Java 应用线上问题排查思路、常用工具小结
前言
本文总结了一些常见的线上应急现象和对应排查步骤和工具。分享的主要目的是想让对线上问题接触少的同学有个预先认知,免得在遇到实际问题时手忙脚乱。毕竟作者自己也是从手忙脚乱时走过来的。
只不过这里先提示一下。在线上应急过程中要记住,只有一个总体目标:尽快恢复服务,消除影响。 不管处于应急的哪个阶段,我们首先必须想到的是恢复问题,恢复问题不一定能够定位问题,也不一定有完美的解决方案,也许是通过经验判断,也许是预设开关等,但都可能让我们达到快速恢复的目的,然后保留部分现场,再去定位问题、解决问题和复盘。
在大多数情况下,我们都是先优先恢复服务,保留下当时的异常信息(内存dump、线程dump、gc log等等,在紧急情况下甚至可以不用保留,等到事后去复现),等到服务正常,再去复盘问题。
常见现象:CPU 利用率高/飙升
场景预设:
监控系统突然告警,提示服务器负载异常。
预先说明:
CPU飙升只是一种现象,其中具体的问题可能有很多种,这里只是借这个现象切入。
注:CPU使用率是衡量系统繁忙程度的重要指标。但是CPU使用率的安全阈值是相对的,取决于你的系统的IO密集型还是计算密集型。一般计算密集型应用CPU使用率偏高load偏低,IO密集型相反。
常见原因:
频繁 gc
死循环、线程阻塞、io wait…etc
模拟
这里为了演示,用一个最简单的死循环来模拟CPU飙升的场景,下面是模拟代码,
在一个最简单的SpringBoot Web 项目中增加CpuReaper这个类,
/**
* 模拟 cpu 飙升场景
* @author Richard_yyf
*/
@Component
public class CpuReaper {
@PostConstruct
public void cpuReaper() {
int num = 0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000;
while (true) {
num = num + 1;
if (num == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
System.out.println("reset");
num = 0;
}
if ((System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000) - start > 1000) {
return;
}
}
}
}
打包成jar之后,在服务器上运行。java -jar cpu-reaper.jar &
第一步:定位出问题的线程
方法 a: 传统的方法
top定位CPU 最高的进程
执行top命令,查看所有进程占系统CPU的排序,定位是哪个进程搞的鬼。在本例中就是咱们的java进程。PID那一列就是进程号。(对指示符含义不清楚的见【附录】)

2. top -Hp pid定位使用 CPU 最高的线程

printf '0x%x' tid线程 id 转化 16 进制
> printf '0x%x' 12817
> 0x3211
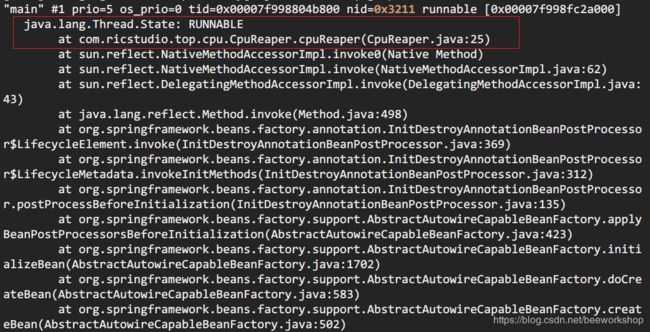
jstack pid | grep tid找到线程堆栈
> jstack 12816 | grep 0x3211 -A 30
小插曲:
非 Java 应用可使用 perf查看:
perf top -p 线程号
可使用yum install perf安装
perf是Linux 2.6+内核中的一个工具,在内核源码包中的位置 tools/perf。
perf利用Linux的trace特性,可以用于实时跟踪,统计event计数(perf stat);或者使用采样(perf record),报告(perf report|script|annotate)的使用方式进行诊断。
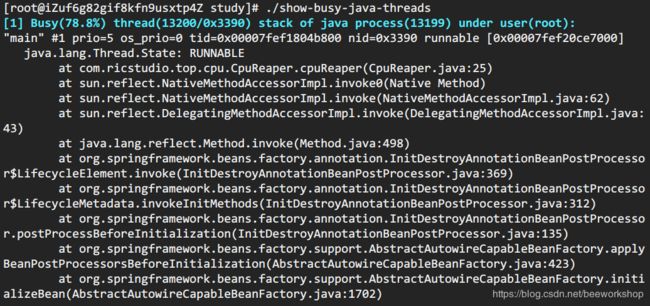
方法 b: show-busy-java-threads
这个脚本来自于github上一个开源项目,项目提供了很多有用的脚本,show-busy-java-threads就是其中的一个。使用这个脚本,可以直接简化方法A中的繁琐步骤。如下:
> wget --no-check-certificate https://raw.github.com/oldratlee/useful-scripts/release-2.x/bin/show-busy-java-threads
> chmod +x show-busy-java-threads
> ./show-busy-java-threads
show-busy-java-threads脚本
#!/bin/bash
# @Function
# Find out the highest cpu consumed threads of java processes, and print the stack of these threads.
#
# @Usage
# $ ./show-busy-java-threads
#
# @online-doc https://github.com/oldratlee/useful-scripts/blob/dev-2.x/docs/java.md#-show-busy-java-threads
# @author Jerry Lee (oldratlee at gmail dot com)
# @author superhj1987 (superhj1987 at 126 dot com)
readonly PROG="`basename $0`"
readonly -a COMMAND_LINE=("$0" "$@")
# Get current user name via whoami command
# See https://www.lifewire.com/current-linux-user-whoami-command-3867579
# Because if run command by `sudo -u`, env var $USER is not rewritten/correct, just inherited from outside!
readonly USER="`whoami`"
################################################################################
# util functions
################################################################################
# NOTE: $'foo' is the escape sequence syntax of bash
readonly ec=$'\033' # escape char
readonly eend=$'\033[0m' # escape end
colorEcho() {
local color=$1
shift
# if stdout is console, turn on color output.
[ -t 1 ] && echo "$ec[1;${color}m$@$eend" || echo "$@"
}
colorPrint() {
local color=$1
shift
colorEcho "$color" "$@"
[ -n "$append_file" -a -w "$append_file" ] && echo "$@" >> "$append_file"
[ -n "$store_dir" -a -w "$store_dir" ] && echo "$@" >> "${store_file_prefix}$PROG"
}
normalPrint() {
echo "$@"
[ -n "$append_file" -a -w "$append_file" ] && echo "$@" >> "$append_file"
[ -n "$store_dir" -a -w "$store_dir" ] && echo "$@" >> "${store_file_prefix}$PROG"
}
redPrint() {
colorPrint 31 "$@"
}
greenPrint() {
colorPrint 32 "$@"
}
yellowPrint() {
colorPrint 33 "$@"
}
bluePrint() {
colorPrint 36 "$@"
}
die() {
redPrint "Error: $@" 1>&2
exit 1
}
logAndRun() {
echo "$@"
echo
"$@"
}
logAndCat() {
echo "$@"
echo
cat
}
usage() {
local -r exit_code="$1"
shift
[ -n "$exit_code" -a "$exit_code" != 0 ] && local -r out=/dev/stderr || local -r out=/dev/stdout
(( $# > 0 )) && { echo "$@"; echo; } > $out
> $out cat <<EOF
Usage: ${PROG} [OPTION]... [delay [count]]
Find out the highest cpu consumed threads of java processes,
and print the stack of these threads.
Example:
${PROG} # show busy java threads info
${PROG} 1 # update every 1 second, (stop by eg: CTRL+C)
${PROG} 3 10 # update every 3 seconds, update 10 times
Output control:
-p, --pid find out the highest cpu consumed threads from
the specified java process.
default from all java process.
-c, --count set the thread count to show, default is 5.
-a, --append-file specifies the file to append output as log.
-S, --store-dir specifies the directory for storing
the intermediate files, and keep files.
default store intermediate files at tmp dir,
and auto remove after run. use this option to keep
files so as to review jstack/top/ps output later.
delay the delay between updates in seconds.
count the number of updates.
delay/count arguments imitates the style of
vmstat command.
jstack control:
-s, --jstack-path specifies the path of jstack command.
-F, --force set jstack to force a thread dump. use when jstack
does not respond (process is hung).
-m, --mix-native-frames set jstack to print both java and native frames
(mixed mode).
-l, --lock-info set jstack with long listing.
prints additional information about locks.
CPU usage calculation control:
-d, --top-delay specifies the delay between top samples.
default is 0.5 (second). get thread cpu percentage
during this delay interval.
more info see top -d option. eg: -d 1 (1 second).
-P, --use-ps use ps command to find busy thread(cpu usage)
instead of top command.
default use top command, because cpu usage of
ps command is expressed as the percentage of
time spent running during the *entire lifetime*
of a process, this is not ideal in general.
Miscellaneous:
-h, --help display this help and exit.
EOF
exit $exit_code
}
################################################################################
# Check os support
################################################################################
uname | grep '^Linux' -q || die "$PROG only support Linux, not support `uname` yet!"
################################################################################
# parse options
################################################################################
# NOTE: ARGS can not be declared as readonly!!
# readonly declaration make exit code of assignment to be always 0, aka. the exit code of `getopt` in subshell is discarded.
# tested on bash 4.2.46
ARGS=`getopt -n "$PROG" -a -o p:c:a:s:S:Pd:Fmlh -l count:,pid:,append-file:,jstack-path:,store-dir:,use-ps,top-delay:,force,mix-native-frames,lock-info,help -- "$@"`
[ $? -ne 0 ] && { echo; usage 1; }
eval set -- "${ARGS}"
while true; do
case "$1" in
-c|--count)
count="$2"
shift 2
;;
-p|--pid)
pid="$2"
shift 2
;;
-a|--append-file)
append_file="$2"
shift 2
;;
-s|--jstack-path)
jstack_path="$2"
shift 2
;;
-S|--store-dir)
store_dir="$2"
shift 2
;;
-P|--use-ps)
use_ps=true
shift
;;
-d|--top-delay)
top_delay="$2"
shift 2
;;
-F|--force)
force=-F
shift
;;
-m|--mix-native-frames)
mix_native_frames=-m
shift
;;
-l|--lock-info)
more_lock_info=-l
shift
;;
-h|--help)
usage
;;
--)
shift
break
;;
esac
done
count=${count:-5}
update_delay=${1:-0}
[ -z "$1" ] && update_count=1 || update_count=${2:-0}
(( update_count < 0 )) && update_count=0
top_delay=${top_delay:-0.5}
use_ps=${use_ps:-false}
# check the directory of append-file(-a) mode, create if not exsit.
if [ -n "$append_file" ]; then
if [ -e "$append_file" ]; then
[ -f "$append_file" ] || die "$append_file(specified by option -a, for storing run output files) exists but is not a file!"
[ -w "$append_file" ] || die "file $append_file(specified by option -a, for storing run output files) exists but is not writable!"
else
append_file_dir="$(dirname "$append_file")"
if [ -e "$append_file_dir" ]; then
[ -d "$append_file_dir" ] || die "directory $append_file_dir(specified by option -a, for storing run output files) exists but is not a directory!"
[ -w "$append_file_dir" ] || die "directory $append_file_dir(specified by option -a, for storing run output files) exists but is not writable!"
else
mkdir -p "$append_file_dir" || die "fail to create directory $append_file_dir(specified by option -a, for storing run output files)!"
fi
fi
fi
# check store directory(-S) mode, create directory if not exsit.
if [ -n "$store_dir" ]; then
if [ -e "$store_dir" ]; then
[ -d "$store_dir" ] || die "$store_dir(specified by option -S, for storing output files) exists but is not a directory!"
[ -w "$store_dir" ] || die "directory $store_dir(specified by option -S, for storing output files) exists but is not writable!"
else
mkdir -p "$store_dir" || die "fail to create directory $store_dir(specified by option -S, for storing output files)!"
fi
fi
################################################################################
# check the existence of jstack command
################################################################################
if [ -n "$jstack_path" ]; then
[ -f "$jstack_path" ] || die "$jstack_path is NOT found!"
[ -x "$jstack_path" ] || die "$jstack_path is NOT executalbe!"
elif which jstack &> /dev/null; then
jstack_path="`which jstack`"
else
[ -n "$JAVA_HOME" ] || die "jstack not found on PATH and No JAVA_HOME setting! Use -s option set jstack path manually."
[ -f "$JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack" ] || die "jstack not found on PATH and \$JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack($JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack) file does NOT exists! Use -s option set jstack path manually."
[ -x "$JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack" ] || die "jstack not found on PATH and \$JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack($JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack) is NOT executalbe! Use -s option set jstack path manually."
jstack_path="$JAVA_HOME/bin/jstack"
fi
################################################################################
# biz logic
################################################################################
readonly run_timestamp="`date "+%Y-%m-%d_%H:%M:%S.%N"`"
readonly uuid="${PROG}_${run_timestamp}_${RANDOM}_$$"
readonly tmp_store_dir="/tmp/${uuid}"
if [ -n "$store_dir" ]; then
readonly store_file_prefix="$store_dir/${run_timestamp}_"
else
readonly store_file_prefix="$tmp_store_dir/${run_timestamp}_"
fi
mkdir -p "$tmp_store_dir"
cleanupWhenExit() {
rm -rf "$tmp_store_dir" &> /dev/null
}
trap "cleanupWhenExit" EXIT
headInfo() {
colorEcho "0;34;42" ================================================================================
echo "$(date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%N") [$(( i + 1 ))/$update_count]: ${COMMAND_LINE[@]}"
colorEcho "0;34;42" ================================================================================
echo
}
if [ -n "${pid}" ]; then
readonly ps_process_select_options="-p $pid"
else
readonly ps_process_select_options="-C java -C jsvc"
fi
# output field: pid, thread id(lwp), pcpu, user
# order by pcpu(percentage of cpu usage)
findBusyJavaThreadsByPs() {
# 1. sort by %cpu by ps option `--sort -pcpu`
# 2. use wide output(unlimited width) by ps option `-ww`
# avoid trunk user column to username_fo+ or $uid alike
local -a ps_cmd_line=(ps $ps_process_select_options -wwLo pid,lwp,pcpu,user --sort -pcpu --no-headers)
local -r ps_out="$("${ps_cmd_line[@]}")"
if [ -n "$store_dir" ]; then
echo "$ps_out" | logAndCat "${ps_cmd_line[@]}" > "${store_file_prefix}$(( i + 1 ))_ps"
fi
echo "$ps_out" | head -n "${count}"
}
# top with output field: thread id, %cpu
__top_threadId_cpu() {
# 1. sort by %cpu by top option `-o %CPU`
# unfortunately, top version 3.2 does not support -o option(supports from top version 3.3+),
# use
# HOME="$tmp_store_dir" top -H -b -n 1
# combined
# sort
# instead of
# HOME="$tmp_store_dir" top -H -b -n 1 -o '%CPU'
# 2. change HOME env var when run top,
# so as to prevent top command output format being change by .toprc user config file unexpectedly
# 3. use option `-d 0.5`(update interval 0.5 second) and `-n 2`(update 2 times),
# and use second time update data to get cpu percentage of thread in 0.5 second interval
# 4. top v3.3, there is 1 black line between 2 update;
# but top v3.2, there is 2 blank lines between 2 update!
local -a top_cmd_line=(top -H -b -d $top_delay -n 2)
local -r top_out=$(HOME="$tmp_store_dir" "${top_cmd_line[@]}")
if [ -n "$store_dir" ]; then
echo "$top_out" | logAndCat "${top_cmd_line[@]}" > "${store_file_prefix}$(( i + 1 ))_top"
fi
echo "$top_out" |
awk 'BEGIN { blockIndex = 0; currentLineHasText = 0; prevLineHasText = 0; } {
currentLineHasText = ($0 != "")
if (prevLineHasText && !currentLineHasText)
blockIndex++ # from text line to empty line, increase block index
if (blockIndex == 3 && ($NF == "java" || $NF == "jsvc")) # $NF(last field) is command field
# only print 4th text block(blockIndex == 3), aka. process info of second top update
print $1 " " $9 # $1 is thread id field, $9 is %cpu field
prevLineHasText = currentLineHasText # update prevLineHasText
}' | sort -k2,2nr
}
__complete_pid_user_by_ps() {
# ps output field: pid, thread id(lwp), user
local -a ps_cmd_line=(ps $ps_process_select_options -wwLo pid,lwp,user --no-headers)
local -r ps_out="$("${ps_cmd_line[@]}")"
if [ -n "$store_dir" ]; then
echo "$ps_out" | logAndCat "${ps_cmd_line[@]}" > "${store_file_prefix}$(( i + 1 ))_ps"
fi
local idx=0
local -a line
while IFS=" " read -a line ; do
(( idx < count )) || break
local threadId="${line[0]}"
local pcpu="${line[1]}"
# output field: pid, threadId, pcpu, user
local output_fields="$( echo "$ps_out" |
awk -v "threadId=$threadId" -v "pcpu=$pcpu" '$2==threadId {
printf "%s %s %s %s\n", $1, threadId, pcpu, $3; exit
}' )"
if [ -n "$output_fields" ]; then
(( idx++ ))
echo "$output_fields"
fi
done
}
# output format is same as function findBusyJavaThreadsByPs
findBusyJavaThreadsByTop() {
__top_threadId_cpu | __complete_pid_user_by_ps
}
printStackOfThreads() {
local -a line
local idx=0
while IFS=" " read -a line ; do
local pid="${line[0]}"
local threadId="${line[1]}"
local threadId0x="0x`printf %x ${threadId}`"
local pcpu="${line[2]}"
local user="${line[3]}"
(( idx++ ))
local jstackFile="${store_file_prefix}$(( i + 1 ))_jstack_${pid}"
[ -f "${jstackFile}" ] || {
local -a jstack_cmd_line=( "$jstack_path" ${force} $mix_native_frames $more_lock_info ${pid} )
if [ "${user}" == "${USER}" ]; then
# run without sudo, when java process user is current user
logAndRun "${jstack_cmd_line[@]}" > ${jstackFile}
elif [ $UID == 0 ]; then
# if java process user is not current user, must run jstack with sudo
logAndRun sudo -u "${user}" "${jstack_cmd_line[@]}" > ${jstackFile}
else
# current user is not root user, so can not run with sudo; print error message and rerun suggestion
redPrint "[$idx] Fail to jstack busy(${pcpu}%) thread(${threadId}/${threadId0x}) stack of java process(${pid}) under user(${user})."
redPrint "User of java process($user) is not current user($USER), need sudo to rerun:"
yellowPrint " sudo ${COMMAND_LINE[@]}"
normalPrint
continue
fi || {
redPrint "[$idx] Fail to jstack busy(${pcpu}%) thread(${threadId}/${threadId0x}) stack of java process(${pid}) under user(${user})."
normalPrint
rm "${jstackFile}" &> /dev/null
continue
}
}
bluePrint "[$idx] Busy(${pcpu}%) thread(${threadId}/${threadId0x}) stack of java process(${pid}) under user(${user}):"
if [ -n "$mix_native_frames" ]; then
local sed_script="/--------------- $threadId ---------------/,/^---------------/ {
/--------------- $threadId ---------------/b # skip first separator line
/^---------------/d # delete second separator line
p
}"
elif [ -n "$force" ]; then
local sed_script="/^Thread ${threadId}:/,/^$/ {
/^$/d; p # delete end separator line
}"
else
local sed_script="/ nid=${threadId0x} /,/^$/ {
/^$/d; p # delete end separator line
}"
fi
{
sed "$sed_script" -n ${jstackFile}
echo
} | tee ${append_file:+-a "$append_file"} ${store_dir:+-a "${store_file_prefix}$PROG"}
done
}
################################################################################
# Main
################################################################################
main() {
local i
# if update_count <= 0, infinite loop till user interrupted (eg: CTRL+C)
for (( i = 0; update_count <= 0 || i < update_count; ++i )); do
(( i > 0 )) && sleep "$update_delay"
[ -n "$append_file" -o -n "$store_dir" ] && headInfo | tee ${append_file:+-a "$append_file"} ${store_dir:+-a "${store_file_prefix}$PROG"} > /dev/null
(( update_count != 1 )) && headInfo
if $use_ps; then
findBusyJavaThreadsByPs
else
findBusyJavaThreadsByTop
fi | printStackOfThreads
done
}
main
show-busy-java-threads
# 从所有运行的Java进程中找出最消耗CPU的线程(缺省5个),打印出其线程栈
# 缺省会自动从所有的Java进程中找出最消耗CPU的线程,这样用更方便
# 当然你可以手动指定要分析的Java进程Id,以保证只会显示你关心的那个Java进程的信息
show-busy-java-threads -p <指定的Java进程Id>
show-busy-java-threads -c <要显示的线程栈数>
方法 c: arthas thread
阿里开源的arthas现在已经几乎包揽了我们线上排查问题的工作,提供了一个很完整的工具集。在这个场景中,也只需要一个thread -n命令即可。
curl -O https://arthas.gitee.io/arthas-boot.jar # 下载

要注意的是,arthas的cpu占比,和前面两种cpu占比统计方式不同。前面两种针对的是Java进程启动开始到现在的cpu占比情况,arthas这种是一段采样间隔内,当前JVM里各个线程所占用的cpu时间占总cpu时间的百分比。
具体见官网:https://alibaba.github.io/arthas/thread.html
后续
通过第一步,找出有问题的代码之后,观察到线程栈之后。我们就要根据具体问题来具体分析。这里举几个例子。
情况一:发现使用CPU最高的都是GC 线程。
GC task thread#0 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x00007fd99001f800 nid=0x779 runnable
GC task thread#1 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x00007fd990021800 nid=0x77a runnable
GC task thread#2 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x00007fd990023000 nid=0x77b runnable
GC task thread#3 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x00007fd990025000 nid=0x77c runnabl
gc 排查的内容较多,所以我决定在后面单独列一节讲述。
情况二:发现使用CPU最高的是业务线程
- io wait
比如此例中,就是因为磁盘空间不够导致的io阻塞 - 等待内核态锁,如 synchronized
- jstack -l pid | grep BLOCKED 查看阻塞态线程堆栈
- dump 线程栈,分析线程持锁情况。
- arthas提供了thread -b,可以找出当前阻塞其他线程的线程。针对 synchronized 情况
常见现象:频繁 GC
- 方法a : 查看gc 日志
- 方法b : jstat -gcutil 进程号 统计间隔毫秒 统计次数(缺省代表一致统计
- 方法c : 如果所在公司有对应用进行监控的组件当然更方便(比如Prometheus + Grafana)
这里对开启 gc log 进行补充说明。一个常常被讨论的问题(惯性思维)是在生产环境中GC日志是否应该开启。因为它所产生的开销通常都非常有限,因此我的答案是需要开启。但并不一定在启动JVM时就必须指定GC日志参数。
HotSpot JVM有一类特别的参数叫做可管理的参数。对于这些参数,可以在运行时修改他们的值。我们这里所讨论的所有参数以及以“PrintGC”开头的参数都是可管理的参数。这样在任何时候我们都可以开启或是关闭GC日志。比如我们可以使用JDK自带的jinfo工具来设置这些参数,或者是通过JMX客户端调用HotSpotDiagnostic MXBean的setVMOption方法来设置这些参数。
这里再次大赞arthas❤️,它提供的vmoption命令可以直接查看,更新VM诊断相关的参数。
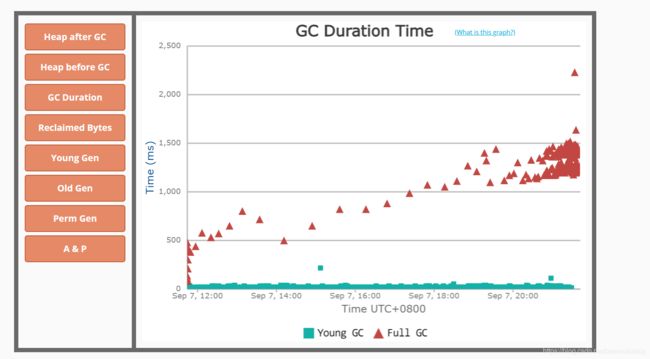
获取到gc日志之后,可以上传到GC easy帮助分析,得到可视化的图表分析结果。
从S区晋升的对象在老年代也放不下导致 FullGC(fgc 回收无效则抛 OOM)。
可能原因:
-
survivor 区太小,对象过早进入老年代
-
查看 SurvivorRatio 参数
-
大对象分配,没有足够的内存
dump 堆,profiler/MAT 分析对象占用情况
old 区存在大量对象
dump 堆,profiler/MAT 分析对象占用情况
你也可以从full GC 的效果来推断问题,正常情况下,一次full GC应该会回收大量内存,所以 正常的堆内存曲线应该是呈锯齿形。如果你发现full gc 之后堆内存几乎没有下降,那么可以推断: 堆中有大量不能回收的对象且在不停膨胀,使堆的使用占比超过full GC的触发阈值,但又回收不掉,导致full GC一直执行。换句话来说,可能是内存泄露了。
一般来说,GC相关的异常推断都需要涉及到内存分析,使用jmap之类的工具dump出内存快照(或者 Arthas的heapdump)命令,然后使用MAT、JProfiler、JVisualVM等可视化内存分析工具。
至于内存分析之后的步骤,就需要小伙伴们根据具体问题具体分析啦。
常见现象:线程池异常
场景预设:
业务监控突然告警,或者外部反馈提示大量请求执行失败。
异常说明:
Java 线程池以有界队列的线程池为例,当新任务提交时,如果运行的线程少于 corePoolSize,则创建新线程来处理请求。如果正在运行的线程数等于 corePoolSize 时,则新任务被添加到队列中,直到队列满。当队列满了后,会继续开辟新线程来处理任务,但不超过 maximumPoolSize。当任务队列满了并且已开辟了最大线程数,此时又来了新任务,ThreadPoolExecutor 会拒绝服务。
常见问题和原因
这种线程池异常,一般可以通过开发查看日志查出原因,有以下几种原因:
- 下游服务 响应时间(RT)过长
这种情况有可能是因为下游服务异常导致的,作为消费者我们要设置合适的超时时间和熔断降级机制。
另外针对这种情况,一般都要有对应的监控机制:比如日志监控、metrics监控告警等,不要等到目标用户感觉到异常,从外部反映进来问题才去看日志查。
- 数据库慢 sql 或者数据库死锁
查看日志中相关的关键词。
- Java 代码死锁
jstack –l pid | grep -i –E ‘BLOCKED | deadlock’
四、常见问题恢复
这一部分内容参考自此篇文章
五、Arthas
这里还是想单独用一节安利一下Arthas这个工具。
Arthas 是阿里巴巴开源的Java 诊断工具,基于 Java Agent 方式,使用 Instrumentation 方式修改字节码方式进行 Java 应用诊断。
-
dashboard :系统实时数据面板, 可查看线程,内存,gc 等信息
-
thread :查看当前线程信息,查看线程的堆栈,如查看最繁忙的前 n 线程
-
getstatic:获取静态属性值,如 getstatic className attrName 可用于查看线上开关真实值
-
sc:查看 jvm 已加载类信息,可用于排查 jar 包冲突
-
sm:查看 jvm 已加载类的方法信息
-
jad:反编译 jvm 加载类信息,排查代码逻辑没执行原因
-
logger:查看logger信息,更新logger level
-
watch:观测方法执行数据,包含出参、入参、异常等
-
trace:方法内部调用时长,并输出每个节点的耗时,用于性能分析
-
tt:用于记录方法,并做回放
以上内容节选自Arthas官方文档。
另外,Arthas里的 还集成了 ognl 这个轻量级的表达式引擎,通过ognl,你可以用arthas 实现很多的“骚”操作。
其他的这里就不多说了,感兴趣的可以去看看arthas的官方文档、github issue。
六、涉及工具
再说下一些工具。
- Arthas(超级推荐❤️❤️)
- useful-scripts
- GC easy
- Smart Java thread dump analyzer - thread dump analysis in seconds
- PerfMa - Java虚拟机参数/线程dump/内存dump分析
- Linux 命令
- Java N 板斧
- MAT、JProfiler…等可视化内存分析工具
结语
我知道我这篇文章对于线上异常的归纳并不全面,还有网络(超时、TCP队列溢出…)、堆外内存等很多的异常场景没有涉及。主要是因为自己接触很少,没有深刻体会研究过,强行写出来免不得会差点意思,更怕的是误了别人。
还有想说的就是,Java 应用线上排查实际非常考究一个人基础是否扎实、解决问题能力是否过关。比如线程池运行机制、gc分析、Java 内存分析等等,如果基础不扎实,看了更多的是一头雾水。另外就是,多看看网上一些有实际场景的关于异常排查的经验文章,学习他们解决排查问题的思路和工具。这样即使自己暂时遇不到,但是会在脑海里面慢慢总结出一套解决类似问题的结构框架,到时候真的遇到了,也就是触类旁通的事情罢了。
参考
- https://developer.aliyun.com/article/757655
- Arthas 3.2.0 文档
- 《分布式服务架构:原理、设计与实战》
附录
top 命令显示的指示符的含义
| 指示符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| PID | 进程id |
| USER | 进程所有者 |
| PR | 进程优先级 |
| NI | nice值。负值表示高优先级,正值表示低优先级 |
| VIRT | 进程使用的虚拟内存总量,单位kb。VIRT=SWAP+RES |
| RES | 进程使用的、未被换出的物理内存大小,单位kb。RES=CODE+DATA |
| SHR | 共享内存大小,单位kb |
| S 进程状态。 | D=不可中断的睡眠状态 R=运行 S=睡眠 T=跟踪/停止 Z=僵尸进程 |
| %CPU | 上次更新到现在的CPU时间占用百分比 |
| %MEM | 进程使用的物理内存百分比 |
| TIME+ | 进程使用的CPU时间总计,单位1/100秒 |
| COMMAND | 进程名称(命令名/命令行) |