Netty实战一 Netty实现文件的上传和下载
目录
一、Netty应用场景
二、Netty实现文件的上传和下载
三、程序演示
1、下载演示
2、上传演示
一、Netty应用场景
讲了一些Netty的组件,来聊一聊大家最关心的事情吧,他能够做什么?毕竟,我们学习就是拿来用的嘛。我可以简单的概括一下,凡是牵扯到网络相关的,都可以使用Neety去实现!
- 构建高性能、低时延的各种 Java 中间件,例如 MQ、分布式服务框架、ESB 消息总线等,Netty 主要作为基础通信框架提供高性能、低时延的通信服务;
- 公有或者私有协议栈的基础通信框架,例如可以基于 Netty 构建异步、高性能的 WebSocket 协议栈;
- 各领域应用,例如大数据、游戏等,Netty 作为高性能的通信框架用于内部各模块的数据分发、传输和汇总等,实现模块之间高性能通信。
接下来的几篇,会围绕Netty实现相关功能进行展开。
二、Netty实现文件的上传和下载
1、MultipartRequest
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.multipart.FileUpload;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 请求对象
*
* @author DarkKing
*/
public class MultipartRequest {
private Map fileUploads;
private JSONObject params;
public Map getFileUploads() {
return fileUploads;
}
public void setFileUploads(Map fileUploads) {
this.fileUploads = fileUploads;
}
public JSONObject getParams() {
return params;
}
public void setParams(JSONObject params) {
this.params = params;
}
}
定义了一个http封装的对象。保存对应的传参数。
2、FileServer
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* 作者:DarkKIng
* 创建日期:2019/12/17
* 类说明:文件下载服务端
*/
public class FileServer {
private final int port;
public FileServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int port = 9999;
FileServer fileServer = new FileServer(port);
System.out.println("服务器即将启动");
fileServer.start();
System.out.println("服务器关闭");
}
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
final FileServerHandle serverHandler = new FileServerHandle();
/*线程组*/
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Pipeline pipeline = new Pipeline();
try {
/*服务端启动必须*/
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(group)/*将线程组传入*/
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)/*指定使用NIO进行网络传输*/
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))/*指定服务器监听端口*/
/*服务端每接收到一个连接请求,就会新启一个socket通信,也就是channel,
所以下面这段代码的作用就是为这个子channel增加handle*/
.childHandler(pipeline);
ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync();/*异步绑定到服务器,sync()会阻塞直到完成*/
System.out.println("Netty server start,port is " + port);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();/*阻塞直到服务器的channel关闭*/
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();/*优雅关闭线程组*/
}
}
}
使用netty实现服文件服务器端。
3、Pipeline
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseEncoder;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultEventExecutorGroup;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup;
/**
* 作者:DarkKIng
* 创建日期:2019/12/17
* 作用:职责链
*/
public class Pipeline extends ChannelInitializer {
private EventExecutorGroup businessEventExecutorGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(10);
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
/**
* http服务器端对response编码
*/
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder());
/**
* http服务器端对request解码3.
*/
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder());
/**
* 合并请求
*/
pipeline.addLast("aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(655300000));
/**
* 正常业务逻辑处理
*/
pipeline.addLast(businessEventExecutorGroup, new FileServerHandle());
}
}
编写职责链,请求会从入栈以次从上到下经过编解码,请求和秉承HTTPObject,最后执行业务类FileServerHandle。
4、FileServerHandle
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler.Sharable;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.multipart.*;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* 作者:DarkKIng
* 创建日期:2019/12/17
* 类说明:文件下载handler
*/
@Sharable
public class FileServerHandle extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
/*客户端读到数据以后,就会执行*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request)
throws Exception {
//打印请求url
System.out.println(request.uri());
//下载任务处理
if (request.uri().equals("/downFile")) {
responseExportFile(ctx, "D://model.txt", "model.txt");
}
//上传接口处理
if (request.uri().equals("/upLoadFile")) {
MultipartRequest MultipartBody = getMultipartBody(request);
Map fileUploads = MultipartBody.getFileUploads();
//输出文件信息
for (String key : fileUploads.keySet()) {
//获取文件对象
FileUpload file = fileUploads.get(key);
System.out.println("fileName is" + file.getFile().getPath());
//获取文件流
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file.getFile());
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String content = bf.lines().collect(Collectors.joining("\n"));
//打印文件
System.out.println("content is \n" + content);
}
//输出参数信息
JSONObject params = MultipartBody.getParams();
//输出文件信息
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(params));
}
}
/*连接建立以后*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(
"Hello Netty", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
/**
*
* 返回下载内容
*
*
* @param ctx
* @author DarkKing 2019-12-17
*/
public static void responseExportFile(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String path, String name) {
File file = new File(path);
try {
//随机读取文件
final RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
long fileLength = raf.length();
//定义response对象
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK);
//设置请求头部
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, fileLength);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/octet-stream; charset=UTF-8");
response.headers().add(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_DISPOSITION,
"attachment; filename=\"" + URLEncoder.encode(file.getName(), "UTF-8") + "\";");
ctx.write(response);
//设置事件通知对象
ChannelFuture sendFileFuture = ctx
.write(new DefaultFileRegion(raf.getChannel(), 0, fileLength), ctx.newProgressivePromise());
sendFileFuture.addListener(new ChannelProgressiveFutureListener() {
//文件传输完成执行监听器
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelProgressiveFuture future)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("file {} transfer complete.");
}
//文件传输进度监听器
@Override
public void operationProgressed(ChannelProgressiveFuture future,
long progress, long total) throws Exception {
if (total < 0) {
System.out.println("file {} transfer progress: {}");
} else {
System.out.println("file {} transfer progress: {}/{}");
}
}
});
//刷新缓冲区数据,文件结束标志符
ctx.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 功能描述
* 解析文件上传
*
* @author DarkKing 2019/10/9 15:24
* @params [ctx, httpDecode]
*/
private static MultipartRequest getMultipartBody(FullHttpRequest request) {
try {
//创建HTTP对象工厂
HttpDataFactory factory = new DefaultHttpDataFactory(true);
//使用HTTP POST解码器
HttpPostRequestDecoder httpDecoder = new HttpPostRequestDecoder(factory, request);
httpDecoder.setDiscardThreshold(0);
if (httpDecoder != null) {
//获取HTTP请求对象
final HttpContent chunk = (HttpContent) request;
//加载对象到加吗器。
httpDecoder.offer(chunk);
if (chunk instanceof LastHttpContent) {
//自定义对象bean
MultipartRequest multipartRequest = new MultipartRequest();
//存放文件对象
Map fileUploads = new HashMap<>();
//存放参数对象
JSONObject body = new JSONObject();
//通过迭代器获取HTTP的内容
java.util.List InterfaceHttpDataList = httpDecoder.getBodyHttpDatas();
for (InterfaceHttpData data : InterfaceHttpDataList) {
//如果数据类型为文件类型,则保存到fileUploads对象中
if (data != null && InterfaceHttpData.HttpDataType.FileUpload.equals(data.getHttpDataType())) {
FileUpload fileUpload = (FileUpload) data;
fileUploads.put(data.getName(), fileUpload);
}
//如果数据类型为参数类型,则保存到body对象中
if (data.getHttpDataType() == InterfaceHttpData.HttpDataType.Attribute) {
Attribute attribute = (Attribute) data;
body.put(attribute.getName(), attribute.getValue());
}
}
//存放文件信息
multipartRequest.setFileUploads(fileUploads);
//存放参数信息
multipartRequest.setParams(body);
return multipartRequest;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
业务执行类,实现了文件上传和下载的接口。当请求为downFile则下载文件,请求为upLoadFile则为上传文件
三、程序演示
1、下载演示
启动服务器端
浏览器执行下载文件,正确的下载到文件test.txt
2、上传演示
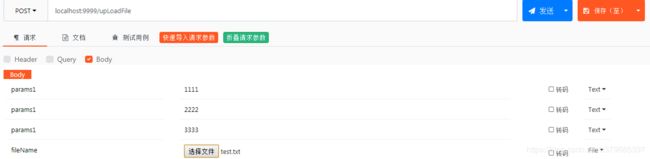
使用apipost或者postman执行文件上传操作
文件上传成功并成功读取文件内容
本博文主要演示了如何不使用spring或者tomcat当做服务器,使用netty实现自己的文件上传和下载服务。并根据请求来实现对应的api接口操作。当然,如果想使用netty像spring那样简单并规范化的封装自己的api,那么就要考自己去封装实现了。有兴趣的朋友可以自己尝试下