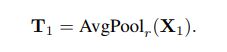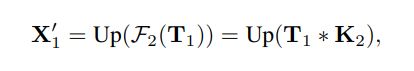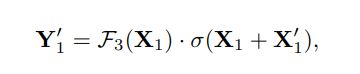Improving Convolutional Networks with Self-Calibrated Convolutions
论文链接:http://mftp.mmcheng.net/Papers/20cvprSCNet.pdf CVPR2020的一篇文章
代码:https://github.com/backseason/SCNet
主要思想:SCnet,提出了一个self-calibrated convolutions,其实感觉就是在channel上做attention,按照文中的说法Benefiting from such heterogeneous convolutions and between-filter communication, the receptive field for each spatial location can be effectively enlarged.实验证明该模块在分类,检测,分割任务上都有提升。
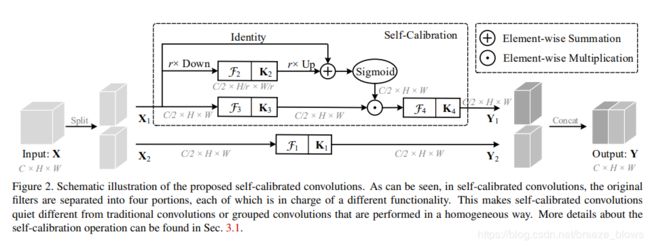
整个框架图如上图所示,输入X先通过两个conv分成两个feature X1,X2。剩下的过程可以公式化为:
这里的UP是双线性插值,下采样比例r默认为4
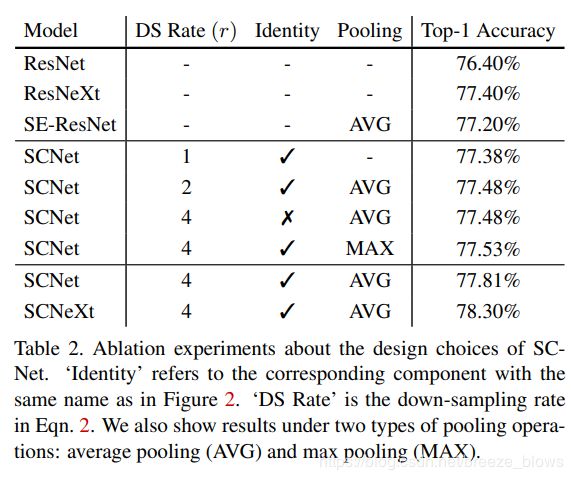
文中对self-calibration是否进行上采样,如何上采样(最大池化层还是平均池化层), 以及是否保留那个identify做了消融实验,从实验可以看出identify是有用的,Average Pooling 要优于 Max Pooling,按照文中的解释We argue that this may be due to the fact that, unlike max pooling, average pooling builds connections among locations within the whole pooling window, which can better capture local contextual information.另外r等4的效果最好
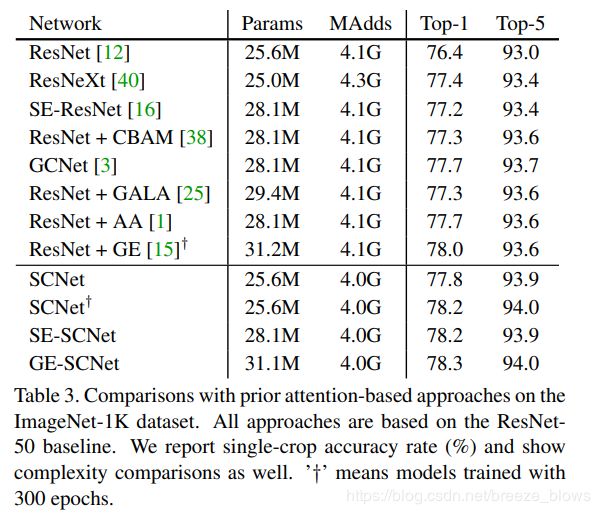
和其他attention对比
和检测作对比
文中还对instance seg和key point做了对比,就不展示了
SCNet50结构:https://gist.github.com/breezelj/7775cbf33bfdc81e9f877407fde5c207,较于resnet50:
- figure2中input X经过两个conv即conv_a conv_b分成X1,X2,而不是单纯的split,这一步可类比于resnet中的每个layer中的Bottleneck的conv1,scconv操作相当于resnet中的每个layer中的Bottleneck的conv2
- k2的下采样是用AvgPool2d(kernel_size=4, stride=4, padding=0)完成的,上采样是用F.interpolate
- 每个layer的downsample是通过k1,k4的Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)完成的,shortcut中的downsample通过Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)完成
代码(来自:https://github.com/backseason/SCNet):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
__all__ = ['SCNet', 'scnet50', 'scnet101']
model_urls = {
'scnet50': 'https://backseason.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/scnet/scnet50-dc6a7e87.pth',
'scnet101': 'https://backseason.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/scnet/scnet101-44c5b751.pth',
}
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, groups=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, groups=groups, bias=False)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class SCConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, planes, stride, pooling_r):
super(SCConv, self).__init__()
self.k2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=pooling_r, stride=pooling_r),
conv3x3(planes, planes),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),
)
self.k3 = nn.Sequential(
conv3x3(planes, planes),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),
)
self.k4 = nn.Sequential(
conv3x3(planes, planes, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = torch.sigmoid(
torch.add(identity, F.interpolate(self.k2(x), identity.size()[2:]))) # sigmoid(identity + k2)
out = torch.mul(self.k3(x), out) # k3 * sigmoid(identity + k2)
out = self.k4(out) # k4
return out
class SCBottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
pooling_r = 4 # down-sampling rate of the avg pooling layer in the K3 path of SC-Conv.
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(SCBottleneck, self).__init__()
planes = int(planes / 2)
self.conv1_a = conv1x1(inplanes, planes)
self.bn1_a = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.k1 = nn.Sequential(
conv3x3(planes, planes, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.conv1_b = conv1x1(inplanes, planes)
self.bn1_b = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.scconv = SCConv(planes, stride, self.pooling_r)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(planes * 2, planes * 2 * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 2 * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out_a = self.conv1_a(x)
out_a = self.bn1_a(out_a)
out_a = self.relu(out_a)
out_a = self.k1(out_a)
out_b = self.conv1_b(x)
out_b = self.bn1_b(out_b)
out_b = self.relu(out_b)
out_b = self.scconv(out_b)
out = self.conv3(torch.cat([out_a, out_b], dim=1))
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class SCNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000):
super(SCNet, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def scnet50(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a SCNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = SCNet(SCBottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['scnet50']))
return model
def scnet101(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a SCNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = SCNet(SCBottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['scnet101']))
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
images = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
model = scnet50(pretrained=False)
# model = model.cuda(0)
out = model(images)
print(model(images).size())