static成员变量与返回对象的引用
(1)用static修饰类成员变量(属性),表明该变量是静态的,无论创建多少对象,都只创建一个一个静态属性副本,也就是对象们共享同一个静态属性,这个方法常用的一个用途就是用来计算程序调用了多少次这个类来创建对象也就是创建过多少个对象。
#ifndef TIME_H_
#define TIME_H_
#include
using namespace std;
class Time
{
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
int seconds;
static int count;
public:
Time();
Time(int h = 0, int m = 0, int s = 0); #include "Time.h"
#include //支持abort()函数
int Time::count = 0;//初始化时不用加static
Time::Time()
{
hours = minutes = seconds = 0;
count++;
}
Time::Time(int h, int m, int s)
{
if (h < 0 || h > 24 || m > 60 || m < 0 || s > 60 || s < 0)
{
cout << "初始化参数输入有误,程序终止!" << endl;
abort();
}
hours = h;
minutes = m;
seconds = s;
count++;
} 同时,若非整形/枚举型const的静态属性,都必须在实现文件(.cpp)中进行初始化,且初始化时独立于其他成员函数的,也就是不能在构造函数中初始化静态属性:
int Time::count = 0;//初始化时不用加static若是整形/枚举型const的静态属性,才可以并且必须在声明文件(.h)中初始化,且在声明中初始化的整形/枚举型static属性,必须声明为const类型。
(2)同时这里说一下“返回对象的引用”这个方法,
Time Time::max(const Time &t1, const Time &t2)
{
return t1;
}这种返回方法需要创建一份t1对象的副本(调用复制构造函数),效率比较低。而下面这个方法:
const Time& Time::max(const Time &t1, const Time &t2)
{
return t1;
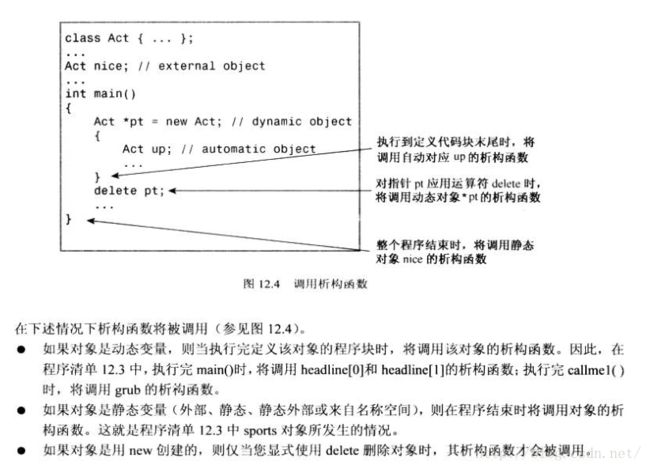
}(3)最后再讲一个小知识点,就是用new关键字来创建类的对象,
Time *a = new TIme();这句话之后必须同时搭配
delete a;这个知识点援引自《C++ primer plus》(第六版中文版)12.5.1节:
Time.h:
#pragma once
/*
* Time.h
*
* Created on: 2016-4-16
* Author: lvlang
*/
#ifndef TIME_H_
#define TIME_H_
#include
using namespace std;
class Time
{
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
int seconds;
static int count;
public:
Time();
Time(int h = 0, int m = 0, int s = 0);//如果不传入值则自动初始化为0
void AddHr(int h);
void AddMin(int m);
void reset(int h = 0, int m = 0, int s = 0);
void show()const;//const在这里表明本函数不会也不能去修改属性
Time sum(const Time &t)const; //传引用比传值效率高
Time operator+(const Time &t)const;
const Time &max(const Time &t1, const Time &t2);
~Time();
};
#endif /* TIME_H_ */
Time.cpp:
/*
* Time.cpp
*
* Created on: 2016-4-16
* Author: lvlang
*/
#include "Time.h"
#include //支持abort()函数
int Time::count = 0;
Time::Time()
{
hours = minutes = seconds = 0;
count++;
}
Time::Time(int h, int m, int s)
{
if (h < 0 || h > 24 || m > 60 || m < 0 || s > 60 || s < 0)
{
cout << "初始化参数输入有误,程序终止!" << endl;
abort();
}
hours = h;
minutes = m;
seconds = s;
count++;
}
void Time::AddHr(int h)
{
hours = (hours + h) % 24;
}
void Time::AddMin(int m)
{
int temp = this->minutes + m;
this->hours += temp / 60;
this->minutes = temp % 60;
}
void Time::reset(int h, int m, int s)
{
if (h < 0 || h > 24 || m > 60 || m < 0 || s > 60 || s < 0)
{
cout << "参数输入有误,程序终止!" << endl;
abort();
}
this->hours = h;
this->minutes = m;
this->seconds = s;
}
void Time::show()const
{
cout << "Hours: " << this->hours << " Minutes: " << this->minutes
<< " Seconds: " << this->seconds <<" Count: "<seconds + t.seconds) / 60;
temp.seconds = (this->seconds + t.seconds) % 60;
temp.minutes = (this->minutes + t.minutes + ts) % 60;
int tm = (this->minutes + t.minutes + ts) / 60;
temp.hours = (this->hours + t.hours + tm) % 24;
return temp;
//return *this;//返回当前对象(this为指向当前对象的指针)
}
Time Time::operator+(const Time &t)const
{
Time temp(0,0,0);
int ts = (this->seconds + t.seconds) / 60;
temp.seconds = (this->seconds + t.seconds) % 60;
temp.minutes = (this->minutes + t.minutes + ts) % 60;
int tm = (this->minutes + t.minutes + ts) / 60;
temp.hours = (this->hours + t.hours + tm) % 24;
return temp;//return之后会自动调用一次析构函数把temp的空间回收
}
const Time& Time::max(const Time &t1, const Time &t2)
{
return t1;
}
Time::~Time()
{
cout << "析构函数被调用" << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "Time.h"
int main()
{
Time time(10,10,10);
time.show();
time.AddHr(2);
time.show();
time.AddMin(20);
time.show();
Time t(1, 1, 1);
t.show();
t.reset(9, 9, 9);
t.sum(time);
t.show();
/*t = t + time;
t.show();*/
return 0;
}