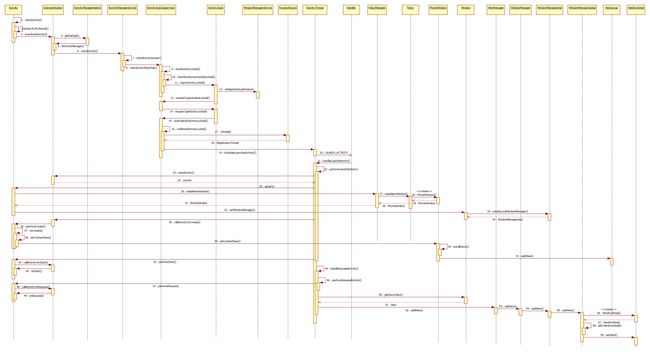
Activity启动过程中做了哪些事情?下面的时序图展示里启动过程中函数的调用过程, 从图中可以知道大概流程。
在介绍细节的时候是从上往下函数调用过程介绍的,如果不知道某个函数是在哪里被谁调用的,可以回过头来看下时序图。下面是对一些细节进行介绍。
1. 在Android中有两种操作会引发Activity的启动,一种用户点击Launcher的应用程序图标时,Launcher会为启动应用程序的主Activity。另外一种是在已经起来的Activity内部通过调用startActvity接口启动新的Activity。每一个Activity都可以在内部启动新的Activity。图中就是从一个Activity调用startActivity启动另外一个Activity开始。
startActivity()@Activity.java
public void startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}
startActivity()中调用携带requestCode参数的startActivityForResult()启动新的activity。
startActivityForResult()@Activity.java
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
//一般的Activity的mParent为null
if (mParent == null) {
//调用Instrumentation.execStartActivity()启动新的Activity。mMainThread类型为ActivityThread, 在attach()函数被回调时被赋值。
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar = mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this, intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) { // 如果activity之前已经启动,而且处于阻塞状态,execStartActivity函数直接返回要启动的activity的result或者null。(注意:这就是Activity.onActivityResult()会在启动另外一个activity启动时被回调的原因。
// 若result非空,发送结果给本activity,即onActivityResult会被调用。
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(mToken, mEmbeddedID, requestCode, ar.getResultCode(),
ar.getResultData());
}
if (requestCode >= 0) {
// 如果这次启动需要被启动的activity返回一个结果,则在收到返回结果前,本activity保持不可见。
mStartedActivity = true;
}
final View decor = mWindow != null ? mWindow.peekDecorView() : null;
if (decor != null) {
decor.cancelPendingInputEvents();
}
// TODO Consider clearing/flushing other event sources and events for child windows.
} else {
//在ActivityGroup内部的Activity调用startActivity的时候会走到这里,内部处理逻辑和上面是类似的
if (options != null) {
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode, options);
} else {
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode);
}
}
}
Instrumentation类的功能是辅助Activity的监控和测试,接着看execStartActivity()函数的实现。
execStartActivity()@Instrumentation.java
1 public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
2 Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
3 Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
4 //将contextThread转成ApplicationThread.
5 IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
6 if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
7 synchronized (mSync) {
8 //检查是否存在这个activity
9 final int N = mActivityMonitors.size();
10 for (int i=0; i= 0 ? am.getResult() : null;
16 }
17 break;
18 }
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 try {
23 intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData(); //转移数据
24 intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(); //准备让intent离开一个app进程
25 //通过AcitivityManagerNative与ActivityManagerService关联起来,两个类的关系如下图,由ActivityManagerService去执行实际动作。
26 int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
27 .startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
28 intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
29 token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
30 requestCode, 0, null, null, options);
31 //检查启动结果,如果无法打开activity,则抛出诸如ActivityNotFoundException类似的各种异常
32 checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
33 } catch (RemoteException e) {
34 }
35 return null;
36 }
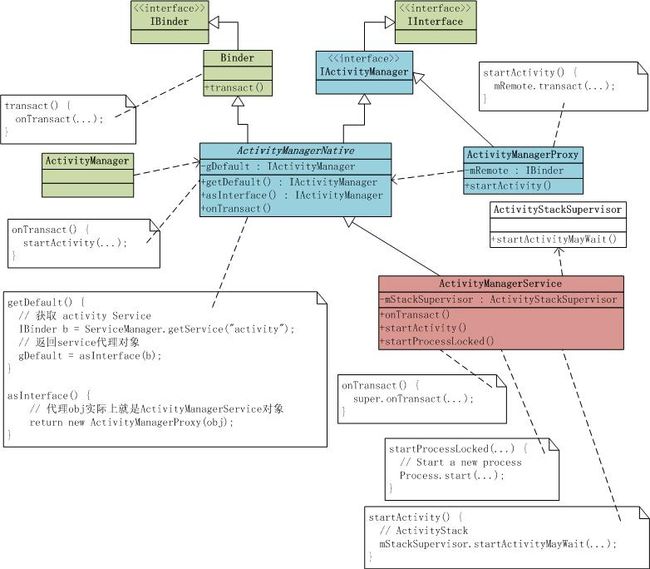
2. ActivityManager的功能是与系统中所有运行着的Activity交互提供了接口,主要的接口围绕着运行中的进程信息,任务信息,服务信息等,它的大多数功能都是调用了ActivityManagerNative类接口来完成的。
ActivityManager相关静态类图如下图,可以看出这是典型的Proxy模式:
结合面的类结构图,其中ActivityManager是一个客户端,为了减少它与ActivityManagerService的耦合度,在这中间使用了ActivityManagerNative类,该类内部使用ActivityManagerProxy代理类,所有对 ActivityManagerService的访问都转换成对代理类的访问,这样ActivityManager就与ActivityManagerService解耦了。
为了让代理类与被代理类保持一致的接口,由IActivityManager作为ActivityManagerProxy和ActivityManagerNative的公共接口,ActivityManagerService继承于ActivityManagerNative,也具有相同的接口。
图中绿色的部分是在SDK中开放给应用程序开发人员的接口,蓝色的部分是Proxy模式的实现,红色的部分是底层的服务实现,是真正的动作执行者。
3. startActivity()@ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
String profileFile, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, Bundle options) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profileFile, profileFd, options, UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
@Override
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo,
String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
String profileFile, ParcelFileDescriptor profileFd, Bundle options, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId,
false, true, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType,
resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profileFile, profileFd,
null, null, options, userId);
}
类ActivityStackSupervisor是用来辅助ActivityManagerService对Activity和Task的管理的。其中用ActivityStackSupervisor类型来进行对Task的操作,用ActivityStack对Acitivity进行操作。
4. 调用mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait()函数后,会执行下面几个函数,调用关系参照时序图,函数里涉及很多细节,这里只简单描述下它们的主要功能:
调用9. ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityLocked(): 检查启动权限,创建新的ActivityRecord。
调用10. ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityUncheckedLocked():处理intent携带的launch flags, launchMode。(后面再研究launch相关的flag和mode)
调用11. ActivityStack.startActivityLocked():将activity放到所属task的顶部,重置Task(resetTaskIfNeededLocked),调用WindowManager.setAppStartingWindow()。
调用13. ActivityStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked():判断ActivityStack数组中是否存在target ActivityStack。
调用14. ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(): 从当前activity切换到要启动的activity。
调用15. ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked():获取ProcessRecord(若要启动的activity的应用已经在运行),若获取ProcessRecord存在则调用realStartActivityLocked(),否则调用 ActivityManagerServices.startProcessLocked()创建新的ProcessRecord,最后调用Process.start()启动新的进程(最终调用Zygote启动新的进程,为了避免混淆,这部分在时序图中没有体现,后面再研究)。
调用16. ActivityStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked(): 调用mWindowManager.setAppVisibility()设置app可见。
调用19. ActivityThread.scheduleLauncherActivity(): 发送Message LAUNCH_ACTIVITY给Handler.
5. Handler接收到message后,执行ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity()。
handleLaunchActivity()@ActivityThread.java
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
......
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent); // 返回一个activity.
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward, !r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed);
if (!r.activity.mFinished && r.startsNotResumed) {
// 当这个activity没有finished而且没有处于resumed状态时,Acivity Manager实际上想要这个activity以paused状态开始,因为它需要可见,但是又不在前台。
// 为此,需要经过正常启动(因为activity希望在它们的window被显示前,它们第一次运行时通过onResume),然后暂停它。The activity manager actually wants this one to start out
//然而,在这种情况下,不需要走完整的暂停周期(比如freezing等),因为activity假定它可以刚好保留它当前的所有状态。
try {
r.activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity);
......
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
......
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
r.paused = true;
}
} else {
......
}
}
6.进一步看performLaunchActivity(),这个函数做了几件重要的事情:创建activity实例,调用Activity.attach()设置参数,触发Activity.onCreate()。
performLaunchActivity()@ActivityThread.java
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) { // 填充package info
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component); //设置Component
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent); // 根据Activity的类名,通过Java反射机制创建对应的Activity.
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
try {
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (activity != null) {
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity); // Activity中getContext()函数返回的就是这个对象。
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
......
// 将Context,ActivityThread,Instrumentation,Application等设置给新建的Activity,供activity使用。
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme); // 设置theme
}
activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state); // 这个函数会使Activity的onCreate()函数被调用
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart(); // 这个函数会使Activity的onStart()函数被调用
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
......
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
return activity;
}
7.下面分析下Activity.attach()函数,它创建window对象,设置window manager。
attach()@Activity.java
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config) {
attachBaseContext(context); // 把context赋值给父类的mBase成员
mFragments.attachActivity(this, mContainer, null);
mWindow = PolicyManager.makeNewWindow(this); // 调用PolicyManager的函数创建Window对象。
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
if (info.softInputMode != WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED) {
mWindow.setSoftInputMode(info.softInputMode); //设置输入法mode
}
if (info.uiOptions != 0) {
mWindow.setUiOptions(info.uiOptions);
}
mUiThread = Thread.currentThread();
// 赋值给Acitivity的各个成员
mMainThread = aThread; //mMainThread实际上为ActivityThread。
mInstrumentation = instr;
mToken = token;
mIdent = ident;
mApplication = application;
mIntent = intent;
mComponent = intent.getComponent();
mActivityInfo = info;
mTitle = title;
mParent = parent;
mEmbeddedID = id;
mLastNonConfigurationInstances = lastNonConfigurationInstances;
// 创建WindowManager对象并设置给window,供window使用.
mWindow.setWindowManager((WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager(); // 保存WindowManager对象.
mCurrentConfig = config;
}
8. 其中一个关键的函数PolicyManager.makeNewWindow()返回的Window对象,实际上是一个PhoneWindow对象。
具体创建过程参考下面代码:
class [email protected]
public final class PolicyManager {
private static final String POLICY_IMPL_CLASS_NAME =
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.Policy";
private static final IPolicy sPolicy; // sPolicy为单例的IPolicy对象。
static {
// Pull in the actual implementation of the policy at run-time
try {
Class policyClass = Class.forName(POLICY_IMPL_CLASS_NAME);
sPolicy = (IPolicy)policyClass.newInstance(); // 创建Policy对象。
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
......
}
}
// Cannot instantiate this class
private PolicyManager() {}
// The static methods to spawn new policy-specific objects
public static Window makeNewWindow(Context context) {
return sPolicy.makeNewWindow(context); //通过Policy对象的makeNewWindow创建一个Window。
}
......
}
class [email protected]
public class Policy implements IPolicy {
private static final String TAG = "PhonePolicy";
private static final String[] preload_classes = {
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.PhoneLayoutInflater",
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.PhoneWindow",
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.PhoneWindow$1",
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.PhoneWindow$DialogMenuCallback",
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.PhoneWindow$DecorView",
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.PhoneWindow$PanelFeatureState",
"com.android.internal.policy.impl.PhoneWindow$PanelFeatureState$SavedState",
};
static {
// For performance reasons, preload some policy specific classes when
// the policy gets loaded.
for (String s : preload_classes) { // 加载所有的类
try {
Class.forName(s);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
......
}
}
}
public Window makeNewWindow(Context context) {
return new PhoneWindow(context); // 实际返回的PhoneWindow对象。
}
......
}
9. setWindowManager()@Window.java
public void setWindowManager(WindowManager wm, IBinder appToken, String appName,
boolean hardwareAccelerated) {
mAppToken = appToken;
mAppName = appName;
mHardwareAccelerated = hardwareAccelerated || SystemProperties.getBoolean(PROPERTY_HARDWARE_UI, false);
if (wm == null) {
wm = (WindowManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
mWindowManager = ((WindowManagerImpl)wm).createLocalWindowManager(this); // 创建一个WindowManagerImpl对象
}
到这里可以看到,Activity成员变量mWindow实际上是PhoneWindow类型, 变量mWindowManager实际上是WindowManagerImpl。这
10. Acitivity.attach()函数被调用之后,performLaunchActivity还会触发Activity.onCreate()函数被调用,在这个函数中会调用setContentView()函数设置Activity的UI内容。
setContentView()有三种实现,它们的功能基本一致,都是将view添加到mContentParent中:
setContentView()@Activity.java
// 通过一个布局资源设置activity的内容。
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initActionBar();
}
// 直接将View作为内容直接设置到activity的视图层次中。这种方式设置给view的layoutparams将不起作用,默认为MATCH_PARENT.
public void setContentView(View view) {
getWindow().setContentView(view);
initActionBar();
}
// 设置activity的内容为view, 并设置view的LayoutParams.
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
getWindow().setContentView(view, params);
initActionBar();
}
下面给出其中一种实现:
setContentView()@PhoneWindow.java
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor(); // 初始化DecorView和mContentParent.
} else {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
mContentParent.addView(view, params);
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
}
installDecor()@PhoneWindow.java
private void installDecor() {
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor();
......
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
mTitleView = (TextView)findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.title); // 创建标题栏
......
}
}
generateDecor()@PhoneWindow.java
protected DecorView generateDecor() {
return new DecorView(getContext(), -1); // DecorView从FrameLayout派生,同时实现RootViewSurfaceTaker接口。
}
generateLayout()@PhoneWindow.java
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
......
// Inflate the window decor.
int layoutResource; // 根据情况获取相应的标题栏资源ID。
int features = getLocalFeatures();
if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_LEFT_ICON) | (1 << FEATURE_RIGHT_ICON))) != 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
......
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
}
......
}
mDecor.startChanging();
View in = mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResource, null); //inflate 标题栏
decor.addView(in, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT)); // 加入标题栏
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT); // ID_ANDROID_CONTENT:xml布局文件中main layout的ID, 实际上是mDecorView的一部分。
......
mDecor.finishChanging();
return contentParent;
}
findViewById()@Window.java
public View findViewById(int id) {
return getDecorView().findViewById(id);
}
通过上面的代码可以看到,在Activity.onCreate()函数里调用setContentView设置的View,实际上会作为DecorView的子view。DecorView还处理了标题栏显示等工作。
addView()@ViewGroup.java
public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params) {
// addViewInner()函数中设置LayoutParams时会调用child.requestLayout(),在这里调用,为了在这里阻塞child的request.
requestLayout();
invalidate(true); //在下一篇文章中会介绍这个函数
addViewInner(child, index, params, false);
}
11. 我们接着看handleLaunchActivity()中的handleResumeActivity()函数,
handleResumeActivity()@ActivityThread.java
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token, boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume) {
......
ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide); //会调用到Activity.onResume().
if (r != null) {
final Activity a = r.activity;
final int forwardBit = isForward ? WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0;
// If the window hasn't yet been added to the window manager,
// and this guy didn't finish itself or start another activity,
// then go ahead and add the window.
// 若这个activity的window没有加到window manager中,而且它没有自己finish或者启动另外一个acitivity,那就继续,添加这个window.
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
if (!willBeVisible) {
try {
willBeVisible = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().willActivityBeVisible(a.getActivityToken());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow(); // 获得在attach()函数中创建出来的window对象。
View decor = r.window.getDecorView(); // 获得一个View对象
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager(); // 获得ViewManager对象
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l); // 添加View对象到WindowManager中。
}
} else if (!willBeVisible) { // 如果window已经被添加了,但在resume时启动另外的activity,这个window将隐藏。
r.hideForNow = true;
}
// Get rid of anything left hanging around.
cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r);
// 如果window添加了,执行到这的时候就可见了。
if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible && r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
if (r.newConfig != null) {
performConfigurationChanged(r.activity, r.newConfig);
freeTextLayoutCachesIfNeeded(r.activity.mCurrentConfig.diff(r.newConfig));
r.newConfig = null;
}
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
if ((l.softInputMode & WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION) != forwardBit) {
l.softInputMode = (l.softInputMode
& (~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION))
| forwardBit;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
wm.updateViewLayout(decor, l); // 根据输入法显示模式调整winddow layout。
}
}
r.activity.mVisibleFromServer = true;
mNumVisibleActivities++;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
r.activity.makeVisible();
}
}
if (!r.onlyLocalRequest) {
r.nextIdle = mNewActivities;
mNewActivities = r;
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new Idler());
}
r.onlyLocalRequest = false;
// Tell the activity manager we have resumed.
if (reallyResume) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityResumed(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
} else {
// If an exception was thrown when trying to resume, then just end this activity.
// 如果resume过程出现异常,就finish这个activity.
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().finishActivity(token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
}
addView()@WindowManagerGlobal.java
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
......
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
......
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); // 创建ViewRootImpl对象
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
}
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView); // setView()内调用requestLayout(). 在被加到WindowManager之前调度第一次layout,确保收到系统事件之前重新进行了布局。
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
......
}
}
ViewRootImpl及setView()涉及到了UI绘制。启动相关更多的细节在下一篇中进行分析。