Java中的IO流(中)——字符输入输出流
字节流操作中文不是很方便,故java提供了转换流。
即:字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表。
一、编码规则
1、常见的编码表
ASCII:美国国家信息标准码
ISO-8859-1:拉丁码(识别不了中文)
GBK/GB2312/GB18030:简体中文
BIG5:繁体中文
Unicode:支持世界上所有语言的编码(UTF-8 UTF-16 UTF-32)
2、乱码
乱码是由于编码与解码时使用的编码表不一样。
3、将String编码为字节序列
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1、使用默认的编码表(GBK)进行编码
String str = "好晴朗";
byte[] bs = str.getBytes();
//2、使用指定的编码表(utf-8)进行编码
byte[] bs1 = str.getBytes("utf-8");
System.out.println("GBK:"+Arrays.toString(bs));
//[-70, -61, -57, -25, -64, -54]
System.out.println("utf-8"+Arrays.toString(bs1));
//[-27, -91, -67, -26, -103, -76, -26, -100, -105]
}
}
4、解码
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用默认的编码表(GBK)进行编码
String str = "好晴朗";
byte[] bs = str.getBytes();
//进行解码
//1、使用默认的编码表(GBK)进行解码
String str1 = new String(bs);
//2、使用指定的编码表(UTF-8)进行解码
String str2 = new String(bs,"utf-8");
System.out.println("GBK:"+str1);
//GBK:好晴朗
System.out.println("utf-8:"+str2);
//utf-8:??????
//解码与编码所使用的编码表不一致时,会出现乱码
}
}
5、小思考
不同编码,英文部分、中文部分以及符号部分有相同之处吗?不同之处有何规律?
二、字符输入输出流
1、InputStreamReader
可以直接创建对象,要包装InputStream输入字节流对象。
第二个参数可以是字符集的名字, 如"utf-8"or"GBK"等。
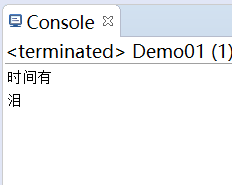
文件内容:时间有泪
(1)每次读取一个字符
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr =
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
int b = -1;
while((b = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println((char)b);
}
isr.close();//关流
}
}
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr =
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
//2、每次读取一个字符数组
int length = -1;
char[] chs = new char[3];
while((length = isr.read(chs)) != -1) {
String str = new String(chs,0,length);
System.out.println(str);
}
isr.close();
}
}
2、OutputStreamWriter
可以直接创建对象,要包装OutputStream输入字节流对象。
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStreamWriter osw =
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("test.txt"));
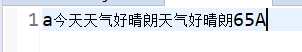
osw.write('a');
osw.write("今天天气好晴朗");
osw.write("今天天气好晴朗",2,5);
osw.write("65");
osw.write(65);
System.out.println("写入成功");
osw.close();
}
}
3、综合:复制粘贴小说
package day2020061401;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class Homework_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr =
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("src/day2020061401/xiaoshuo.txt"));
OutputStreamWriter osw =
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("src/day2020061401/xiaoshuo2.txt"));
long time1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
//以字节数组去读取
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int length = -1;
while((length = isr.read(chs)) != -1) {
osw.write(chs,0,length);
}
long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((time2-time1));
//关流
osw.close();
isr.close();
}
}
4、FileReader与FileWriter
FileReader是InputStreamReader的子类。
FileWriter是OutputStreamReader的子类。
说明:
它们虽然不能去设置编码方式,但是可以直接操作文件,故而不需要去套用直接输入输出流。
代码演示:
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("test.txt");
//写入
fw.write(65);
fw.write("时间有泪");
fw.close();
System.out.println("写入成功");
/*
* 文件中的内容结果为:A时间有泪
*/
//读取
FileReader fr = new FileReader("test.txt");
int b = -1;
while((b = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char)b);
}
System.out.println("读取成功");
fr.close();
}
}
三、字符缓冲输入输出流
1、BufferedReader
字符缓冲输入流。
构造方法:
字符缓冲输入流–>字符输入流对象–>字节输入流对象
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("test.txt")));
//读取内容
String str = null;
while((str = br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
2、BufferedWriter
字符缓冲输出流。
构造方法:
字符缓冲输出流–>字符输出流对象–>字节输出流对象
换行:
流.newLine();
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("test.txt")));
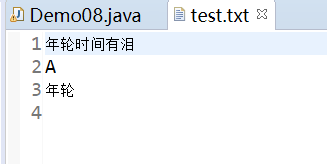
char[] chs = "年轮".toCharArray();
bw.write(chs);
bw.newLine();
bw.write(65);
bw.newLine();
bw.write("年轮");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();//强制刷新
System.out.println("写入成功");
bw.close();
}
}
3、PrintWriter
PrintWriter:自动刷新功能,即在释放资源之前就写入数据。
构造方法有多种:

public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("test.txt"));
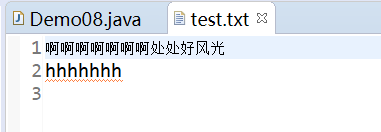
pw.print("啊啊啊啊啊啊啊");
pw.println("处处好风光");
pw.println("hhhhhhh");
pw.close();
}
}
4、综合:赋值粘贴小说
package day20200617;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Homework_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("src/day20200617/xiaoshuo.txt")));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(
new FileOutputStream("src/day20200617/xiaoshuo1.txt"));
String str = null;
while((str = br.readLine())!=null) {
pw.println(str);//注意此处
}
//关流
pw.close();
br.close();
System.out.println("复制成功");
}
}