C++ STL容器的学习使用(vector、queue、list、set、map)
1.STL组成:
STL有三大核心部分:容器(Container)、算法(Algorithms)、迭代器(Iterator),容器适配器(containeradaptor),函数对象(functor),除此之外还有STL其他标准组件。通俗的讲:
容器:装东西的东西,装水的杯子,装咸水的大海,装人的教室……STL里的容器是可容纳一些数据的模板类。
算法:就是往杯子里倒水,往大海里排污,从教室里撵人……STL里的算法,就是处理容器里面数据的方法、操作。
迭代器:往杯子里倒水的水壶,排污的管道,撵人的那个物业管理人员……STL里的迭代器:遍历容器中数据的对象。对存储于容器中的数据进行处理时,迭代器能从一个成员移向另一个成员。他能按预先定义的顺序在某些容器中的成员间移动。对普通的一维数组、向量、双端队列和列表来说,迭代器是一种指针。
容器: 学习list/vector/deque/set/multisets/map/multimaps/
(1)vector:动态数组,向量。(具体用法看代码)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
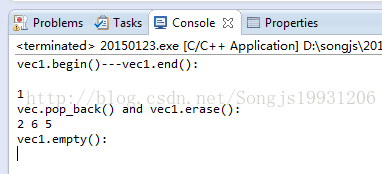
(2)queue:双端队列:支持vector不支持的push_front();
void put_deque(INTDEQUE deque,char *name){
INTDEQUE::iterator pdeque; //定义迭代器输出
cout<<"The contents of "<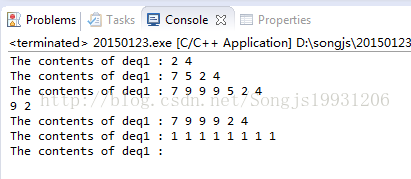
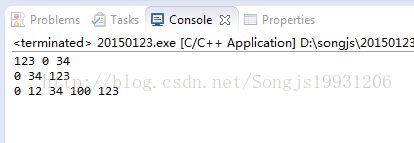
(3)list:链表,双向链表,只能顺序访问,不能使用[]进行随机访问
void printList(list n){
for(list::iterator i=n.begin();i!=n.end();i++)
cout<< *i << " ";
cout< list1,list2;
list1.push_back(123);
list1.push_back(0);
list1.push_back(34);
list2.push_back(100);
list2.push_back(12);
//测试list排序功能
printList(list1);
list1.sort();
printList(list1);
list2.sort();
list1.merge(list2); //两个链表排序后进行合并,合并完仍然有序
printList(list1);
return 0;
} 
(4)set和multisets:集和多集:默认是排好序的!
·set:包含元素唯一
·multisets:包含元素可不唯一
int main(){
set set1;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) set1.insert(i);
for(set::iterator p = set1.begin();p!=set1.end();p++){
cout<<*p<<" ";
}cout< A;
A.insert(set1.begin(),set1.end());
A.insert(4); //插入之后默认排好序
for(multiset::iterator i=A.begin();i!=A.end();i++)
cout<<*i<<" "; cout< 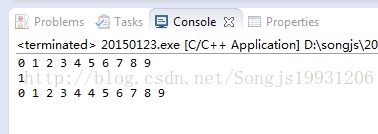
(5)map和multimaps:映射和多重映射
set中的key和value是Key类型的,而map中的key和value是一个pair结构中的两个分量。Map支持下表运算符operator[],用访问普通数组的方式访问map,不过下标为map的键。在multimap中一个键可以对应多个不同的值。
int main(){
//定义map: char是键的类型,int是值的类型
map > map1;
map >::iterator mapIter;
//注意这里: 两个>>符号之间 要有一个空格
//初始化
map1['c'] = 3;
map1['d'] = 4;
map1['a'] = 1;
//打印
for(mapIter=map1.begin();mapIter!=map1.end();mapIter++){
cout<<" "<<(*mapIter).first<<" : "<<(*mapIter).second;
}cout< >::const_iterator t = map1.find('d');
cout<<"t:"<<(*t).first<<"对应值:"<<(*t).second< >mulmap;
multimap >::iterator p;
typedef multimap >::value_type vt;
//注意multimap中不支持map中的[]下标操作!!!
//mulmap[string("songjs")] = string("bjfu"); --- 是错误的
mulmap.insert(vt(string("songjs"),string("is a boy")));
mulmap.insert(vt(string("songjs"),string("is a girl")));
//打印输出
for(p=mulmap.begin();p!=mulmap.end();p++){
cout<<(*p).first<<" "<<(*p).second< 