VS2017 C/C++调用python脚本文件
文章目录
- 值得注意的是
- 1、环境配置
- 2.一个例子
- 3,API详解
在实际的工作中,为了方便利用python写的程序(因为python中有很多功能强大的函数库),有时需要进行c、c++与python的混合编程,特别是需要在c程序中调用python脚本。这时候就到了python展现自己"胶水语言"的一面了。
值得注意的是
对于纯python程序而言,用c程序来调用是比较适合的,如果python程序中包含了其他第三方库,则调用极可能出错,且不易查明原因。往往一个大型的python项目,比如SSD目标检测等,都是需要调用很多第三方库,而且多模块互相交织,虽然说当你把python项目环境的路径在VS里面配置好了,相对路径搞明白了,理论上应该没啥问题,但是实践中还是会有一些令人头大的错误出来,所以如果你只想用python项目的生成结果的话,可以通过文件进行连接
下面就简单说在c语言里面怎么调用python
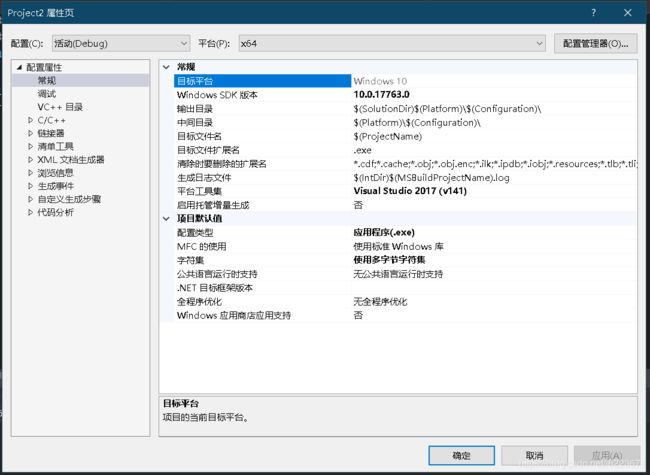
1、环境配置
①将vs工程配置为和你的pytho环境里的解释器的为啥相同,比如你用到是X64的python环境,VS工程就要配置成X64
②添加包含目录和库目录, 添加你的python项目环境里面的include和libs文件夹路径,比如 D:\anaconda\include
-
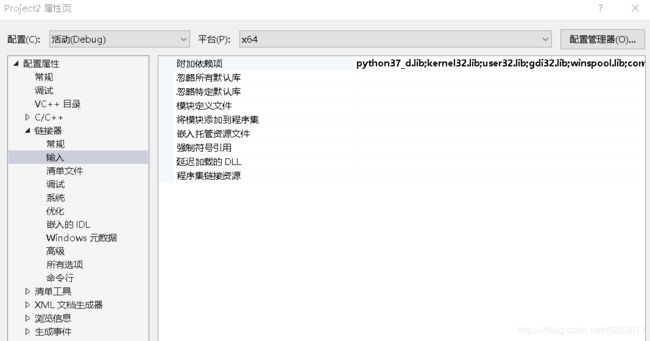
添加依赖项
找到链接器-输入,附加依赖项,添加libs目录里面的python37_d.lib,注意这里一开始是没有这个的,只有pyth37.lib,这里复制一份重命名为python37_d.lib,因为VS默认会检测后者,不改的话肯能会报错。
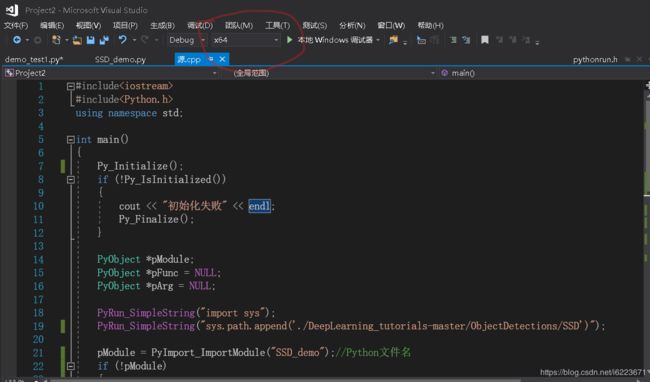
配置完成之后先来看一个简单的例子
2.一个例子
demo_test.py
#coding:utf-8
import os
def run(com):
return com
def main():
print(run(("4",3)))
if __name__=='__main__':
main()
源.cpp
#include这里注意,vs的当前目录表示的是。vcxproj文件所在的位置,用".“表示,上级目录用”. ."
![]()
看不懂上面的函数没关系,下面全面详细介绍,Python.h 头文件里面都有哪些API
3,API详解
1、运行Python指令
PyRun_SimpleString("print(os.getcwd(),a)");
pyext.eval(R"(a+='qwer')");
2、加载Python模块
PyObject * pModule =PyImport_ImportModule("tp"); //test:Python文件名,若脚本有错则返回空
PyRun_SimpleString("import os");
3、给Python的变量赋值
对于数值,使用Py_BuildValue:
Py_BuildValue("") None
Py_BuildValue("i", 123) 123
Py_BuildValue("iii", 123, 456, 789) (123, 456, 789)
Py_BuildValue("s", "hello") 'hello'
Py_BuildValue("ss", "hello", "world") ('hello', 'world')
Py_BuildValue("s#", "hello", 4) 'hell'
Py_BuildValue("()") ()
Py_BuildValue("(i)", 123) (123,)
Py_BuildValue("(ii)", 123, 456) (123, 456)
Py_BuildValue("(i,i)", 123, 456) (123, 456)
Py_BuildValue("[i,i]", 123, 456) [123, 456]
Py_BuildValue("{s:i,s:i}", "abc", 123, "def", 456) {'abc': 123, 'def': 456}
对于其他数据结构,使用相应的函数设置,例如:
PyObject *pArgs = PyTuple_New(1);
PyObject *pDict = PyDict_New(); //创建字典类型变量
PyDict_SetItemString(pDict, "Name", Py_BuildValue("s", "WangYao")); //往字典类型变量中填充数据
PyDict_SetItemString(pDict, "Age", Py_BuildValue("i", 25)); //往字典类型变量中填充数据
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 0, pDict);//0---序号 将字典类型变量添加到参数元组中
构造好对象以后,通过PyObject_SetAttrString来设置进入Python中:
PyObject *ps=PyUnicode_DecodeUTF8(val,strlen(val),"ignore"); //构造了一个对象
PyObject_SetAttrString(p_main_Module,key,ps); //设置
4、获取Python变量的值
首先取得变量的指针,然后通过PyArg_Parse解析
pModule =PyImport_ImportModule("__main__");
pReturn = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "a"); //可以获得全局变量
int size = PyDict_Size(pReturn);
PyObject *pNewAge = PyDict_GetItemString(pReturn, "Age");
int newAge;
PyArg_Parse(pNewAge, "i", &newAge);
对于元组的解析:
int ok;
ok = PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "s", &s); //Python call: f('whoops!')
ok = PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "lls", &k, &l, &s);//Python call: f(1, 2,'three')
ok = PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "(ii)s#", &i, &j, &s, &size);//Python call: f((1, 2), 'three')
ok = PyArg_ParseTuple(args, "s|si", &file, &mode, &bufsize);//Python calls:
//f('spam')
//f('spam', 'w')
//f('spam', 'wb', 100000)
5、调用Python函数
PyObject * pfun=PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "testdict"); //testdict:Python文件中的函数名
PyObject *pReturn = PyEval_CallObject(pfun, pArgs); //调用函数
6、设置函数让Python调用
首先定义c函数,然后声明方法列表,然后声明模块,然后增加这个模块,最后调用
static int numargs=1890;
static PyObject* emb_numargs(PyObject *self, PyObject *args) //C函数
{
if(!PyArg_ParseTuple(args, ":numargs"))
return NULL;
return PyLong_FromLong(numargs);
}
static PyMethodDef EmbMethods[] = { //方法列表
{"numargs", emb_numargs, METH_VARARGS,
"Return the number of arguments received by the process."},
{NULL, NULL, 0, NULL}
};
static PyModuleDef EmbModule = { //模块声明
PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT, "emb", NULL, -1, EmbMethods,
NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL
};
static PyObject* PyInit_emb(void) //模块初始化函数
{
return PyModule_Create(&EmbModule);
}
//增加模块:
PyImport_AppendInittab("emb", &PyInit_emb); //增加一个模块