JavaScript事件的防抖和节流
JavaScript事件的防抖和节流
为什么要用函数防抖和节流
- 浏览器操作中我们经常会遇到短时间内频繁触发的事件,类似于:
- 监听window的scroll 事件,检测滚动位置,根据滚动位置显示返回顶部按钮
- 监听window的resize 事件,对某些自适应页面调整DOM的渲染(通过CSS实现的自适应不再此范围内)
- 监听input的keyup 事件,监听文字输入并调用接口进行模糊匹配,还有change或input事件、keyup、keydown和keypress事件等
- 所以会加重浏览器的负担,导致用户体验非常糟糕。此时我们可以采用debounce(防抖)和throttle(节流)的方式来减少调用频率,同时又不影响实际效果。
防抖和节流简单实现
// 防抖
function debounce(func,wait){
var timeout;
return function(){
var self = this;
var args = arguments;
if(timeout) clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(()=>{
func.apply(self,args);
},wait)
}
}
// 节流
function throttle(func,wait){
var timeout;
return function(){
var self = this;
var args = arguments;
if(!timeout){
timeout = setTimeout(()=>{
timeout = null;
func.apply(self,args)
},wait)
}
}
}
函数防抖(Debounce)
https://www.cnblogs.com/momo798/p/9177767.html
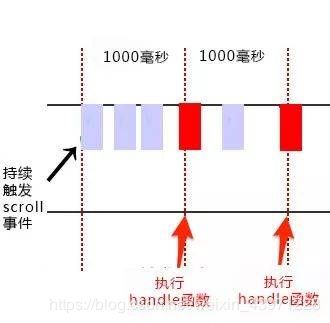
- 函数防抖(debounce):当持续触发事件时,一定时间段内没有再触发事件,事件处理函数才会执行一次,如果设定的时间到来之前,又一次触发了事件,就重新开始延时。如下图,持续触发scroll事件时,并不执行handle函数,当1000毫秒内没有触发scroll事件时,才会延时触发scroll事件。

- 原理:对处理函数进行延时操作,若设定的延时到来之前,再次触发事件,则清除上一次的延时操作定时器,重新定时
- 不适用场景:
当我们做图片懒加载(lazyload)时,需要通过滚动位置,实时显示图片时,如果使用防抖函数,懒加载(lazyload)函数将会不断被延时,
只有停下来的时候才会被执行,对于这种需要实时触发事件的情况,就显得不是很友好了。 - 下面开始介绍函数节流,通过设定时间片,控制事件函数间断性的触发
var timer; // 维护同一个timer
function debounce(fn, delay) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(function(){
fn();
}, delay);
}
// test
function testDebounce() {
console.log('test');
}
document.onmousemove = () => {
debounce(testDebounce, 1000);
}
上面例子中的debounce就是防抖函数,在document中鼠标移动的时候,会在onmousemove最后触发的1s后执行回调函数testDebounce;如果我们一直在浏览器中移动鼠标(比如10s),会发现会在10 + 1s后才会执行testDebounce函数(因为clearTimeout(timer)),这个就是函数防抖。
在上面的代码中,会出现一个问题,var timer只能在setTimeout的父级作用域中,这样才是同一个timer,并且为了方便防抖函数的调用和回调函数fn的传参问题,我们应该用闭包来解决这些问题。
/**
* 防抖函数
* @param method 事件触发的操作
* @param delay 多少毫秒内连续触发事件,不会执行
* @returns {Function}
*/
function debounce(method,delay) {
let timer = null;
return function () {
let self = this,
args = arguments;
timer && clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(function () {
method.apply(self,args);
},delay);
}
}
window.onscroll = debounce(function () {
let scrollTop = document.body.scrollTop || document.documentElement.scrollTop;
console.log('滚动条位置:' + scrollTop);
},200)
https://blog.csdn.net/a5161586/article/details/83149859
/**
*@param fn {function} 事件触发执行的函数
*@param wait {number} 固定时间(事件停止触发多久之后执行函数)
*/
debounce(fn,wait)
function debounce(fn,wait){
var timer;
return function(){
var args = Array.prototype.slice.apply(arguments);
if(timer){
clearTimeout(timer);
};
timer = setTimeout(function(){
fn.apply(this,args);
},wait);
}
}
<body>
<div id="app">111</div>
<h2></h2>
<script>
var app = document.getElementById('app')
var h2 = document.querySelector('h2')
var count = 0;
//频繁触发
/*app.onmousemove = function() {
h2.innerHTML = count
count++
}*/
//防抖函数
/*function debounce(func,wait){
var timeout;
return function(){
clearTimeout(timeout)
timeout=setTimeout(func, wait);
}
}
app.onmousemove = debounce(function(){
h2.innerHTML = count
count++
},1000)*/
/*在上面的代码中,会出现一个问题,var timer只能在setTimeout的父级作用域中,
这样才是同一个timer,并且为了方便防抖函数的调用和回调函数fn的传参问题,
我们应该用闭包来解决这些问题。*/
//改进后防抖函数
function debounce(func,wait){
var timeout;
return function(){
var context = this
var args = arguments
clearTimeout(timeout)
timeout=setTimeout(function(){
func.apply(context,args)
}, wait);
}
}
app.onmousemove = debounce(function(ev){
console.log(ev)
h2.innerHTML = count
count++
},1000)
</script>
</body>
函数节流(Throttle)
-
定义:事件触发后执行函数执行期间内事件再次触发,执行函数将不会执行,等规定时间之后事件触发,执行函数方可再次执行。
-
原理:对处理函数进行延时操作,若设定的延时到来之前,再次触发事件,则清除上一次的延时操作定时器,重新定时
-
防抖有一个问题,那就是如果事件一直在触发,那么执行函数永远都得不到执行。这种情况下,函数节流此时是较好的方法。
-
它与防抖最大的区别就是,无论事件触发多么频繁,都可以保证在规定时间内可以执行一次执行函数。
函数节流(throttle):当持续触发事件时,保证一定时间段内只调用一次事件处理函数。节流通俗解释就比如我们水龙头放水,阀门一打开,水哗哗的往下流,秉着勤俭节约的优良传统美德,我们要把水龙头关小点,最好是如我们心意按照一定规律在某个时间间隔内一滴一滴的往下滴。如下图,持续触发scroll事件时,并不立即执行handle函数,每隔1000毫秒才会执行一次handle函数。
定时器实现节流函数:
function throttle(fn, delay) {
var timer;
return function () {
var _this = this;
var args = arguments;
if (timer) {
return;
}
timer = setTimeout(function () {
fn.apply(_this, args);
timer = null; // 在delay后执行完fn之后清空timer,此时timer为假,throttle触发可以进入计时器
}, delay)
}
}
//测试用例:
function testThrottle(e, content) {
console.log(e, content);
}
var testThrottleFn = throttle(testThrottle, 1000); // 节流函数
document.onmousemove = function (e) {
testThrottleFn(e, 'throttle'); // 给节流函数传参
}
函数节流的目的,是为了限制函数一段时间内只能执行一次。因此,定时器实现节流函数通过使用定时任务,延时方法执行。在延时的时间内,方法若被触发,则直接退出方法。从而,实现函数一段时间内只执行一次。
根据函数节流的原理,我们也可以不依赖 setTimeout实现函数节流。
时间戳实现节流函数:
function throttle(fn, delay) {
var previous = 0;
// 使用闭包返回一个函数并且用到闭包函数外面的变量previous
return function() {
var _this = this;
var args = arguments;
var now = new Date();
if(now - previous > delay) {
fn.apply(_this, args);
previous = now;
}
}
}
// test
function testThrottle(e, content) {
console.log(e, content);
}
var testThrottleFn = throttle(testThrottle, 1000); // 节流函数
document.onmousemove = function (e) {
testThrottleFn(e, 'throttle'); // 给节流函数传参
}
其实现原理,通过比对上一次执行时间与本次执行时间的时间差与间隔时间的大小关系,来判断是否执行函数。若时间差大于间隔时间,则立刻执行一次函数。并更新上一次执行时间。
常见应用场景
- 函数防抖的应用场景
连续的事件,只需触发一次回调的场景有:
1.搜索框搜索输入。只需用户最后一次输入完,再发送请求
2.手机号、邮箱验证输入检测
3.窗口大小Resize。只需窗口调整完成后,计算窗口大小。防止重复渲染。 - 函数节流的应用场景
间隔一段时间执行一次回调的场景有:
1.滚动加载,加载更多或滚到底部监听
2.谷歌搜索框,搜索联想功能
3.高频点击提交,表单重复提交