【2019.07.10】python + OpenCV + adb 实现 自动 微信跳一跳
采用python + OpenCV + adb的方案实现实心跳一跳
分四步走
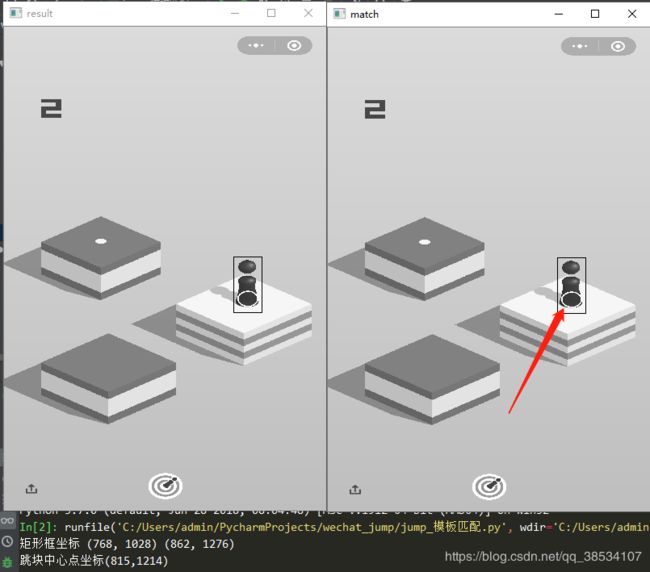
- 模板匹配:通过OpenCV 获取到跳块中心点的坐标
# 使用标准相关系数匹配,1表示完美匹配, -1表示糟糕匹配, 0表示没有任何相关性 result = cv2.matchTemplate(img, temple, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
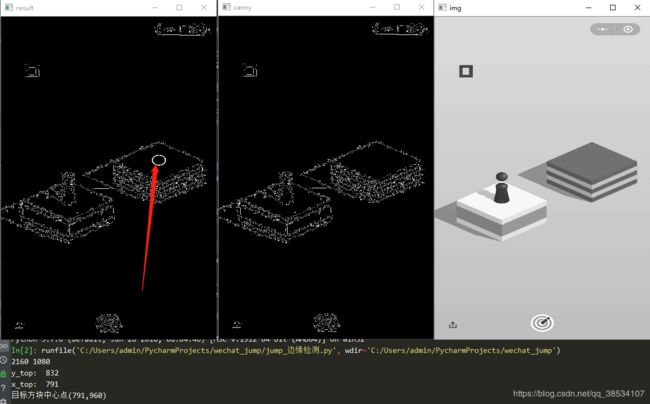
- 边缘检测:通过OpenCV判断下一跳方块的中心坐标
这里用到了 高斯模糊
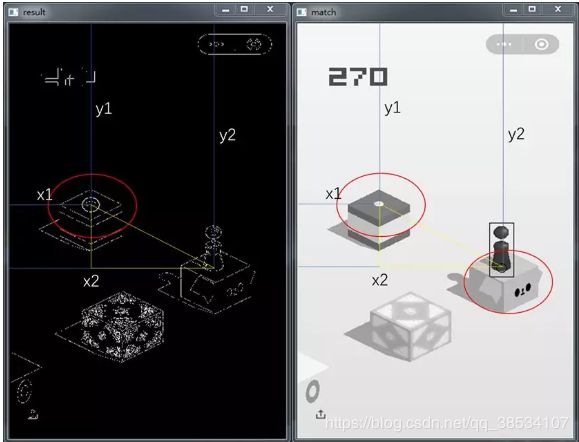
- 计算距离:根据目标中心点和跳块中心点的坐标,勾股定理,计算出距离
4.adb 跳动
涉及到3个ADB命令- 手机截图
adb shell /system/bin/screencap -p /sdcard/screencap.png - 把手机截图发送到电脑上
adb pull /sdcard/screencap.png screencap.png - 模拟长按手机屏幕 adb shell input swipe 坐标 坐标 时间
- 手机截图
执行代码
- 手机进入USB调试模式,打开跳一跳小程序,到开始按手机跳动的页面
- 电脑adb环境正常
- 直接执行
jump_跳一跳.py
代码
Github项目地址https://github.com/ybsdegit/wechat_jump
或点击前往Github
1. 模板匹配
import time
import cv2
# 读取待检测图像
img = cv2.imread('game1.png', 0)
# 读取模板图像
temple = cv2.imread('temple.png', 0)
# 显示灰度处理后的待检测图像
cv2.namedWindow('sample', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('sample', 400, 600)
cv2.imshow('sample', img)
# 显示灰度处理后的模板图像
cv2.namedWindow('target', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('target', 400, 600)
cv2.imshow('target', temple)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 获取模板图像的高和宽
th, tw = temple.shape[:2]
# print(th, tw)
# 使用标准相关系数匹配,1表示完美匹配, -1表示糟糕匹配, 0表示没有任何相关性
result = cv2.matchTemplate(img, temple, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
# TM_CCOEFF_NORMED 方法处理后的结果图像
cv2.namedWindow('match_r', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('match_r', 400, 600)
cv2.imshow('match_r', result)
cv2.waitKey(10)
# 使用函数 minMaxloc, 确定匹配结果矩阵的最大值和最小值(val),以及它们的位置(loc)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
# 此处选取最大值的位置,为图像的左上角
t1 = max_loc
# 获取图像的右下角
br = (t1[0] + tw, t1[1] + th)
# 绘制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img, t1, br, (0,0,225),2)
print("矩形框坐标",t1,br)
t_x_center = (t1[0]+br[0]) // 2
t_y_center = int(max_loc[1]*0.25 + br[1]*0.75)
print(f"跳块中心点坐标({t_x_center},{t_y_center})")
# 绘制以方块中心点为圆心的圆
cv2.circle(img, (t_x_center, t_y_center), 33, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.namedWindow('result', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('result', 400, 600)
cv2.imshow('result', img)
# 设置显示窗口
cv2.namedWindow('match', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('match', 400, 600)
# 显示窗口
cv2.imshow('match', img)
# 结束
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2.边缘检测
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 读取原图像
img = cv2.imread('game.png', 0)
# 显示原图像
cv2.namedWindow('img', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('img', 400, 600)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
# 高斯模糊
img_rgb = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5,5), 0)
canny_img = cv2.Canny(img_rgb, 1, 10)
# 显示边缘检测图像
cv2.namedWindow('canny', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('canny', 400, 600)
cv2.imshow('canny', canny_img)
# 输出边缘检测图像的高和宽
H, W = canny_img.shape
print(H, W)
# 第一个顶点的高度,row为列表(代表每一行的像素值), max(row) 获取列表中最大的像素值
# 对图像高度大于400的行进行遍历(这样可以去除上方数字以及小程序块的影响)。
# np.nonzero() 表示获取列表元素数值不为0的位置,
y_top = np.nonzero([max(row) for row in canny_img[420:]])[0][0] + 420
print('y_top: ',y_top)
# 获取第一个顶点的宽度值
x_top = int(np.mean(np.nonzero(canny_img[y_top])))
print('x_top: ',x_top)
# 跳过小白圈,然后遍历
y_bottom = y_top + 125
for row in range(y_bottom, H):
if canny_img[row, x_top] != 0:
y_bottom = row
break
# 得到方块的中心点
x_center, y_center = x_top, (y_top + y_bottom)//2
# 绘制以方块中心点为圆心的圆
cv2.circle(canny_img, (x_center, y_center), 33, (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.namedWindow('result', 0)
cv2.resizeWindow('result', 400, 600)
cv2.imshow('result', canny_img)
print(f"目标方块中心点({x_center},{y_center})",)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
全部代码
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
# @software: PyCharm
# @time: 2019/7/10 15:39
# @author: Paulson●Wier
# @file: jump_跳一跳.py
# @desc:
import os
import random
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
def get_screenshot():
# 截取手机的屏幕
os.system('adb shell /system/bin/screencap -p /sdcard/screencap.png')
# 把模拟器里面的文件传到电脑上
os.system('adb pull /sdcard/screencap.png screencap.png')
def get_start(img):
"""
模板匹配,获取跳一跳起点的位置参数(小跳棋)
:param img:跳一跳当前图片
:return 跳块中心点坐标(x,y)
"""
# 使用标准相关系数匹配,1表示完美匹配, -1表示糟糕匹配, 0表示没有任何相关性
result = cv2.matchTemplate(img, temple, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
# 使用函数 minMaxloc, 确定匹配结果矩阵的最大值和最小值(val),以及它们的位置(loc)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
# 此处选取最大值的位置,为图像的左上角
t1 = max_loc
# 获取图像的右下角
br = (t1[0] + tw, t1[1] + th)
t_x_center = (t1[0] + br[0]) // 2
t_y_center = int(max_loc[1] * 0.25 + br[1] * 0.75)
print(f"跳块中心点坐标({t_x_center},{t_y_center})")
return t_x_center, t_y_center
def get_next(img):
"""
获取下一跳目标方块中心点坐标
:param img:
:return:
"""
# 高斯模糊
img_rgb = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5, 5), 0)
canny_img = cv2.Canny(img_rgb, 1, 10)
# 输出边缘检测图像的高和宽
H, W = canny_img.shape
# 第一个顶点的高度,row为列表(代表每一行的像素值), max(row) 获取列表中最大的像素值
# 对图像高度大于400的行进行遍历(这样可以去除上方数字以及小程序块的影响)。
# np.nonzero() 表示获取列表元素数值不为0的位置,
y_top = np.nonzero([max(row) for row in canny_img[420:]])[0][0] + 420
# 获取第一个顶点的宽度值
x_top = int(np.mean(np.nonzero(canny_img[y_top])))
# 跳过小白圈,然后遍历
y_bottom = y_top + 125
for row in range(y_bottom, H):
if canny_img[row, x_top] != 0:
y_bottom = row
break
# 得到方块的中心点
x_center, y_center = x_top, (y_top + y_bottom) // 2
print(f"目标方块中心点({x_center},{y_center})",)
return x_center, y_center
def game_over(img):
"""
模板匹配,检测是否要将程序结束
"""
# 如果在游戏截图中匹配到带"再玩一局"字样的模板,则循环中止
res_end = cv2.matchTemplate(img, temp_end, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
if cv2.minMaxLoc(res_end)[1] > 0.95:
print('Game over!')
return True
def jump(distance, flag=1.35):
# 设置按压时间,系数为默认为1.35
press_time = int(distance * flag)
# 生成随机手机屏幕模拟触摸点,防止成绩无效
# 生成随机整数(0-9),最终数值为(0-90)
rand = random.randint(0, 9) * 10
# adb长按操作,即在手机屏幕上((320-410),(410-500))坐标处长按press_time毫秒
cmd = ('adb shell input swipe %i %i %i %i ' + str(press_time)) % (320 + rand, 410 + rand, 320 + rand, 410 + rand)
# 输出adb命令
print(cmd)
# 执行adb命令
os.system(cmd)
def main():
i = 0
while True:
# 将安卓手机上的截图移到电脑当前文件夹下
i += 1
get_screenshot()
# 读取截图图像
img = cv2.imread('screencap.png', 0)
if game_over(img):
print(f"第{i-1}次跳动失败")
break
print(f"第{i-1}次跳动成功") # 提示上一次跳动是否成功
begin_x, begin_y = get_start(img)
target_x, target_y = get_next(img)
distance = ((begin_x-target_x)**2 + (begin_y-target_y)**2) ** 0.5
# 将起点位置绘制出来,一个圆
cv2.circle(img, (begin_x, begin_y), 20, 255, -1)
# 将终点位置绘制出来,一个圆
img_end = cv2.circle(img, (target_x, target_y), 20, 188, -1)
# 保存图片
cv2.imwrite('last.png', img_end)
# 根据获得的距离来设置按压时长
jump(distance)
time.sleep(1.3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 游戏结束的模板图像
temp_end = cv2.imread('end.jpg', 0)
# 读取小跳棋模板图像
temple = cv2.imread('temple.png', 0)
# 获取小跳棋模板图像的高和宽
th, tw = temple.shape[:2]
main()