碎碎念
我在写app的时候,无论是布局上的字符串还是代码中的,我都喜欢直接敲上去,无视那个善意提醒的波浪线。
对于小项目来说,我觉得无可厚非,虽然不规范但方便直观,不需要苦于给字符串起名字。
如果你在项目初期就想着要将应用推向国际市场,就要注意字符串一定要养成习惯全部写在string.xml里,不然后期再加真的很崩溃。
创建多语言的string.xml
我们的目标是,应用跟随系统语言改变而改变。
首先是创建对应的语言的string.xml文件。
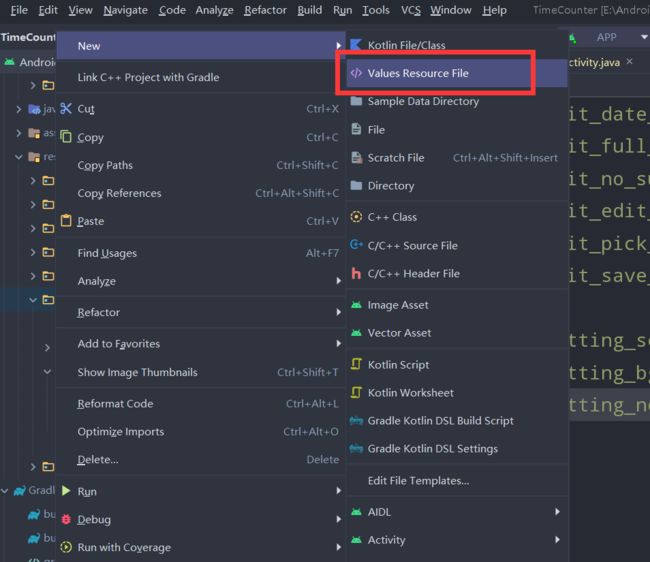
选中res/values文件夹,右键新建一个资源文件。
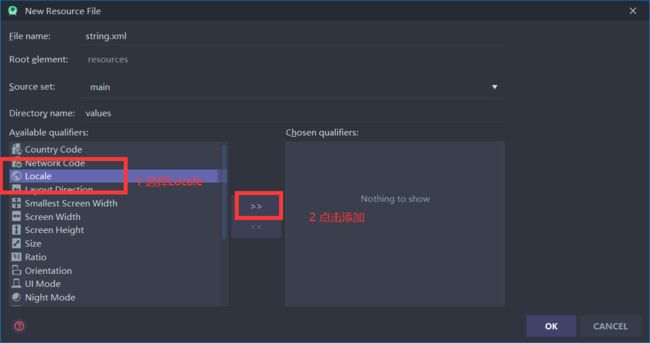
然后选择Locale类别,添加进来,名称就叫string.xml
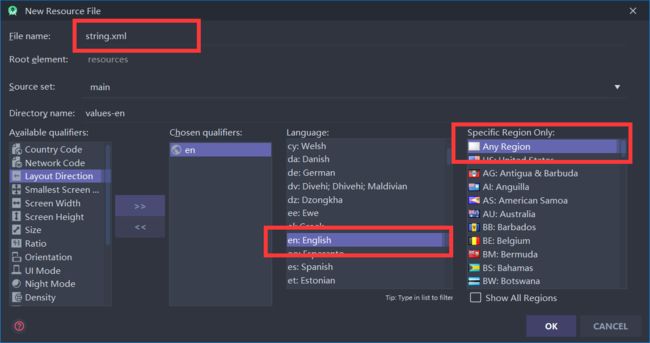
然后选择对应的语言,地区选择全部
这样你就得到了两份string.xml文件,一份是原版的即中文,另一份是英文的对照版本。
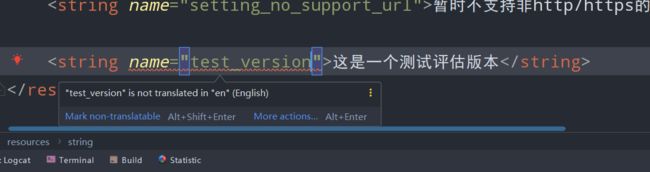
在中文的中创建一个字符串,会有相应的提示需要在英文对照版本中创建一份翻译的版本。
如何使用
在布局中可以直接使用@string形式来加载,在代码中使用:
/** * 加载字符串 * @param id 字符串id * */ public static String getStaticString(Context context,int id){ return context.getResources().getString(id); }
自动切换
为了实现自动切换功能,我们需要封装一个LanguageUtil(参考自 简书)
import android.content.Context; import android.content.SharedPreferences; import android.content.res.Configuration; import android.os.Build; import android.util.DisplayMetrics; import com.google.gson.Gson; import java.util.Locale; public class LanguageUtil { private static final String LOCALE_SP = "LOCALE_SP"; private static final String LOCALE_SP_KEY = "LOCALE_SP_KEY"; public static Locale getLocale(Context context) { SharedPreferences spLocale = context.getSharedPreferences(LOCALE_SP, Context.MODE_PRIVATE); String localeJson = spLocale.getString(LOCALE_SP_KEY, ""); Gson gson = new Gson(); return gson.fromJson(localeJson, Locale.class); } private static void setLocale(Context pContext, Locale pUserLocale) { SharedPreferences spLocal = pContext.getSharedPreferences(LOCALE_SP, Context.MODE_PRIVATE); SharedPreferences.Editor edit = spLocal.edit(); String json = new Gson().toJson(pUserLocale); edit.putString(LOCALE_SP_KEY, json); edit.apply(); } public static boolean updateLocale(Context context, Locale locale) { if (needUpdateLocale(context, locale)) { Configuration configuration = context.getResources().getConfiguration(); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR1) { configuration.setLocale(locale); } else { configuration.locale = locale; } DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics(); context.getResources().updateConfiguration(configuration, displayMetrics); setLocale(context, locale); return true; } return false; } public static boolean needUpdateLocale(Context pContext, Locale newUserLocale) { return newUserLocale != null && !getCurrentLocale(pContext).equals(newUserLocale); } public static Locale getCurrentLocale(Context context) { Locale locale; if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) { //7.0有多语言设置获取顶部的语言 locale = context.getResources().getConfiguration().getLocales().get(0); } else { locale = context.getResources().getConfiguration().locale; } return locale; } }
紧接着我们创建一个Application来自动加载
public class MyApplication extends Application { @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); languageWork(); } @Override public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) { super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig); languageWork(); } private void languageWork() { Locale locale = LanguageUtil.getLocale(this); LanguageUtil.updateLocale(this, locale); } }
在AndroidManifest.xml中配置一下:
android:name=".MyApplication"
如图所示:
愉快的去使用吧~