Python算法系列(四):链表
任何数据结构,在物理上都分为顺序存储和链式存储,其中以数组为典型代表的顺序存储在上一章讲解过了,本文介绍以另一种存储方式进行数据存储的数据结构代表——链表,Python的链表
单链表
关于链表的概念、定义,在我之前的文章中已经详细解释了(不再赘述
Python中实现一个链表类(体现面向对象的便利性)
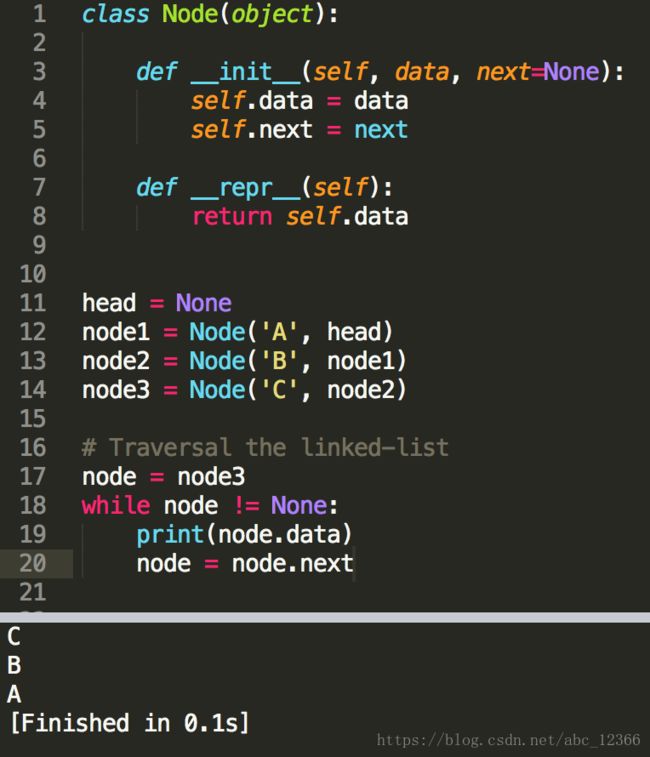
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data, next=None): # By default, next is None
self.data = data
self.next = next
# Operations goes here头插法
case1)head is None
case2)head is not None
head = Node(newItem, head)效果:把新元素插到head的指向的下一个位置
尾插法
case1)head is None
case2)head is not None
newItem = Node(newItem) # 定义新元素,指针域默认为None
if head is None:
head = newItem
else:
node = head
while node.next != None
node = node.next
node.next = newItem效果:把新元素插到链表末尾的的下一个位置
循环链表(单循环)
让链表的最后一个元素的指针域指向第一个元素,在逻辑上就产生了循环
head = Node(None, None)
head.next = head我们把第一个结点叫做『哑头结点』(dummy header node),在空的循环链表中,头结点指针指向哑头结点,而哑头结点指向其自身
在第i个位置插入新结点
node = head
while index > 0 and node.next != head:
node = node.next
index -= 1
node.next = Node(newItem, node.next)双链表
相比于单链表,双链表每个结点有两个自由度(向左、向右),且可以直接移动到链表的末尾(因为除了头指针head,双链表还定义了尾指针tail)
class DoubleNode(Node): # 双链表继承了单链表
def __init__(self, data, prev=None, next=None)
super(Double, self).__init__(data, next)
self.prev = prev代码实现(单链表)
单链表、双链表,无非是换汤不换药——考虑到LinkedList和Node的嵌套定义,链表这种结果最适合用嵌套内部类来写了
""" Create a LinkedList that contains the structure of nodes.
As a principle, I don't put any data in head node.
The nodes that contain the real data should be counted from node number one.
"""
class LinkedList(object):
def __init__(self, head=None):
self.head = head
def __len__(self):
""" Return the length of the linkedlist, not including the head node. """
length = 0
if self.head is None or self.head.next is None:
return None
node = self.head.next
while node:
length += 1
node = node.next
return length
def __contains__(self, item):
""" To suggest whether the item is in the linkedlist or not. """
if self.head is None or self.head.next is None:
return None
node = self.head
while node:
if node is item or node.data == item:
return True
node = node.next
return False
def __reversed__(self):
""" Return the reversed linkedlist. e.g. head->node1->node2->node3 ==> node3->node2->node1->head. Now node3 is the now head node. """
if self.head is None or self.head.next is None:
return None
curl = self.head
prev = None
# pntr = None
while curl:
# pntr = curl
temp = curl.next
curl.next = prev
prev = curl
curl = temp
# return pntr
return prev
def isEmpty(self):
return len(self) == 0
def append(self, value):
""" Append a new node after the tail of the linkedlist. Special case: if head node is none, let the new item be the head. """
item = self.Node(value)
if self.head is None:
self.head = item
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
node.next = item
def butt(self, value, old_head_value):
""" Put a new node before the head node of the linkedlist. Special case: if head node is none, let the new item be the head."""
item = self.Node(value)
if self.head is None:
self.head = item
else:
self.head.data = old_head_value # Give a data field to the old head node.
item.next = self.head
self.head = item
def printNode(self):
""" Traversal the linkedlist, and print the data of the nodes. """
if self.head is None or self.head.next is None:
return None
node = self.head.next
while node is not None:
print(node.data, end=" ")
node = node.next
def reverse(self):
""" Reverse the linkedlist. e.g. head->node1->node2->node3 ==> node3->node2->node1->head. Now node3 is the now head node. """
if self.head is None or self.head.next is None:
return None
prev = None
curl = self.head
# pntr = None
while curl:
# pntr = curl
temp = curl.next
curl.next = prev
prev = curl
curl = temp
# self.head = pntr
self.head = prev
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data=None, next=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
def main():
lyst = LinkedList()
head = lyst.Node()
node1 = lyst.Node(1)
node2 = lyst.Node(2)
node3 = lyst.Node(3)
node4 = lyst.Node(4)
node5 = lyst.Node(5)
lyst.head = head # Set the head node
head.next = node1
node1.next = node2
node2.next = node3
node3.next = node4
node4.next = node5
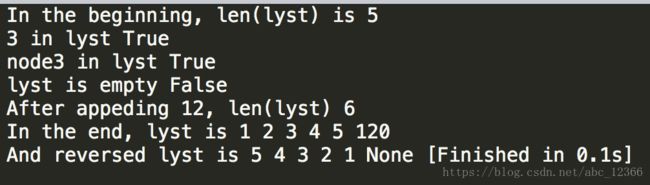
print("In the beginning, len(lyst) is", len(lyst))
print("3 in lyst", 3 in lyst)
print("node3 in lyst", node3 in lyst)
print("lyst is empty",lyst.isEmpty())
lyst.append(120)
print("After appeding 12, len(lyst)", len(lyst))
print("In the end, lyst is ", end="")
lyst.printNode()
print("\nAnd reversed lyst is ", end="")
lyst_reversed = LinkedList(reversed(lyst))
lyst_reversed.printNode()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()