Flink源码阅读(四)JobManager和TaskManager的rpc
引言
我们知道,jobmanager和taskmanager在集群模式下,是部署在不同机器上面的,那么现在就有一个问题,jobmanager和taskmanager是如何相互调用的。
分析
切入点
1 考虑以taskExecutor方法的submitTask方法为入口,查看调用关系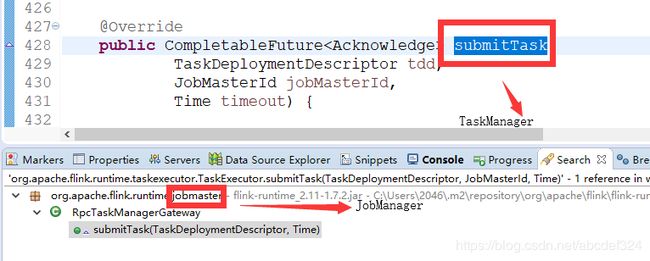
图中并没有提供明显的线索,看RpcTaskManagerGateway所处的包,猜测其位于JobManager,然后突然调用到了TaskManager,很是困惑。
3.在org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.RpcTaskManagerGateway.submitTask(TaskDeploymentDescriptor, Time)中增加断点
结论
经过上面的分析,flink中的rpc已经相当清楚了
客户端
客户端被AkkaInvocationHandler代理,调用下面方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
Object result;
if (declaringClass.equals(AkkaBasedEndpoint.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(Object.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcGateway.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(StartStoppable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(MainThreadExecutable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcServer.class)) {
result = method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (declaringClass.equals(FencedRpcGateway.class)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("AkkaInvocationHandler does not support the call FencedRpcGateway#" +
method.getName() + ". This indicates that you retrieved a FencedRpcGateway without specifying a " +
"fencing token. Please use RpcService#connect(RpcService, F, Time) with F being the fencing token to " +
"retrieve a properly FencedRpcGateway.");
} else {
//代理的方法
result = invokeRpc(method, args);
}
return result;
}
private Object invokeRpc(Method method, Object[] args) throws Exception {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
Time futureTimeout = extractRpcTimeout(parameterAnnotations, args, timeout);
final RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = createRpcInvocationMessage(methodName, parameterTypes, args);
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
final Object result;
if (Objects.equals(returnType, Void.TYPE)) {
tell(rpcInvocation);
result = null;
} else if (Objects.equals(returnType, CompletableFuture.class)) {
// execute an asynchronous call
result = ask(rpcInvocation, futureTimeout);
} else {
// execute a synchronous call
CompletableFuture<?> futureResult = ask(rpcInvocation, futureTimeout);
result = futureResult.get(futureTimeout.getSize(), futureTimeout.getUnit());
}
return result;
}
消息传递
消息传递使用了akka,但因为对这块并不熟悉,所以略过
服务端
服务端通过AkkaRpcActor类的onReceive方法接收数据,观察里面的调用逻辑,发现执行了下面的方法
private void handleRpcInvocation(RpcInvocation rpcInvocation) {
Method rpcMethod = null;
try {
String methodName = rpcInvocation.getMethodName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = rpcInvocation.getParameterTypes();
//获得对应的方法
rpcMethod = lookupRpcMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error("Could not load method arguments.", e);
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not load method arguments.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Could not deserialize rpc invocation message.", e);
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not deserialize rpc invocation message.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
} catch (final NoSuchMethodException e) {
log.error("Could not find rpc method for rpc invocation.", e);
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not find rpc method for rpc invocation.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
}
//反射获取结果,并发回客户端
if (rpcMethod != null) {
try {
// this supports declaration of anonymous classes
rpcMethod.setAccessible(true);
if (rpcMethod.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)) {
// No return value to send back
rpcMethod.invoke(rpcEndpoint, rpcInvocation.getArgs());
}
else {
final Object result;
try {
result = rpcMethod.invoke(rpcEndpoint, rpcInvocation.getArgs());
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
log.trace("Reporting back error thrown in remote procedure {}", rpcMethod, e);
// tell the sender about the failure
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(e.getTargetException()), getSelf());
return;
}
if (result instanceof CompletableFuture) {
final CompletableFuture<?> future = (CompletableFuture<?>) result;
Promise.DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new Promise.DefaultPromise<>();
future.whenComplete(
(value, throwable) -> {
if (throwable != null) {
promise.failure(throwable);
} else {
promise.success(value);
}
});
Patterns.pipe(promise.future(), getContext().dispatcher()).to(getSender());
} else {
// tell the sender the result of the computation
getSender().tell(new Status.Success(result), getSelf());
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error while executing remote procedure call {}.", rpcMethod, e);
// tell the sender about the failure
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(e), getSelf());
}
}
}
总结
总的来说,flink自己实现了一个rpc框架,客户端动态代理生成调用方,将需要调用的信息(例如方法名,参数值,参数类型)序列化之后通过akka发送给服务方,服务方收到请求的数据,解析后,获取method,反射调用获取结果,返回客户端。
其实也可以考虑用netty来替换akka,或者用一些市场上比较成熟的rpc框架来替换flink的rpc。此外,作为一个源码的阅读者,真的不是特别喜欢代理。
最后,参考flink的命名习惯,有理由相信 gateway(例如TaskExecutorGateway) 结尾的类都是跨服务器通讯的代理类。
