JMeter BeanShell详解
一、BeanShell介绍
下面直接引用官网的介绍译文:
BeanShell是一个小型,免费,可嵌入的Java源代码解释器,具有用Java编写的对象脚本语言功能。 BeanShell动态执行标准Java语法,并使用常见的脚本编写方便性扩展它,例如松散类型,命令和方法闭包,如Perl和JavaScript中的那些。
官网地址:http://www.beanshell.org/ 。
BeanShell Github:https://github.com/beanshell/beanshell 。
二、BeanShell组件
JMeter有如下BeanShell组件:
-
BeanShell Timer(定时器)
-
BeanShell PreProcessor(前置处理器)
-
BeanShell Sampler(采样器)
-
BeanShell PostProcessor(后置处理器)
-
BeanShell Assertion(断言)
-
BeanShell Listener(监听器)
一般我们用得最多的就是BeanShell PreProcessor、Sampler、PostProcessor和Assertion。
三、JMeter BeanShell的基础用法
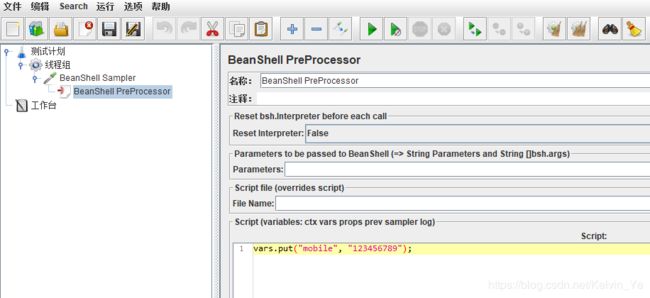
这里以BeanShell PreProcessor为例,为接口数据添加随机数。
首先添加线程组,在线程组下添加BeanShell Sampler和查看结果树,再在Sampler下添加BeanShell PreProcessor,BeanShell PreProcessor的脚本内容如下:
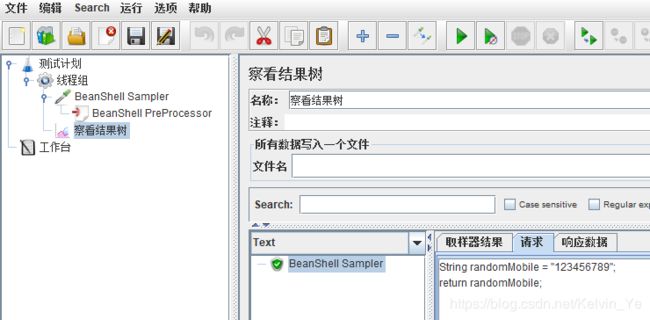
vars.put("mobile", "123456789");BeanShell Sampler内容如下:
String randomMobile = "${mobile}";
return randomMobile;BeanShell执行到return时,就会把return的值作为responseData并且脚本执行结束。
四、JMeter BeanShell的内置变量
JMeter在内嵌BeanShell时默认创建了一些内置变量,以方便使用者调用,以下是一些常用的BeanShell内置变量:
- vars
- props
- ctx
- log
- Label / SampleLabel
- data / SamplerData
- IsSuccess
- prev / SampleResult
- ResponseData
- ResponseCode
- ResponseMessage
- Failure
- FailureMessage
- Response.setStopThread(boolean)
- Response.setStopTest(boolean)
请注意,以上变量并不是每个BeanShell组件都有,也并不是每个变量都支持读和写,具体请查看组件的详细说明,接下来将一一讲解。
1)vars
vars可以说是最常用的内置变量,其类型为JMeterVariables,其作用是添加或获取JMeter线程变量:
// 添加JMeter线程变量
vars.put("key", "name");
// 获取JMeter线程变量
vars.get("key");
// 在脚本文本中引用变量
${key}JavaDoc:http://jmeter.apache.org/api/org/apache/jmeter/threads/JMeterVariables.html 。
2)props
vars是不能跨线程组使用的,即在线程组A中put的值在线程组B中时get不到的,props就是为了解决上述问题:
// 添加属性变量
props.put("key", "name");
// 获取属性变量
props.get("key");
// 在脚本文本中引用变量
${__P(key)}JavaDoc:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Properties.html 。
3)ctx
ctx是当前线程的上下文,其类型为JMeterContext,该变量能做的事非常多,一般需要的动作在其他内置变量里都有提供,除非要做一些复杂的线程控制,详细查看JavaDoc。
JavaDoc:http://jmeter.apache.org/api/org/apache/jmeter/threads/JMeterContext.html 。
4)log
log就是输出不同等级的日志:
log.debug("xxx");
log.info("xxx");
log.warn("xxx");
log.error("xxx");JavaDoc:https://www.slf4j.org/api/org/slf4j/Logger.html 。
5)data和SamplerData
data和SamplerData就是sampler data(请求数据),其类型为byte []:
String samplerData = new String(data);6)Label和SampleLabel
Label和SampleLabel是sampler的标题,其类型是String。
7)IsSuccess
IsSuccess表示sampler的成功失败,其类型为boolean。
8)prev和SampleResult
prev和SampleResult是当前sampler的结果,其类型为SampleResult,它可以读写sampler的信息和控制sampler的行为。
JavaDoc:http://jmeter.apache.org/api/org/apache/jmeter/samplers/SampleResult.html 。
9)ResponseData
ResponseData就是sampler response data(响应数据),其类型为byte []:
String samplerData = new String(ResponseData);10)ResponseCode和ResponseMessage
ResponseCode和ResponseMessage是响应报文的响应码和响应信息,其类型为String。
11)Failure和FailureMessage
Failure和FailureMessage是BeanShell Assertion组件独有的内置变量,其作用是设置当前sampler的测试结果(成功或失败),Failure的类型是boolean,FailureMessage的类型是String。
// 设置sampler为测试通过
Failure = true;
// 设置sampler为测试失败
Failure = false;
FailureMessage = "测试失败";12)Response
Response其实就是SampleResult,为啥这样设计我也不懂,估计是满足不同的语意吧。
在BeanShell Assertion组件,有两个常用的方法Response.setStopThread(boolean)、Response.setStopTest(boolean),其作用是停止执行当前sampler。他们的区别是:
- setStopThread(boolean)只停止sampler所在的线程
- setStopTest(boolean)停止整个jmeter测试
Failure = false;
FailureMessage = "测试失败";
Response.setStopThread(true)一般应用的场景是使用BeanShell Assertion组件进行复杂的数据断言时,如断言失败则停止继续执行测试。