Ubuntu18.04下安装mysql5.7+(tar.gz)详细步骤--亲测通过
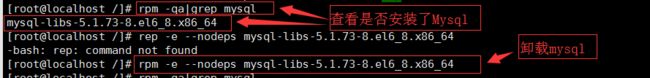
检查是否已经安装了Mysql
rpm -qa|grep mysql
rpm -e --nodeps 程序名
上传文件
mysql-5.7.22-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
解压文件,并将解压后的文件重命名,移动到/usr/local/mysql
tar -zxvf mysql-5.7.22-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
mv mysql-5.7.22-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql
cd /usr/local/mysql
添加一个Mysql 用户组
groupadd mysql
添加一个用户
useradd -r -g mysql mysql
创建文件夹 用来存放数据
/usr/local/mysql/data
mkdir /usr/local/mysql/data
进入mysql包中, 给这个包授权 给mysql
/usr/local/mysql
chown -R mysql:mysql ./
chown -R mysql:mysql data
进入mysql文件名 basedir 为mysql 的路径, datadir 为mysql的 data 路径,里面 存放着mysql自己的包
bin/mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data
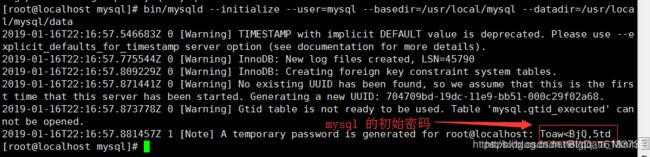
注意::运行上面个命令可能会报错:这里可能会提示缺少libaio1和libnuma1这个库,只要安装即可: sudo apt-get install libaio1;sudo apt-get install libnuma1
进入support-file 文件夹
cd support-files/
复制文件
cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
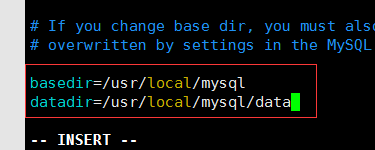
修改basedir= 自己的路径 修改datadir= 自己的路径
vim /etc/init.d/mysqld
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data
启动Mysql
bin/mysqld_safe --user=mysql &
//或者
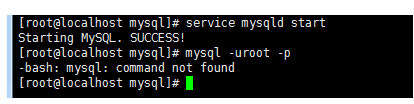
service mysqld start
让mysql 启动
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld start
查看状态
$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld status
或者使用service命令,让mysql 启动,停止
$ sudo service mysqld [status|start|stop]
加入开机启动项目(这种方法不管用的话可以使用下面一种)
chkconfig --add mysqld
//查看开机启动項
chkconfig --list
0.让mysql开机自己启动
$ sudo update-rc.d -f mysqld defaults
如果不想让mysql开机自己启动,可以使用
$ sudo update-rc.d -f mysqld remove
重启Mysql
/etc/init.d/mysqld restart
bin目录下 连接数据库
./mysql -uroot -p 临时密码
执行:
ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/bin
修改密码
set password= password('root');
//或者
alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'root';
//刷新权限
flush privileges;
//授权新用户
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root1'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'root' WITH GRANT OPTION;
vi /etc/profile
//加入
PATH=/data/mysql/bin:/data/mysql/lib:$PATH
export PATH
//配置文件立即生效
source /etc/profile
解决 数据库乱码问题
将my.cnf拷贝到/etc/下
# For advice on how to change settings please see
# http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-configuration-defaults.html
[client]
# pipe
# # socket=0.0
port=3306
default-character-set=utf8
[mysql]
port=3306
default-character-set=utf8
#
[mysqld]
#
# Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data
# cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%.
# innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M
#
# Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging
# changes to the binary log between backups.
# log_bin
#
# Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers.
# The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs.
# Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values.
# join_buffer_size = 128M
# sort_buffer_size = 2M
# read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M
datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data
#socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
server_id=1
expire_logs_days=3
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
symbolic-links=0
port=3306
character-set-server=utf8
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
#pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
pid-file=/usr/local/mysql/data/localhost.localdomain.pid