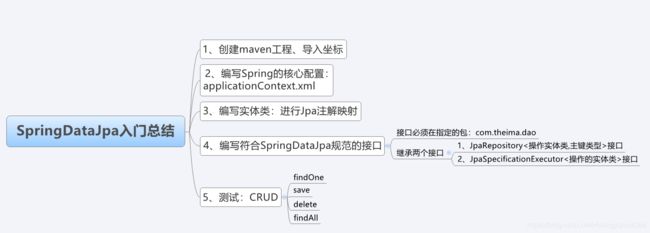
Spring Data Jpa底层原理剖析、JPQL查询、方法命名规则查询
1.1 Spring Data Jpa底层原理解析
- 目标:知道它是怎么运行的?底层到底封装的是谁?、
- 明确一点:我们所使用的所有框架,底层大多数都使用了动态代理技术、反射技术来封装实现。
分析步骤:
- 我们只写了接口,但是没有写实现类,这个实现类就是Spring在运行的时候,注入的代理对象。
- Spring怎么知道生成的那个dao的实现类?因为在配置文件中指定了dao接口所在的包
- 生成的是什么对象?代理对象:通过jdk生成的动态代理对象
Proxy.newProxyInstance(类加载器,实现的接口列表,InvocationHandler)
JdkDynamicAopProxy: 这个是个对象,实现了InvocationHandler接口,所以这个类有invoke方法- 在JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法中有个target对象,这个对象就是真正干活的对象
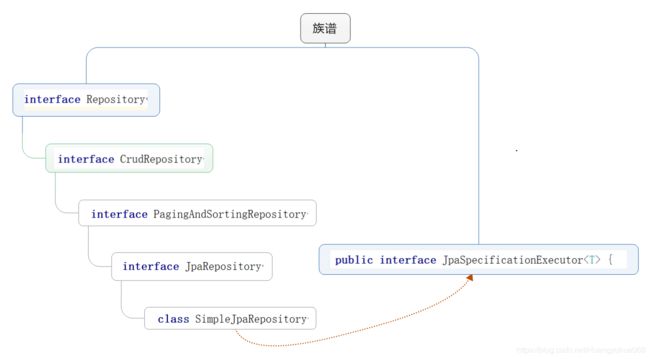
- 真正干活的对象:SimpleJpaRepository
- SimpleJpaRepository实现了我们dao接口继承的那两个接口,所以这个类中肯定有接口的所有方法
- 我们看到findOne方法中调用了em.find方法,这个em到底是谁?
1.2 Spring Data Jpa常用接口分析
2.1 查询方式一:接口定义方法查询:查询一个的两种方法
- 目标:查询一个对象的两种方法
- findOne(主键值):底层调用的是em.find() :立即加载
- getOne(主键值) : 底层调用的是em.getReference() : 延迟加载
package com.sunny.SpringDataJpaTest;
import com.sunny.dao.CustomerDao;
import com.sunny.domain.Customer;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//替换运行器
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:/applicationContext.xml")//指定核心配置文件
public class Interface_Method_Query {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* 查询一个对象
* findOne(); em.finc(Class,id) 立即加载
* getOne(); em.getReference(Class,id) 延迟加载
*
* 细节:
* 在使用延迟加载的时候,需要用到事务,如果没有事务,会报错
* could not initialize proxy - no Session 异常
*
* 为了解决这个异常:我们手动在测试方法中加入@Transactional注解
* 在以后真正的项目中,我们配置了声明式事务,这个注解就不用写了
*
*/
@Test
@Transactional
public void test01(){
//Customer c = customerDao.findOne(2L);
Customer c = customerDao.getOne(2L);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
2.2 查询方式一:接口定义方法查询:查询所有的分页与排序查询
目标:查询所有的分页与排序查询
import com.sunny.dao.CustomerDao;
import com.sunny.domain.Customer;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//替换运行器
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:/applicationContext.xml")//指定核心配置文件
public class Interface_Method_Query {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* 查询所有:
* 1)排序
* 2)分页
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
//排序对象
/**
* 第一个参数: 排序规则: asc | desc
* 第二个参数: 排序的实体类的属性名称
*/
Sort s = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"custId");
//分页
/**
* 第一个参数:当前页: 从0开始,0代表第一页;1代表第二页;2代表第三页........
* 第二个参数:页大小
* 第三个参数:排序对象,可以为空
*/
Pageable p = new PageRequest(0,2,s);
//查询
Page page = c ustomerDao.findAll(p);
System.out.println("总记录数:"+page.getTotalElements());
System.out.println("总页数:"+page.getTotalPages());
System.out.println("当前页数据======================");
for (Customer customer : page.getContent()) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
}
} 2.3 查询方式一:接口定义方法查询:统计所有和判断一个对象是否存在
目标:掌握统计查询和如何判断一个对象是否存在
/**
* 统计所有: count(*) = count(1) > count(custId)
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
long count = customerDao.count();
System.out.println(count);
}
/**
* 判断一个对象是否存在:
* 1)根据id把对象查询出来是【select * 】,如果返回对象,说明存在;反之不存在
* 2)统计查询【select count(*)】:如果大于0存在;等于0 不存在 【推荐】
*
* 判断一个对象是否存在:exists方法 ; spring用的是第二种
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
boolean exists = customerDao.exists(7888888888888888888L);
System.out.println(exists);
}2.4 查询方式二:使用JPQL的方式查询:查询操作
- 使用Spring Data JPA提供的查询方法已经可以解决大部分的应用场景,但是对于某些业务来说,我们还需要灵活的构造查询条件,这时就可以使用@Query注解,结合JPQL的语句方式来完成查询。
- @Query 注解的使用非常简单,只需要在方法上面标注该注解,同时提供一个JPQL查询语句即可。
- JPQL查询规则:
- 在dao接口中编写方法
- 在方法上使用@Query(value=“JPQL语句”)
- 返回值,自己定,如果是单个对象,你就写单个对象,如果多个,就用List
dao代码:
/**
* 编写符合SpringDataJpa规范的dao层接口
* 1)dao接口所在的包已经在核心配置文件中固定
* 2)dao接口必须继承两个接口:
* * JpaRepository<操作的实体类,主键的类型> 基本的CRUD和复杂查询
* * JpaSpecificationExecutor<操作的实体类> 动态查询
*/
public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository,JpaSpecificationExecutor{
//JPQL查询:查询所有
@Query(value="from Customer")
public List findJPQL();
//JPQL查询:条件查询
@Query(value="from Customer where custId = ?")
public Customer findJPQL2(Long id);
//JPQL查询:多条件: 参数索引: 从1开始,第一个参数就是1
@Query(value="from Customer where custId = ?2 or custName like ?1")
public List findJPQL3(String name,Long id);
} 测试代码:
/**
* Spring整合Junit的方式
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//替换运行器
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:/applicationContext.xml")//指定核心配置文件
public class Test03_JPQL {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* 查询所有
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
List list = customerDao.findJPQL();
for (Customer customer : list) {
System.out.pri ntln(customer);
}
}
/**
* 条件查询
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
System.out.println(customerDao.findJPQL2(7L));
}
/**
* 条件查询
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
List customers = customerDao.findJPQL3("小%", 7L);
for (Customer customer : customers) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
}
} 2.5 查询方式二:使用JPQL的方式查询:更新操作
目标:掌握如何使用JPQL实现更新对象的操作
dao代码:
//更新操作: 需要两个注解
//第一个注解中写的update语句
@Query(value = "update Customer set custName = ?1 where custId = ?2")
//第二个注解告诉spring我们要进行更新操作
@Modifying
public void updateCustName(String name,Long id);测试代码:
/**
* 更新操作
*/
@Test
@Transactional
//虽然没有报错,但是数据没有进入数据库: 原因
//在测试方法中,更新之后,在最后spring会回滚操作,要想看到结果
@Rollback(false)//让spring不回滚
public void test4(){
customerDao.updateCustName("三分归元气",7L);
}2.6 查询方式三:SQL查询
目标:了解JPA中的SQL查询
- SQL查询规格:
- 在dao接口中编写方法
- 在方法上使用@Query(value=“SQL语句”,nativeQuery=true)
- 返回值,自己定,如果是单个对象,就写单个对象,如果是多个,就写List
dao层代码:
//sql查询
@Query(value="select * from cst_customer where cust_id = ?2 or cust_name like ?1",nativeQuery = true)
public List findSql(String name,Long id);
测试代码:
/**
* Spring整合Junit的方式
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//替换运行器
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:/applicationContext.xml")//指定核心配置文件
public class Test04_sql {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* sql查询
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
List list = customerDao.findSql("小%",7L);
for (Customer customer : list) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
}
}
2.7 查询方式四:根据方法名规则查询
- Dao接口的方法名规则:
- 以findBy开头
- 后面跟的是查询的属性条件:属性名首字母大写
- 属性名后面跟的是查询规则:模糊【like】、精确【不加规则代表精确查询】
- 多个条件以and、or拼接
- 重复以上步骤,从第二步开始
- 顾名思义,方法命名规则查询就是根据方法的名字,就能创建查询。只需要按照Spring Data JPA提供的方法命名规则定义方法的名称,就可以完成查询工作。Spring Data JPA在程序执行的时候会根据方法名称进行解析,并自动生成查询语句进行查询。
- 按照Spring Data JPA定义的规则,查询方法以findBy开头,涉及条件查询时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,要注意的是:条件属性首字母需要大写。框架在进行方法名解析时,会先把方法名多余的前缀截取掉,然后对剩下部分进行解析。
dao代码:
//方法名规则查询:精确查询
public List findByCustId(Long id);
//方法名规则查询:模糊查询
public List findByCustNameLike(String name);
//方法名规则查询:多条件查询
public List findByCustNameLikeOrCustId(String name,Long id); 测试代码:
/**
* Spring整合Junit的方式
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)//替换运行器
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:/applicationContext.xml")//指定核心配置文件
public class Test05_Method_Name_Query {
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* 方法名规则查询
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
List list = customerDao.findByCustId(7L);
for (Customer customer : list) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
}
/**
* 方法名规则查询
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
List list = customerDao.findByCustNameLike("小%");
for (Customer customer : list) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
}
/**
* 方法名规则查询
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
List list = customerDao.findByCustNameLikeOrCustId("小%",7L);
for (Customer customer : list) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
}
} 具体的关键字,使用方法和生产成SQL如下表所示
| Keyword |
Sample |
JPQL |
| And |
findByLastnameAndFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| Or |
findByLastnameOrFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
| Is,Equals |
findByFirstnameIs, findByFirstnameEquals |
… where x.firstname = ?1 |
| Between |
findByStartDateBetween |
… where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan |
findByAgeLessThan |
… where x.age < ?1 |
| LessThanEqual |
findByAgeLessThanEqual |
… where x.age ⇐ ?1 |
| GreaterThan |
findByAgeGreaterThan |
… where x.age > ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual |
findByAgeGreaterThanEqual |
… where x.age >= ?1 |
| After |
findByStartDateAfter |
… where x.startDate > ?1 |
| Before |
findByStartDateBefore |
… where x.startDate < ?1 |
| IsNull |
findByAgeIsNull |
… where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull,NotNull |
findByAge(Is)NotNull |
… where x.age not null |
| Like |
findByFirstnameLike |
… where x.firstname like ?1 |
| NotLike |
findByFirstnameNotLike |
… where x.firstname not like ?1 |
| StartingWith |
findByFirstnameStartingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
| EndingWith |
findByFirstnameEndingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
| Containing |
findByFirstnameContaining |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
| OrderBy |
findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc |
… where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
| Not |
findByLastnameNot |
… where x.lastname <> ?1 |
| In |
findByAgeIn(Collection ages) |
… where x.age in ?1 |
| NotIn |
findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) |
… where x.age not in ?1 |
| TRUE |
findByActiveTrue() |
… where x.active = true |
| FALSE |
findByActiveFalse() |
… where x.active = false |
| IgnoreCase |
findByFirstnameIgnoreCase |
… where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |