【SpringCloud源码解析】SpringCloud源码探秘之服务注册如何实现
简介
Eureka是一种基于REST(Representational State Transfer)的服务,主要用于AWS云,用于定位服务,以实现中间层服务器的负载平衡和故障转移。我们将此服务称为Eureka Server。Eureka还附带了一个基于Java的客户端组件Eureka Client,它使与服务的交互变得更加容易。客户端还有一个内置的负载均衡器,可以进行基本的循环负载均衡。在Netflix,一个更复杂的负载均衡器包含Eureka基于流量,资源使用,错误条件等多种因素提供加权负载平衡,以提供卓越的弹性。
先看一张 github 上 Netflix Eureka 的一架构图,如下:
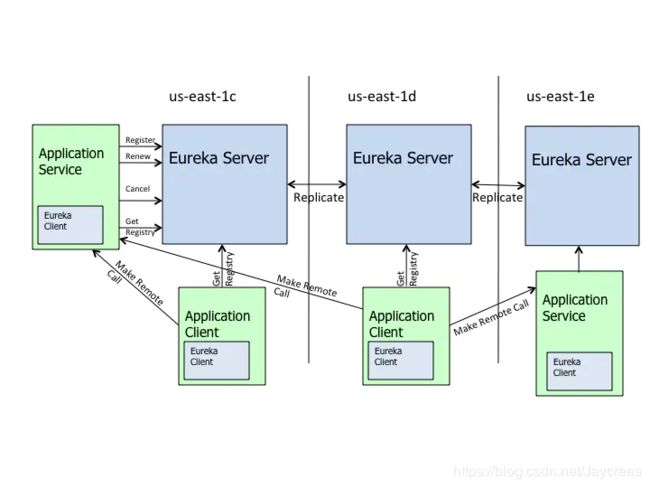
从图可以看出在这个体系中,有2个角色,即Eureka Server和Eureka Client。而Eureka Client又分为Applicaton Service和Application Client,即服务提供者何服务消费者。 每个区域有一个Eureka集群,并且每个区域至少有一个eureka服务器可以处理区域故障,以防服务器瘫痪。
Eureka Client 在 Eureka Server 注册,然后Eureka Client 每30秒向 Eureka Server 发送一次心跳来更新一次租约。如果 Eureka Client 无法续订租约几次,则会在大约90秒内 Eureka Server 将其从服务器注册表中删除。注册信息和续订将复制到群集中的所有 Eureka Server 节点。来自任何区域的客户端都可以查找注册表信息(每30秒发生一次)根据这些注册表信息,Application Client 可以远程调用 Applicaton Service 来消费服务。
源码分析
基于Spring Cloud的 eureka 的 client 端在启动类上加上 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解,就可以 用 NetFlix 提供的 Eureka client。下面就以 @EnableDiscoveryClient 为入口,进行Eureka Client的源码分析。
@EnableDiscoveryClient,通过源码可以发现这是一个标记注解:
/**
* Annotation to enable a DiscoveryClient implementation.
* @author Spencer Gibb
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableDiscoveryClient {
boolean autoRegister() default true;
}
通过注释可以知道 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解是用来 启用 DiscoveryClient 的实现,DiscoveryClient接口代码如下:
public interface DiscoveryClient {
String description();
List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId);
List<String> getServices();
}
代码接口说明:
description():实现描述。
getInstances(String serviceId):获取与特定serviceId关联的所有ServiceInstance
getServices():返回所有已知的服务ID
EurekaDiscoveryClient:Eureka 的 DiscoveryClient 实现类。
CompositeDiscoveryClient:用于排序可用客户端的发现客户端的顺序。
NoopDiscoveryClient:什么都不做的服务发现实现类,已经被废弃。
SimpleDiscoveryClient:简单的服务发现实现类 SimpleDiscoveryClient,具体的服务实例从 SimpleDiscoveryProperties 配置中获取。
EurekaDiscoveryClient 是 Eureka 对 DiscoveryClient接口的实现,代码如下:
public class EurekaDiscoveryClient implements DiscoveryClient {
public static final String DESCRIPTION = "Spring Cloud Eureka Discovery Client";
private final EurekaInstanceConfig config;
private final EurekaClient eurekaClient;
public EurekaDiscoveryClient(EurekaInstanceConfig config, EurekaClient eurekaClient) {
this.config = config;
this.eurekaClient = eurekaClient;
}
@Override
public String description() {
return DESCRIPTION;
}
@Override
public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId) {
List<InstanceInfo> infos = this.eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(serviceId,
false);
List<ServiceInstance> instances = new ArrayList<>();
for (InstanceInfo info : infos) {
instances.add(new EurekaServiceInstance(info));
}
return instances;
}
@Override
public List<String> getServices() {
Applications applications = this.eurekaClient.getApplications();
if (applications == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
List<Application> registered = applications.getRegisteredApplications();
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
for (Application app : registered) {
if (app.getInstances().isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
names.add(app.getName().toLowerCase());
}
return names;
}
}
从代码可以看出 EurekaDiscoveryClient 实现了 DiscoveryClient 定义的规范接口,真正实现发现服务的是 EurekaClient,下面是 EurekaClient 依赖结构图:

EurekaClient 唯一实现类 DiscoveryClient,DiscoveryClient 的构造方法如下:
@Inject
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args,
Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider) {
//省略...
try {
// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
//省略...
initScheduledTasks();
try {
Monitors.registerObject(this);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Cannot register timers", e);
}
//省略...
}
可以看到这个构造方法里面,主要做了下面几件事:
创建了scheduler定时任务的线程池,heartbeatExecutor心跳检查线程池(服务续约),cacheRefreshExecutor(服务获取)
然后initScheduledTasks()开启上面三个线程池,往上面3个线程池分别添加相应任务。然后创建了一个instanceInfoReplicator(Runnable任务),然后调用InstanceInfoReplicator.start方法,把这个任务放进上面scheduler定时任务线程池(服务注册并更新)。
服务注册(Registry)
上面说了,initScheduledTasks()方法中调用了InstanceInfoReplicator.start()方法,InstanceInfoReplicator 的 run()方法代码如下:
public void run() {
try {
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
发现 InstanceInfoReplicator的run方法,run方法中会调用DiscoveryClient的register方法。DiscoveryClient 的 register方法 代码如下:
/**
* Register with the eureka service by making the appropriate REST call.
*/
boolean register() throws Throwable {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{}: registering service...", appPathIdentifier);
EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(PREFIX + "{} - registration failed {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
throw e;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - registration status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 204;
}
最终又经过一系列调用,最终会调用到AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient的register方法,代码如下:
public EurekaHttpResponse<Void> register(InstanceInfo info) {
String urlPath = "apps/" + info.getAppName();
ClientResponse response = null;
try {
Builder resourceBuilder = jerseyClient.resource(serviceUrl).path(urlPath).getRequestBuilder();
addExtraHeaders(resourceBuilder);
response = resourceBuilder
.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip")
.type(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_TYPE)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.post(ClientResponse.class, info);
return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatus()).headers(headersOf(response)).build();
} finally {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Jersey HTTP POST {}/{} with instance {}; statusCode={}", serviceUrl, urlPath, info.getId(),
response == null ? "N/A" : response.getStatus());
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
}
}
可以看到最终通过http rest请求eureka server端,把应用自身的InstanceInfo实例注册给server端,我们再来完整梳理一下服务注册流程:
Renew服务续约
服务续约和服务注册非常类似,HeartbeatThread 代码如下:
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
if (renew()) {
//更新最后一次心跳的时间
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
// 续约的主方法
boolean renew() {
EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);
logger.debug(PREFIX + "{} - Heartbeat status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 404) {
REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - Re-registering apps/{}", appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName());
long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime();
boolean success = register();
if (success) {
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);
}
return success;
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 200;
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e);
return false;
}
}
发送心跳 ,请求eureka server 端 ,如果接口返回值为404,就是说服务不存在,那么重新走注册流程。
如果接口返回值为404,就是说不存在,从来没有注册过,那么重新走注册流程。
服务续约流程如下图:

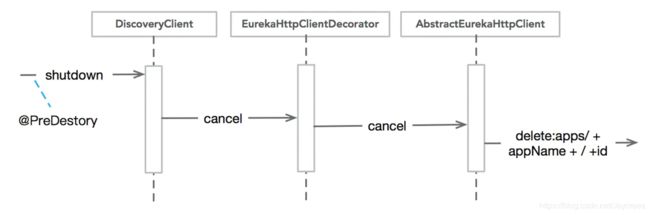
服务下线cancel
在服务shutdown的时候,需要及时通知服务端把自己剔除,以避免客户端调用已经下线的服务,shutdown()方法代码如下:
public synchronized void shutdown() {
if (isShutdown.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
logger.info("Shutting down DiscoveryClient ...");
if (statusChangeListener != null && applicationInfoManager != null) {
applicationInfoManager.unregisterStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener.getId());
}
// 关闭各种定时任务
// 关闭刷新实例信息/注册的定时任务
// 关闭续约(心跳)的定时任务
// 关闭获取注册信息的定时任务
cancelScheduledTasks();
// If APPINFO was registered
if (applicationInfoManager != null
&& clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()
&& clientConfig.shouldUnregisterOnShutdown()) {
// 更改实例状态,使实例不再接收流量
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.DOWN);
//向EurekaServer端发送下线请求
unregister();
}
if (eurekaTransport != null) {
eurekaTransport.shutdown();
}
heartbeatStalenessMonitor.shutdown();
registryStalenessMonitor.shutdown();
logger.info("Completed shut down of DiscoveryClient");
}
}
private void cancelScheduledTasks() {
if (instanceInfoReplicator != null) {
instanceInfoReplicator.stop();
}
if (heartbeatExecutor != null) {
heartbeatExecutor.shutdownNow();
}
if (cacheRefreshExecutor != null) {
cacheRefreshExecutor.shutdownNow();
}
if (scheduler != null) {
scheduler.shutdownNow();
}
}
void unregister() {
// It can be null if shouldRegisterWithEureka == false
if(eurekaTransport != null && eurekaTransport.registrationClient != null) {
try {
logger.info("Unregistering ...");
EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.cancel(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId());
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - deregister status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - de-registration failed{}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}