点仍然是按照递增排序的。
样例
输入:1->3->5 , 2->4->5
输出:1->2->3->4->5->5
解:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1 == null)
return l2;
if(l2 == null)
return l1;
ListNode mergeNode = null;
if(l1.val < l2.val) {
mergeNode = l1;
mergeNode.next = merge(l1.next, l2);
}
else {
mergeNode = l2;
mergeNode.next = merge(l1, l2.next);
}
return mergeNode;
}
}
24.树的子结构
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。
我们规定空树不是任何树的子结构。
样例
树A:
8
/ \
8 7
/ \
9 2
/ \
4 7
树B:
8
/ \
9 2
返回 true ,因为B是A的子结构。
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasSubtree(TreeNode pRoot1, TreeNode pRoot2) {
boolean res = false;
if(pRoot1 != null && pRoot2 != null) {
if(pRoot1.val == pRoot2.val){
res = doesTree1HasTree2(pRoot1, pRoot2);
}
if(!res) {
res = hasSubtree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2);
}
if(!res) {
res = hasSubtree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2);
}
}
return res;
}
public boolean doesTree1HasTree2(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root2 == null)
return true;
if(root1 == null)
return false;
if(root1.val != root2.val)
return false;
return doesTree1HasTree2(root1.left,root2.left) && doesTree1HasTree2(root1.right, root2.right);
}
}
25.二叉树的镜像
输入一个二叉树,将它变换为它的镜像。
样例
输入树:
8
/ \
6 10
/ \ / \
5 7 9 11
[8,6,10,5,7,9,11,null,null,null,null,null,null,null,null]
输出树:
8
/ \
10 6
/ \ / \
11 9 7 5
[8,10,6,11,9,7,5,null,null,null,null,null,null,null,null]
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return;
if(root.left != null || root.right != null) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
mirror(root.left);
mirror(root.right);
}
}
}
26.对称的二叉树
请实现一个函数,用来判断一棵二叉树是不是对称的。
如果一棵二叉树和它的镜像一样,那么它是对称的。
样例
如下图所示二叉树[1,2,2,3,4,4,3,null,null,null,null,null,null,null,null]为对称二叉树:
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
如下图所示二叉树[1,2,2,null,4,4,3,null,null,null,null,null,null]不是对称二叉树:
1
/ \
2 2
\ / \
4 4 3
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return isSymmetric(root, root);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null && root2 == null)
return true;
if(root1 == null || root2 == null)
return false;
if(root1.val != root2.val)
return false;
return isSymmetric(root1.left, root2.right) && isSymmetric(root1.right, root2.left);
}
}
27.包含min函数的栈
设计一个支持push,pop,top等操作并且可以在O(1)时间内检索出最小元素的堆栈。
push(x)–将元素x插入栈中
pop()–移除栈顶元素
top()–得到栈顶元素
getMin()–得到栈中最小元素
样例
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-1);
minStack.push(3);
minStack.push(-4);
minStack.getMin(); --> Returns -4.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> Returns 3.
minStack.getMin(); --> Returns -1.
解:
class MinStack {
/** initialize your data structure here. */
Stack stackData = new Stack();
Stack stackMin = new Stack();
public MinStack() {
}
public void push(int x) {
stackData.push(x);
if(stackMin.size() == 0 || stackMin.peek() > x)
stackMin.push(x);
else
stackMin.push(stackMin.peek());
}
public void pop() {
if(!stackData.isEmpty()) {
stackData.pop();
stackMin.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
return stackData.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return stackMin.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
28.栈的压入、弹出序列
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。
假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。
例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
注意:若两个序列长度不等则视为并不是一个栈的压入、弹出序列。若两个序列都为空,则视为是一个栈的压入、弹出序列。
样例
输入:[1,2,3,4,5]
[4,5,3,2,1]
输出:true
解:借用一个辅助的栈,遍历压栈顺序,先讲第一个放入栈中,这里是1,
然后判断栈顶元素是不是出栈顺序的第一个元素,这里是4,很显然1≠4,所以我们继续压栈,
直到相等以后开始出栈,出栈一个元素,则将出栈顺序向后移动一位,直到不相等,
这样循环等压栈顺序遍历完成,如果辅助栈还不为空,说明弹出序列不是该栈的弹出顺序。
举例:
入栈1,2,3,4,5
出栈4,5,3,2,1
首先1入辅助栈,此时栈顶1≠4,继续入栈2
此时栈顶2≠4,继续入栈3
此时栈顶3≠4,继续入栈4
此时栈顶4=4,出栈4,弹出序列向后一位,此时为5,,辅助栈里面是1,2,3
此时栈顶3≠5,继续入栈5
此时栈顶5=5,出栈5,弹出序列向后一位,此时为3,,辅助栈里面是1,2,3
….
依次执行,最后辅助栈为空。如果不为空说明弹出序列不是该栈的弹出顺序。
class Solution {
public boolean isPopOrder(int [] pushV,int [] popV) {
if(pushV.length == 0 && popV.length == 0)
return true;
if(pushV.length != popV.length)
return false;
int index = 0;
Stack stack = new Stack();
for(int i = 0; i < pushV.length; i++) {
stack.push(pushV[i]);
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popV[index]) {
//当栈不为空且栈顶元素等于弹出序列元素时候,
//就弹出一个,同时让弹出序列后移一个
stack.pop();
index++;
}
}
//如果最后,栈不为空,相当于没有按照给定的弹出popV弹出完毕
//就说明不能按照popV,返回false
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
29.不分行从上往下打印二叉树
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个结点,同一层的结点按照从左到右的顺序打印。
样例
输入如下图所示二叉树[8, 12, 2, null, null, 6, null, 4, null, null, null]
8
/ \
12 2
/
6
/
4
输出:[8, 12, 2, 6, 4]
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList layerList = new ArrayList();
if(root == null)
return layerList;
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
layerList.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
queue.add(node.right);
}
return layerList;
}
}
30.分行从上到下打印二叉树
从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层的结点按从左到右的顺序打印,每一层打印到一行。
样例
输入如下图所示二叉树[8, 12, 2, null, null, 6, null, 4, null, null, null]
8
/ \
12 2
/
6
/
4
输出:[[8], [12, 2], [6], [4]]
解法1:剑指offer书上思路,利用
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
//list嵌套的初始化
List> layerList= new ArrayList>();
if(root == null)
return layerList;
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
int nextLevel = 0; //记录下一层节点数量
int toBePrinted = 1;// 记录当前层还没有打印的节点数
List tmpList = new ArrayList();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
tmpList.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
++nextLevel;
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
++nextLevel;
}
--toBePrinted;
if(toBePrinted == 0) {
// layerList.add(tmpList);
// tmpList = new ArrayList();
layerList.add(new ArrayList<>(tmpList));
tmpList.clear();
toBePrinted = nextLevel;
nextLevel = 0;
}
}
return layerList;
}
}
解法2:每一层结束的时候,往queue里塞一个NULL做标记。
在queue里读取一个数出来之后,先看看是不是level标识符NULL(因为是BFS,当前level读完,下一个level有哪些要读的也都放在queue里了,可以在queue结尾给加一个新的NULL), 是的话再看看是不是整个树读完了(即queue里没有点了)。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
List> layerList= new ArrayList>();
if(root == null)
return layerList;
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
List tmpList = new ArrayList();
queue.add(root);
queue.add(null);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node != null) {
tmpList.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null)
queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
queue.add(node.right);
}
else {
if(!queue.isEmpty())
queue.add(null);
// layerList.add(tmpList);
// tmpList = new ArrayList();
layerList.add(new ArrayList<>(tmpList));
tmpList.clear();
}
}
return layerList;
}
}
31.之字形打印二叉树
请实现一个函数按照之字形顺序从上向下打印二叉树。
即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右到左的顺序打印,第三行再按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
样例
输入如下图所示二叉树[8, 12, 2, null, null, 6, 4, null, null, null, null]
8
/ \
12 2
/ \
6 4
输出:[[8], [2, 12], [6, 4]]
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
List> resList = new ArrayList>();
if(root == null)
return resList;
//两个栈,分别存放偶数层和奇数层的节点
Stack s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack s2 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(root);
int level = 1;
List tmp = new ArrayList<>();
while(!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) {
if(level % 2 != 0) {
while(!s1.empty()) {
TreeNode node = s1.pop();
tmp.add(node.val);
// 因为下层为偶数层,从右往左打印,所以左子树先进栈
if(node.left != null)
s2.push(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
s2.push(node.right);
}
if(!tmp.isEmpty()) {
resList.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
tmp.clear();
level++;
}
}
else {
while(!s2.empty()) {
TreeNode node = s2.pop();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.right != null)
s1.push(node.right);
if(node.left != null)
s1.push(node.left);
}
if(!tmp.isEmpty()) {
resList.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
tmp.clear();
level++;
}
}
}
return resList;
}
}
32.二叉搜索树的后续遍历序列
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。
如果是则返回true,否则返回false。
假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
样例
输入:[4, 8, 6, 12, 16, 14, 10]
输出:true
解:
class Solution {
public boolean verifySequenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if(sequence == null || sequence.length <= 0)
return false;
return isBST(sequence, 0, sequence.length - 1);
}
public boolean isBST(int[] ans, int start, int end) {
if(start >= end)
return true;
int index = start;
for(;index < end;index++) {
if(ans[index] > ans[end])
break;
}
for(int i = index; i < end; i++) {
if(ans[i] < ans[end])
return false;
}
return isBST(ans, start, index - 1) && isBST(ans, index, end - 1);
}
}
33.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。
从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
样例
给出二叉树如下所示,并给出num=22。
5
/ \
4 6
/ / \
12 13 6
/ \ / \
9 1 5 1
输出:[[5,4,12,1],[5,6,6,5]]
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List> resList = new ArrayList>();
private List path = new ArrayList();
public List> findPath(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root == null)
return resList;
path.add(root.val);
sum -= root.val;
if(sum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
resList.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
else {
findPath(root.left, sum);
findPath(root.right, sum);
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1); //返回父节点
return resList;
}
}
34.复杂链表的复制
请实现一个函数可以复制一个复杂链表。
在复杂链表中,每个结点除了有一个指针指向下一个结点外,还有一个额外的指针指向链表中的任意结点或者null。
解法1:将复制的链表连接到原链表 时间复杂度O(n)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next, random;
* ListNode(int x) { this.val = x; }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode copyRandomList(ListNode head) {
clonedNodes(head);
clonedRandom(head);
return reconnectNodes(head);
}
private void clonedNodes(ListNode head) {
ListNode node = head;
while(node != null) {
ListNode clonedNode = new ListNode(node.val);
//ListNode clonedNode = null;
//clonedNode.val = node.val;
clonedNode.random = null;
clonedNode.next = node.next;
node.next = clonedNode;
node = clonedNode.next;
}
}
private void clonedRandom(ListNode head) {
ListNode node = head;
while(node != null) {
ListNode clonedNode = node.next;
if(node.random != null) {
clonedNode.random = node.random.next;
}
node = clonedNode.next;
}
}
private ListNode reconnectNodes(ListNode head) {
ListNode node = head;
ListNode clonedHead = null;
ListNode clonedNode = null;
if(node != null) {
clonedHead = clonedNode = node.next;
node.next = clonedNode.next;
node = node.next;
}
while(node != null) {
clonedNode.next = node.next;
clonedNode = clonedNode.next;
node.next = clonedNode.next;
node = node.next;
}
return clonedHead;
}
}
解法2:利用哈希表,两次遍历原链表,时间复杂度O(n^2)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next, random;
* ListNode(int x) { this.val = x; }
* };
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode copyRandomList(ListNode head) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
ListNode node = head;
while(node !=null) {
map.put(node, new ListNode(node.val));
node = node.next;
}
node = head;
while(node != null) {
map.get(node).next = map.get(node.next);
map.get(node).random = map.get(node.random);
node = node.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
35.二叉搜索树与双向链表
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。
要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
注意:
需要返回双向链表最左侧的节点。
例如,输入下图中左边的二叉搜索树,则输出右边的排序双向链表。
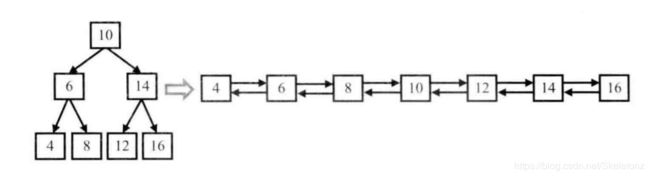
解:递归 中序遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode head = null;
private TreeNode resHead = null;
public TreeNode convert(TreeNode root) {
convertSub(root);
return resHead;
}
private void convertSub(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return;
convertSub(root.left);
if(head == null) {
head = root;
resHead = root;
}
else {
head.right = root;
root.left = head;
head = root;
}
convertSub(root.right);
}
}
36.序列化二叉树
请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
您需要确保二叉树可以序列化为字符串,并且可以将此字符串反序列化为原始树结构。
样例
你可以序列化如下的二叉树
8
/ \
12 2
/ \
6 4
为:"[8, 12, 2, null, null, 6, 4, null, null, null, null]"
注意:
以上的格式是AcWing序列化二叉树的方式,你不必一定按照此格式,所以可以设计出一些新的构造方式。
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return "#,";
String res = root.val + ",";
res = res + serialize(root.left);
res = res + serialize(root.right);
return res;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] values = data.split(",");
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
for(int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
queue.add(values[i]);
}
return reconPre(queue);
}
TreeNode reconPre(Queue queue) {
String value = queue.poll();
if(value.equals("#"))
return null;
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(value));// String转int
head.left = reconPre(queue);
head.right = reconPre(queue);
return head;
}
}
37.数字排列
输入一组数字(可能包含重复数字),输出其所有的排列方式。
样例
输入:[1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
解:
class Solution {
private List> resList;
private int[] path;
private boolean[] st;
public List> permutation(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return null;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
resList = new ArrayList>();
st = new boolean[nums.length];
path = new int[nums.length];
dfs(nums, 0, 0);
return resList;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, int u, int start) {
if(u == nums.length) {
resList.add(Arrays.stream(path).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()));//int[] 转List
return;
}
if(u == 0 || nums[u] != nums[u - 1])
start = 0;
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(!st[i]) { // 判断当前位置是否被用过
st[i] = true;
path[i] = nums[u];
dfs(nums, u + 1, i + 1);
st[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
38.数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。
假设数组非空,并且一定存在满足条件的数字。
思考题:
假设要求只能使用 O(n) 的时间和额外 O(1) 的空间,该怎么做呢?
样例
输入:[1,2,1,1,3]
输出:1
解法1:
* 一次再数组中删除两个不同的数,最后剩下的数有可能是超过一半的。所以要检验一下。 一个数出现次数大于一半,他肯定会被剩下来,但是剩下来的缺不一定满足。
* 算法步骤:
* 如果times为0,就把候选设为当前值。
* 如果下个数和候选一样,times就++。
* 如果下个数和候选不一样,times就–。相当于对子,同归于尽。因为超过一半的数肯定超过剩下的所有数。所以和这个数对,这个数肯定会剩下来。
* 但是剩下的数不一定是,比如 1 2 3 剩下3 比如 1 2 1 3 3 3 2 2 也是剩下3.所以要余外的判断,看是否这个数真的超过。
class Solution {
public int moreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int cand = 0;
int times = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(times == 0) {
cand = nums[i];
times = 1;
}
else if(nums[i] == cand) {
times++;
}
else {
times--;
}
}
times = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] == cand)
times++;
}
if(times*2 > nums.length) {
return cand;
}
else
return 0;
}
}
解法2:排序。数组排序后,如果某个数字出现次数超过数组的长度的一半,则一定会数组中间的位置。所以我们取出排序后中间位置的数,统计一下它的出现次数是否大于数组长度的一半;
class Solution {
public int moreThanHalfNum_Solution(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return 0;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int half = nums.length >> 1;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] == nums[half])
count++;
}
if(count > half)
return nums[half];
else
return 0;
}
}
39.最小的K个数
输入n个整数,找出其中最小的k个数。
注意:
数据保证k一定小于等于输入数组的长度;
输出数组内元素请按从小到大顺序排序;
样例
输入:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] , k=4
输出:[1,2,3,4]
解法1:直接排序,然后遍历
class Solution {
public List getLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
List res = new ArrayList();
if(input == null || k == 0 || k > input.length)
return res;
Arrays.sort(input);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
res.add(input[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
解法2:利用最大堆保存这k个数,每次只和堆顶比,如果比堆顶小,删除堆顶,新数入堆。
class Solution {
public List getLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
List res = new ArrayList();
if(input == null || k == 0 || k > input.length)
return res;
/*
* 优先队列的作用是能保证每次取出的元素都是队列中权值最小的
*(Java的优先队列每次取最小元素,C++的优先队列每次取最大元素)。
* 这里牵涉到了大小关系,元素大小的评判可以通过元素本身的自然顺序(natural ordering),
* 也可以通过构造时传入的比较器(Comparator,类似于C++的仿函数)。
* Java中PriorityQueue实现了Queue接口,不允许放入null元素;其通过堆实现,
*具体说是通过完全二叉树(complete binary tree)实现的小顶堆(任意一个非叶子节点的权值,
*都不大于其左右子节点的权值),也就意味着可以通过数组来作为PriorityQueue的底层实现。
*/
PriorityQueue maxHeap = new PriorityQueue(k, new Comparator() {
public int compare(Integer e1, Integer e2) {
return e2.compareTo(e1);
}
});
for(int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
if(maxHeap.size() != k)
maxHeap.offer(input[i]);
else {
if(maxHeap.peek() > input[i]) {
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(input[i]);
}
}
}
for(Integer i : maxHeap) {
res.add(i); //此时输出的是按照从大到小顺序排列的
}
// 对List进行排序,如无要求,可不写
Collections.sort(res, new Comparator() {
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
});
return res;
}
}
40.数据流中的中位数
如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?
如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。
如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。
样例
输入:1, 2, 3, 4
输出:1,1.5,2,2.5
解释:每当数据流读入一个数据,就进行一次判断并输出当前的中位数。
解:我们可以将数据排序后分为两部分,左边部分的数据总是比右边的数据小。那么,我们就可以用最大堆和最小堆来装载这些数据:
最大堆装左边的数据,取出堆顶(最大的数)的时间复杂度是O(1)
最小堆装右边的数据,同样,取出堆顶(最小的数)的时间复杂度是O(1)
从数据流中拿到一个数后,先按顺序插入堆中:如果左边的最大堆是否为空或者该数小于等于最大堆顶的数,则把它插入最大堆,否则插入最小堆。然后,我们要保证左边的最大堆的size等于右边的最小堆的size或者最大堆的size比最小堆的size大1。
要获取中位数的话,直接判断最大堆和最小堆的size,如果相等,则分别取出两个堆的堆顶除以2得到中位数,不然,就是最大堆的size要比最小堆的size大,这时直接取出最大堆的堆顶就是我们要的中位数。
class Solution {
// 小顶堆(右)默认容量11
private PriorityQueue rHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 大顶堆(左)
private PriorityQueue lHeap = new PriorityQueue(15, new Comparator(){
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
// 保证lHeap.size() >= rHeap.size();
public void insert(Integer num) {
//先按照大小插入,然后再调整
if(lHeap.isEmpty() || num <= lHeap.peek())
lHeap.offer(num);
else
rHeap.offer(num);
if(lHeap.size() < rHeap.size()) {
lHeap.offer(rHeap.peek());
rHeap.poll();
}
else if(lHeap.size() - rHeap.size() == 2) {
rHeap.offer(lHeap.peek());
lHeap.poll();
}
}
public Double getMedian() {
if(lHeap.size() > rHeap.size())
return new Double(lHeap.peek()); // 应该用包装类型Double
else
return new Double(lHeap.peek() + rHeap.peek())/2;
}
}
41.连续字数的最大和
输入一个 非空 整型数组,数组里的数可能为正,也可能为负。
数组中一个或连续的多个整数组成一个子数组。
求所有子数组的和的最大值。
要求时间复杂度为O(n)。
样例
输入:[1, -2, 3, 10, -4, 7, 2, -5]
输出:18
解:
对于一个数组中的一个数x,若是x的左边的数加起来非负,那么加上x能使得值变大,这样我们认为x之前的数的和对整体和是有贡献的。如果前几项加起来是负数,则认为有害于总和。
我们用cur记录当前值, 用max记录最大值,如果cur<0,则舍弃之前的数,让cur等于当前的数字,否则,cur = cur+当前的数字。若cur和大于max更新max。
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int cur = nums[0], max = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
cur = cur > 0 ? cur + nums[i] : nums[i];
if(max < cur)
max = cur;
}
return max;
}
}
42.从 1 到 n 整数中 1 出现的次数
输入一个整数n,求从1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。
例如输入12,从1到12这些整数中包含“1”的数字有1,10,11和12,其中“1”一共出现了5次。
样例
输入: 12
输出: 5
解:
设N = abcde ,其中abcde分别为十进制中各位上的数字。
如果要计算百位上1出现的次数,它要受到3方面的影响:百位上的数字,百位以下(低位)的数字,百位以上(高位)的数字。
① 如果百位上数字为0,百位上可能出现1的次数由更高位决定。比如:12013,则可以知道百位出现1的情况可能是:100199,11001199,21002199,,…,1110011199,一共1200个。可以看出是由更高位数字(12)决定,并且等于更高位数字(12)乘以 当前位数(100)。
② 如果百位上数字为1,百位上可能出现1的次数不仅受更高位影响还受低位影响。比如:12113,则可以知道百位受高位影响出现的情况是:100199,11001199,21002199,,….,1110011199,一共1200个。和上面情况一样,并且等于更高位数字(12)乘以 当前位数(100)。但同时它还受低位影响,百位出现1的情况是:12100~12113,一共114个,等于低位数字(113)+1。
③ 如果百位上数字大于1(29),则百位上出现1的情况仅由更高位决定,比如12213,则百位出现1的情况是:100199,11001199,21002199,…,1110011199,1210012199,一共有1300个,并且等于更高位数字+1(12+1)乘以当前位数(100)。
class Solution {
public int numberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
if(n == 0)
return 0;
int res = 0;
int cur = 0, before = 0, after = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i <= n) {
before = n / (i*10); //当前位置以上的数字
cur = (n/i)%10; // 当前位置上的数字
after = n - n/i*i; // 当前位置以下的数字
if(cur == 0) {
// 如果当前位置上的数为0,出现1的次数由高位决定,等于高位数字 * 当前位数
res += before * i;
}
else if(cur == 1) {
// 如果为1, 出现1的次数由高位和低位决定,高位*当前位+低位+1
res += before * i + after + 1;
}
else {
// 如果大于1, 出现1的次数由高位决定,(高位数字+1)* 当前位数
res += (before + 1) * i;
}
i *= 10;
}
return res;
}
}
43.数字序列中某一位的数字
数字以0123456789101112131415…的格式序列化到一个字符序列中。
在这个序列中,第5位(从0开始计数)是5,第13位是1,第19位是4,等等。
请写一个函数求任意位对应的数字。
样例
输入:13
输出:1
解:
class Solution {
public int digitAtIndex(int n) {
if(n < 0)
return -1;
int digits = 1;
while(true){
int digitNumbers = countOfNumbersFor(digits); //当前位数的数值个数
//数值乘上它的位数等于数字个数
//比如,两位数有90个(10 ~ 99),每个数值有2个数字,总数字个数为180
int countOfNumbers = digitNumbers * digits;
if(countOfNumbers < 0)
countOfNumbers = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(n < countOfNumbers)
return digitAtIndex(n, digits);
else {
n -= countOfNumbers;
digits++;
}
}
}
//digits位数的数字个数
//两位数有9*10个(10 ~ 99) 三位数有9*100(100 ~ 999)
private int countOfNumbersFor(int digits) {
if(digits == 1)
return 10;
int count = (int)Math.pow(10, digits - 1); // pow() 返回第一参数的第二个参数次方
return 9 * count;
}
private int digitAtIndex(int index, int digits) {
// 对应的数值
int number = beginNumberFor(digits) + index / digits;
// 从数值右边开始算的位置
int indexFromRight = digits - index % digits;
// 去除右边的indexFromRight - 1个数字
for(int i = 1; i < indexFromRight; i++) {
number /= 10;
}
return number % 10;
}
// digits位数的第一个数字,两位数从10开始,三位数从100开始
private int beginNumberFor(int digits) {
if(digits == 1)
return 0;
return (int) Math.pow(10,digits - 1);
}
}
44.把数组排成最小的数
输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。
例如输入数组[3, 32, 321],则打印出这3个数字能排成的最小数字321323。
样例
输入:[3, 32, 321]
输出:321323
注意:输出数字的格式为字符串
解:先将数组转换成字符串数组,然后对字符串数组按照规则排序,最后将排好序的字符串数组拼接出来。
关键就是制定排序规则:
若ab > ba 则 a > b
若ab < ba 则 a < b
若ab = ba 则 a = b
解释说明:
a = 21
b = 2
因为 212 < 221, 即 ab < ba ,所以 a < b
所以我们通过对ab和ba比较大小,来判断a在前或者b在前的。
class Solution {
public String printMinNumber(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len == 0)
return "";
if(len == 1)
return String.valueOf(nums[0]);
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
String[] str = new String[len];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
str[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]);
Arrays.sort(str, new Comparator(){
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
String s1 = o1 + o2;
String s2 = o2 + o1;
return s1.compareTo(s2); //o1 - o2 升序, o2 - o1降序
}
});
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
res.append(str[i]);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
45.把数字翻译成字符串
给定一个数字,我们按照如下规则把它翻译为字符串:
0翻译成”a”,1翻译成”b”,……,11翻译成”l”,……,25翻译成”z”。
一个数字可能有多个翻译。例如12258有5种不同的翻译,它们分别是”bccfi”、”bwfi”、”bczi”、”mcfi”和”mzi”。
请编程实现一个函数用来计算一个数字有多少种不同的翻译方法。
样例
输入:“12258”
输出:5
解:从后往前递归,因为从前往后存在重复的情况
class Solution {
public int getTranslationCount(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() <= 0)
return 0;
return getTransCount(s);
}
private int getTransCount(String s) {
// 从后往前递归,因为从前往后会有重复的情况
int len = s.length();
int[] counts = new int[len];
int count = 0;
for(int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
count = 0;
if(i < len -1)
// 当i= 10 && converted <= 25) {
if(i < len - 2)
count += counts[i + 2];
else
// 如果不符合,只加上本位那一种情况
count += 1;
}
}
counts[i] = count;
}
count = counts[0]; // 0 位即为整体的数目
return count;
}
}
46.礼物的最大价值
在一个m×n的棋盘的每一格都放有一个礼物,每个礼物都有一定的价值(价值大于0)。
你可以从棋盘的左上角开始拿格子里的礼物,并每次向右或者向下移动一格直到到达棋盘的右下角。
给定一个棋盘及其上面的礼物,请计算你最多能拿到多少价值的礼物?
注意:
m,n>0
样例:
输入:
[
[2,3,1],
[1,7,1],
[4,6,1]
]
输出:19
解释:沿着路径 2→3→7→6→1 可以得到拿到最大价值礼物。
解法1:
class Solution {
public int getMaxValue(int[][] grid) {
if((grid == null || grid.length == 0) || (grid.length == 1 && grid[0].length == 0))
return 0;
int rows = grid.length, cols = grid[0].length;
int[][] maxValues = new int[rows][cols];
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
int left = 0;
int up = 0;
if(i > 0)
up = maxValues[i - 1][j];
if(j > 0)
left = maxValues[i][j - 1];
maxValues[i][j] = Math.max(left, up) + grid[i][j];
}
}
int maxValue = maxValues[rows - 1][cols - 1];
maxValues = null;
return maxValue;
}
}
解法2:优化版,使用一个一位数组代替二维数组
class Solution {
public int getMaxValue(int[][] grid) {
if((grid == null || grid.length == 0) || (grid.length == 1 && grid[0].length == 0))
return 0;
int rows = grid.length, cols = grid[0].length;
int[] maxValues = new int[cols];
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
int up = 0;
int left = 0;
if(i > 0) {
up = maxValues[j];
}
if(j > 0){
left = maxValues[j - 1];
}
maxValues[j] = Math.max(up, left) + grid[i][j];
}
}
int maxValue = maxValues[cols - 1];
// maxValues = null;
return maxValue;
}
}
47.最长不含重复字符的子字符串
请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子字符串的长度。
假设字符串中只包含从’a’到’z’的字符。
样例
输入:“abcabc”
输出:3
解:动态规划,用f(i)表示以i个字符结尾不包含重复子字符串的最长长度,从左向右扫描
1、若第i个字符在之前没出现过,则 f(i) = f(i-1) + 1;
2、若第i个字符在之前出现过,
计算第i个字符距离上次出现之间的距离为d
(a)若d <= f(i-1),则说明第i个字符上次出现在f(i-1)对应的不重复字符串之内,那么这时候更新 f(i) = d
(b)若d > f(i-1),则无影响,f(i) = f(i-1) + 1
class Solution {
public int longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0)
return 0;
int curlen = 0, maxlen = 0;
int[] position = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)
position[i] = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
int preIndex = position[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
if(preIndex < 0 || i - preIndex > curlen) //没出现过,或者d > f(i-1)
curlen++;
else { //出现过了
if(curlen > maxlen)
maxlen = curlen;
curlen = i - preIndex; // f(i) = d;
}
position[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] = i;
}
if(curlen > maxlen)
maxlen = curlen;
return maxlen;
}
}
48.丑数
我们把只包含因子2、3和5的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。
例如6、8都是丑数,但14不是,因为它包含因子7。
求第n个丑数的值。
样例
输入:5
输出:5
注意:习惯上我们把1当做第一个丑数。
解法1:逐个判断,直观但不够高效
class Solution {
public int getUglyNumber(int n) {
if(n <= 0)
return 0;
int number = 0;
int uglyFound = 0;
while(uglyFound < n) {
++number;
if(isUgly(number))
uglyFound++;
}
return number;
}
private boolean isUgly(int num) {
while(num % 2 == 0)
num /= 2;
while(num % 3 == 0)
num /= 3;
while(num % 5 == 0)
num /= 5;
return (num == 1) ? true : false;
}
}
解法2:只求丑数,不要去管非丑数。每个丑数必然是由小于它的某个丑数乘以2,3或5得到的,这样我们把求得的丑数都保存下来,用之前的丑数分别乘以2,3,5,找出这三这种最小的并且大于当前最大丑数的值,即为下一个我们要求的丑数。这种方法用空间换时间,时间复杂度为O(n)。
class Solution {
public int getUglyNumber(int n) {
if(n <= 0)
return 0;
int t2 = 0, t3 = 0, t5 = 0;
int[] res = new int[n];
res[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) { //for是先判断条件后再执行
res[i] = Math.min(res[t2]*2, Math.min(res[t3]*3, res[t5]*5));
if(res[i] == res[t2]*2)
t2++;
if(res[i] == res[t3]*3)
t3++;
if(res[i] == res[t5]*5)
t5++;
}
return res[n - 1];
}
}
49.字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
在字符串中找出第一个只出现一次的字符。
如输入"abaccdeff",则输出b。
如果字符串中不存在只出现一次的字符,返回#字符。
样例:
输入:“abaccdeff”
输出:‘b’
解法1:利用哈希表
class Solution {
public char firstNotRepeatingChar(String s) {
int len = s.length();
if(s == null || len == 0)
return '#';
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) {
int value = map.get(s.charAt(i));
map.put(s.charAt(i), value + 1);
}
else {
map.put(s.charAt(i), 1);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(map.get(s.charAt(i)) == 1)
return s.charAt(i);
}
return '#';
}
}
解法2:利用数组,char是一个长度为8的数据类型,总共有256种可能,用一个长度为256的数组存储次数即可。
class Solution {
public char firstNotRepeatingChar(String s) {
int len = s.length();
if(s == null || len == 0)
return '#';
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
int[] m = new int[256]; // char是一个长度为8的数据类型,总共有256种可能
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
m[str[i]]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if(m[str[i]] == 1)
return str[i];
}
return '#';
}
}
50.字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符
请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。
例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符”go”时,第一个只出现一次的字符是’g’。
当从该字符流中读出前六个字符”google”时,第一个只出现一次的字符是’l’。
如果当前字符流没有存在出现一次的字符,返回#字符。
样例
输入:“google”
输出:“ggg#ll”
解释:每当字符流读入一个字符,就进行一次判断并输出当前的第一个只出现一次的字符。
解法1:数组
class Solution {
private int[] m = new int[256];
private StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//Insert one char from stringstream
public void insert(char ch){
sb.append(ch);
m[ch]++;
}
//return the first appearence once char in current stringstream
public char firstAppearingOnce(){
char[] str = sb.toString().toCharArray();
for(char c : str) {
if(m[c] == 1)
return c;
}
return '#';
}
}
解法2:哈希表
class Solution {
private HashMap map = new HashMap<>(); // 记录字符出现的次数
private ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>(); // 记录当前的所有字符
//Insert one char from stringstream
public void insert(char ch){
if(map.containsKey(ch))
map.put(ch, map.get(ch) + 1);
else
map.put(ch, 1);
list.add(ch);
}
//return the first appearence once char in current stringstream
public char firstAppearingOnce(){
for(char c : list) {
if(map.get(c) == 1)
return c;
}
return '#';
}
}
51.数组中的逆序对
在数组中的两个数字如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。
输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数。
样例
输入:[1,2,3,4,5,6,0]
输出:6
解: 归并排序
class Solution {
public int inversePairs(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len == 0)
return 0;
return mergeSort(nums, 0, len - 1);
}
private int mergeSort(int[] array, int start, int end) {
if(start == end)
return 0;
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
int left_count = mergeSort(array, start, mid);
int right_count = mergeSort(array, mid + 1, end);
int i = mid, j = end;
int[] copy = new int[end - start + 1];
int copy_index = end - start;
int count = 0;
while(i >= start && j >= mid + 1) {
if(array[i] > array[j]) {
copy[copy_index--] = array[i--];
count += j - mid ;
}
else {
copy[copy_index--] = array[j--];
}
}
while(i >= start) {
copy[copy_index--] = array[i--];
}
while(j >= mid + 1) {
copy[copy_index--] = array[j--];
}
i = 0;
while(start <= end) {
array[start++] = copy[i++];
}
return (left_count + right_count + count);
}
}
52.两个链表的第一个公共节点
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
当不存在公共节点时,返回空节点。
样例
给出两个链表如下所示:
A: a1 → a2
↘
c1 → c2 → c3
↗
B: b1 → b2 → b3
输出第一个公共节点c1
解法1:Stack 可以解决求路径的最后一个公共节点(如树的公共祖先)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode findFirstCommonNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Stack s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack s2 = new Stack<>();
ListNode head1 = headA;
ListNode head2 = headB;
while(head1 != null) {
s1.push(head1);
head1 = head1.next;
}
while(head2 != null) {
s2.push(head2);
head2 = head2.next;
}
ListNode res = null;
//从后往前,找最后一个公共节点
while(!s1.isEmpty() && !s2.isEmpty() && s1.peek() == s2.peek()) {
s1.pop();
res = s2.pop();
}
return res;
}
}
解法2:第一种的改进,去掉了空间消耗,长的链表先走长度那么多步
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode findFirstCommonNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lengthA = getLength(headA);
int lengthB = getLength(headB);
int lengthDif = lengthA - lengthB;
ListNode headLong = headA;
ListNode headShort = headB;
if(lengthB > lengthA) {
headLong = headB;
headShort = headA;
lengthDif = lengthB - lengthA;
}
for(int i = 0;i < lengthDif;i++) {
headLong = headLong.next;
}
while((headLong != null) && (headShort != null) && (headLong != headShort)) {
headLong = headLong.next;
headShort = headShort.next;
}
ListNode firstCommonNode = headLong;
return firstCommonNode;
}
private int getLength(ListNode head) {
int nLength = 0;
ListNode node= head;
while(node != null) {
nLength++;
node = node.next;
}
return nLength;
}
}
53.数字在排序数组中出现的次数
统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数。
例如输入排序数组[1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5]和数字3,由于3在这个数组中出现了4次,因此输出4。
样例
输入:[1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5] , 3
输出:4
解法1:用二分查找法找到第一个K和最后一个K
class Solution {
public int getNumberOfK(int[] nums, int k) {
int number = 0;
if(nums != null && nums.length != 0) {
int first = getFirstK(nums, k, 0, nums.length - 1);
int last = getLastK(nums, k, 0, nums.length - 1);
if(first > -1 && last > -1)
number = last - first + 1;
}
return number;
}
private int getFirstK(int[] nums, int k, int start, int end) {
if(start > end)
return -1;
int midIndex = (start + end) / 2;
int midData = nums[midIndex];
if(midData == k) {
if((midIndex > 0 && nums[midIndex - 1] != k) || midIndex == 0)
return midIndex;
else
end = midIndex - 1;
}
else if(midData > k) {
end = midIndex - 1;
}
else
start = midIndex + 1;
return getFirstK(nums, k, start, end);
}
private int getLastK(int[] nums, int k, int start, int end) {
if(start > end)
return -1;
int midIndex = (start + end) / 2;
int midData = nums[midIndex];
if(midData == k) {
if((midIndex < nums.length - 1 && nums[midIndex + 1] != k) || midIndex == nums.length - 1)
return midIndex;
else
start = midIndex + 1;
}
else if(midData < k) {
start = midIndex + 1;
}
else
end = midIndex - 1;
return getLastK(nums, k, start, end);
}
}
解法2:因为data中都是整数,所以我们不用搜索k的两个位置,而是直接搜索k-0.5和k+0.5这两个数应该插入的位置,然后相减即可。
class Solution {
public int getNumberOfK(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return 0;
return biSearch(nums, k + 0.5) - biSearch(nums, k - 0.5);
}
private int biSearch(int[] nums, double k) {
int start = 0, end = nums.length - 1;
while(start <= end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if(nums[mid] > k) {
end = mid - 1;
}
else {
start = mid + 1;
}
}
return start;
}
}
54.0 到 n-1 中缺失的数字
一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字都在范围0到n-1之内。
在范围0到n-1的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组中,请找出这个数字。
样例
输入:[0,1,2,4]
输出:3
解:
class Solution {
public int getMissingNumber(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length ==0)
return 0;
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length -1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] != mid) {
if(mid == 0 || nums[mid - 1] == mid - 1)
return mid;
right = mid - 1;
}
else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
if(left == nums.length) //注意最后这一步
return nums.length;
return 0;
}
}
55.数组中数值和下标相等的元素
假设一个单调递增的数组里的每个元素都是整数并且是唯一的。
请编程实现一个函数找出数组中任意一个数值等于其下标的元素。
例如,在数组[-3, -1, 1, 3, 5]中,数字3和它的下标相等。
样例
输入:[-3, -1, 1, 3, 5]
输出:3
注意:如果不存在,则返回-1。
解:,递增数组,二分查找
class Solution {
public int getNumberSameAsIndex(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return -1;
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length -1;
while(left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == mid)
return mid;
if(nums[mid] > mid)
right = mid - 1;
else
left = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
}
55.二叉搜索树的第k个节点
给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k小的结点。
你可以假设树和k都存在,并且1≤k≤树的总结点数。
样例
输入:root = [2, 1, 3, null, null, null, null] ,k = 3
2
/ \
1 3
输出:3
解:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int index = 0;
public TreeNode kthNode(TreeNode root, int k) {
if(root != null) {
TreeNode node = kthNode(root.left, k);
if(node != null)
return node;
index++;
if(index == k)
return root;
node = kthNode(root.right, k);
if(node != null)
return node;
}
return null;
}
}
56.二叉树的深度
输入一棵二叉树的根结点,求该树的深度。
从根结点到叶结点依次经过的结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
样例
输入:二叉树[8, 12, 2, null, null, 6, 4, null, null, null, null]如下图所示:
8
/ \
12 2
/ \
6 4
输出:3
解: 递归即可
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int treeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
int left = treeDepth(root.left);
int right = treeDepth(root.right);
return (left > right) ? (left + 1) : (right + 1);
}
}
57.平衡二叉树
输入一棵二叉树的根结点,判断该树是不是平衡二叉树。
如果某二叉树中任意结点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。
注意:
规定空树也是一棵平衡二叉树。
样例
输入:二叉树[5,7,11,null,null,12,9,null,null,null,null]如下所示,
5
/ \
7 11
/ \
12 9
输出:true
解法1:在上一题二叉树的深度上进行修改,但是时间效率低
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return true;
int left = treeDepth(root.left);
int right = treeDepth(root.right);
int dif = left - right;
if(dif > 1 || dif < -1)
return false;
return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
private int treeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
int left = treeDepth(root.left);
int right = treeDepth(root.right);
return (left > right) ? (left + 1) : (right + 1);
}
}
解法2:在获取深度的时候就对树进行判断,如果不满足即退出,提高时间效率
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private boolean isBalancedFlag = true;
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
treeDepth(root);
return isBalancedFlag;
}
private int treeDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
int left = treeDepth(root.left);
int right = treeDepth(root.right);
if(Math.abs(left - right) > 1)
isBalancedFlag = false;
return (left > right) ? (left + 1) : (right + 1);
}
}
58.数组中只出现一次的两个数字
一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了两次。
请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。
你可以假设这两个数字一定存在。
样例
输入:[1,2,3,3,4,4]
输出:[1,2]
解法1:利用HashMap
class Solution {
public int[] findNumsAppearOnce(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return null;
HashMap map = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length;i++) {
if(map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
map.remove(nums[i]);
}
else {
map.put(nums[i], 1);
}
}
int[] res = new int[2];
int i = 0;
for(Integer k : map.keySet()) {
res[i] = k;
i++;
}
return res;
}
}
解法2: 异或法 通过将整个数组异或,然后根据异或后数字的第一个不为1的位,将数组分成都只有一个出现一次的两部分,然后分别异或即可
class Solution {
public int[] findNumsAppearOnce(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return null;
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length;i++)
num ^= nums[i];
int index = 0;
while((num & 1) == 0 && index < 8) {
num = num >> 1;
index++;
}
int[] res = new int[2];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(isa1(nums[i], index))
res[0] ^= nums[i];
else
res[1] ^= nums[i];
}
return res;
}
private boolean isa1(int num, int index) {
num = num >> index;
return (num & 1) == 1;
}
}
59.数组中唯一只出现一次的数字
在一个数组中除了一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。
请找出那个只出现一次的数字。
你可以假设满足条件的数字一定存在。
思考题:
如果要求只使用 O(n) 的时间和额外 O(1) 的空间,该怎么做呢?
样例
输入:[1,1,1,2,2,2,3,4,4,4]
输出:3
解:二进制每位相加,每位依次 % 3,有余数说明那一个数的该位为 1。
class Solution {
public int findNumberAppearingOnce(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int[] bitSum = new int[32];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int bitMask = 1;
for(int j = 31; j >= 0; j--) {
if((nums[i] & bitMask) != 0)
bitSum[j] += 1;
bitMask = bitMask << 1;
}
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
// 因为从高位开始,因此每次需要左移
res = res << 1;
res += bitSum[i] % 3;
}
return res;
}
}
60.和为S的两个数字
输入一个数组和一个数字s,在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是s。
如果有多对数字的和等于s,输出任意一对即可。
你可以认为每组输入中都至少含有一组满足条件的输出。
样例
输入:[1,2,3,4] , sum=7
输出:[3,4]
解:两个指针,大则后指针–,小则前指针++
class Solution {
public int[] findNumbersWithSum(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums == null || nums.length <1)
return null;
int[] res = new int[2];
Arrays.sort(nums); //如果为递增排序数组可省去这一步
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
int sum = nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum == target) {
res[0] = nums[left];
res[1] = nums[right];
break;
}
else if(sum > target) {
right--;
}
else {
left++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
61.和为S的连续正数序列
输入一个正数s,打印出所有和为s的连续正数序列(至少含有两个数)。
例如输入15,由于1+2+3+4+5=4+5+6=7+8=15,所以结果打印出3个连续序列1~5、4~6和7~8。
样例
输入:15
输出:[[1,2,3,4,5],[4,5,6],[7,8]]
解:一个small指针,一个big指针
class Solution {
public List > findContinuousSequence(int sum) {
List> res = new ArrayList>();
List tmp = new ArrayList();
if(sum < 3)
return res;
int small = 1;
int big = 2;
int mid = (1 + sum) / 2;
int cursum = small + big;
while(small < mid) {
if(cursum == sum) {
for(int i = small; i <= big;i++) {
tmp.add(i);
}
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
tmp.clear();
}
while(cursum > sum && small < mid) {
cursum -= small;
small++;
if(cursum == sum) {
for(int i = small; i <= big;i++) {
tmp.add(i);
}
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
tmp.clear();
}
}
big++;
cursum += big;
}
return res;
}
}
62.翻转单词顺序
输入一个英文句子,翻转句子中单词的顺序,但单词内字符的顺序不变。
为简单起见,标点符号和普通字母一样处理。
例如输入字符串"I am a student.",则输出"student. a am I"。
样例
输入:“I am a student.”
输出:“student. a am I”
解: trim() : 去除字符串首尾空格
split() : 对字符串按照所传参数进行分割
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
if(s == null || s.trim().length() == 0)
return s;
String[] tmp = s.split(" ");
String res = "";
for(int i = tmp.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
res += tmp[i];
if(i != 0)
res += " ";
}
return res;
}
}
63.左旋转字符串
字符串的左旋转操作是把字符串前面的若干个字符转移到字符串的尾部。
请定义一个函数实现字符串左旋转操作的功能。
比如输入字符串"abcdefg"和数字2,该函数将返回左旋转2位得到的结果"cdefgab"。
注意:
数据保证n小于等于输入字符串的长度。
样例
输入:“abcdefg” , n=2
输出:“cdefgab”
解:
class Solution {
public String leftRotateString(String str,int n) {
int len = str.length();
if(str == null || len == 0 || n > len)
return "";
String s1 = str.substring(n, len);
String s2 = str.substring(0, n);
return s1 + s2;
}
}
64.滑动窗口的最大值
给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。
例如,如果输入数组[2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5, 1]及滑动窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,它们的最大值分别为[4, 4, 6, 6, 6, 5]。
注意:
数据保证k大于0,且k小于等于数组长度。
样例
输入:[2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5, 1] , k=3
输出: [4, 4, 6, 6, 6, 5]
解:
class Solution {
public int[] maxInWindows(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums == null || nums.length == 0 || k == 0 || k > nums.length)
return null;
LinkedList deque = new LinkedList(); //记录窗口
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 如果新值大于队尾,弹出原队尾
while(!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] <= nums[i])
deque.pollLast(); // deque.removeLast();
deque.addLast(i); //deque.offerLast(i);
// 此时下标已经过期,说明此时滑动窗口已经没有包含这个下标了
if(deque.peekFirst() == i - k)
deque.pollFirst();
// 保证一开始的不存入,假设3 2 1,只有下标大于窗口时,
// 才判断加入此时的队首
if(i >= k - 1)
list.add(nums[deque.peekFirst()]);
}
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++)
res[i] = list.get(i);
return res;
}
}
65.骰子的点数
将一个骰子投掷n次,获得的总点数为s,s的可能范围为n~6n。
掷出某一点数,可能有多种掷法,例如投掷2次,掷出3点,共有[1,2],[2,1]两种掷法。
请求出投掷n次,掷出n~6n点分别有多少种掷法。
样例1
输入:n=1
输出:[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
解释:投掷1次,可能出现的点数为1-6,共计6种。每种点数都只有1种掷法。所以输出[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]。
样例2
输入:n=2
输出:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
解释:投掷2次,可能出现的点数为2-12,共计11种。每种点数可能掷法数目分别为1,2,3,4,5,6,5,4,3,2,1。
所以输出[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]。
解法1:递归处理
class Solution {
private int[] res = null;
private int count;
public int[] numberOfDice(int n) {
// n 为掷骰子的次数,可以理解为有多少个骰子
res = new int[6*n - n + 1];
for(int i = n, j = 0; i <= 6*n ;i++,j++) {
// i 为可能出现的点数,j为相应点数在数组中对应的下标
count = 0;
dfs(n, i);
res[j] = count;
}
return res;
}
// n 为骰子个数,sum为骰子数的和
private void dfs(int n, int sum) {
if(sum == 0 && n == 0) {
count++;
return;
}
if (n == 0)
return;
if (sum < 0)
return;
// 当前骰子可能出现的6种情况
for(int k = 1; k <= 6; k++) {
dfs(n-1, sum - k);
if(sum - k <= 0)
break;
}
}
}
解法2:
class Solution {
public int[] numberOfDice(int n) {
if(n < 1)
return null;
int maxValue = 6;
int[] res = new int[maxValue*n - n + 1];
int[][] f = new int[n + 1][maxValue*n + 1];
f[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= i*maxValue; j++){
for(int k = 1; k <= Math.min(j, 6); k++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i + " j = " + j + " k = " + k);
f[i][j] += f[i-1][j-k];
}
}
}
for(int i = n, j =0; i <= 6*n; i++,j++) {
res[j] = f[n][i];
}
return res;
}
}
66.扑克牌的顺子
从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是一个顺子,即这5张牌是不是连续的。
2~10为数字本身,A为1,J为11,Q为12,K为13,大小王可以看做任意数字。
为了方便,大小王均以0来表示,并且假设这副牌中大小王均有两张。
样例1
输入:[8,9,10,11,12]
输出:true
样例2
输入:[0,8,9,11,12]
输出:true
解:
class Solution {
public boolean isContinuous(int [] numbers) {
if(numbers == null || numbers.length == 0)
return false;
int zeros = 0; //记录0的个数
int diff = 0; //记录空缺的数
Arrays.sort(numbers);
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length - 1; i++) {
if(numbers[i] == 0) {
zeros++;
continue;
}
if(numbers[i] != numbers[i+1]) { // 4 和 8中间空缺3
diff += numbers[i+1] - numbers[i] - 1;
}
else {
return false; //说明有对子,肯定不是顺子
}
}
if(diff <= zeros)
return true; //如果diff小于zeros,那么 0 放在最后就行,因为0代表任意值
return false;
}
}