【JAVA,ArrayList源码】阅读ArrayList源码个人理解
阅读ArrayList源码个人理解
近期阅读了java.util.ArrayList.java的源代码
ArrayList介绍
从贴出代码不难看出,ArrayList是继承了AbstractList,并且实现了List,RandomAccess,Cloneable,java.io.Serializable。
ArrayList可以无限延展下去的特点。
ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,使它可以序列化之后持久的“存在”。
注释:序列化,我很困惑,然后就啪啪去查阅。最终自己的大致理解就是,一个java对象可以通过序列化,转化成一个序列,字节序列,包括这个对象的数据、属性、对象的类型等信息,然后这个序列化之后的对象可以被持久的保存在文件中,可以存储以及传输,之后再对文件通过反序列化之后实例成对象。
ArrayList属性分析
public class ArrayList extends AbstractList
implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
transient Object[] elementData;
private int size;
...
...
} serialVersionUID:这个是序列化的标识,序列化和反序列化会通过这个标识进行校验。
DEFAULT_CAPACITY:这个是初始化的数组大小。
EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA:初始化空的示例数组。
DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA:初始化的时候利用DEFAULT_CAPACITY来限定实例数组的长度大小。
elementData:使用transient关键字修饰的elementData。它是存储数组的变量,对于ArrayList非常重要。
注释:transient,java关键字,其修饰的对象不会进行序列化。
size:记录ArrayList的大小。
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}ArrayList构造参数:为带长度大小的,不带参数的。
/**
* Trims the capacity of this ArrayList instance to be the
* list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an ArrayList instance.
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
trimToSize:这个方法是为了,节省空间的,每次ArrayList扩容的时候到会多出一点点,然后可以使用这方法删除多余的空间,这样就可以节约空间。
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}ensureCapacity:对ArrayList进行扩容。简而言之,通过定量的扩充ArrayList的长度,避免在add()的时候,多次扩容,减少扩容的时间。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/nzh1234/article/details/22752095;
ensureExplicitCapacity:进行扩容的操作。
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}grow:扩容的方法。对elementData进行操作。
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}indexOf:用来判断是否包含相应的对象,如果没有就返回-1。
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is
* negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access,
* which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative.
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* A version of rangeCheck used by add and addAll.
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}这里是几个异常的输出,基本就是判断是否越界。
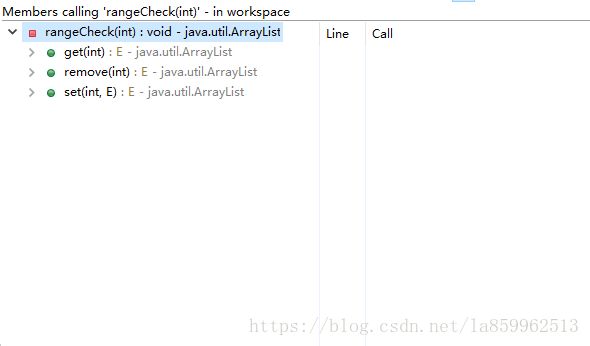
rangeCheck:主要是对于获取指定位置的对象,移除指定位置的对象,已经更新指定位置的对象这些操作的检查。
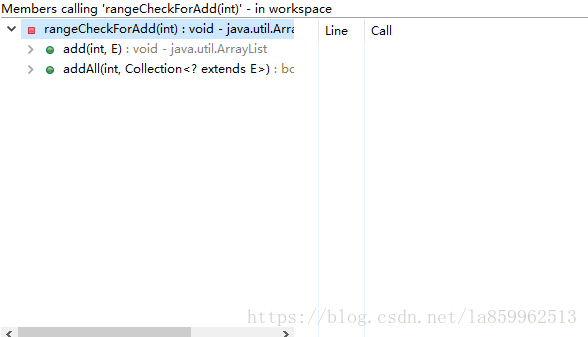
rangeCheckForAdd:对新增对象,超过ArrayList的容量。
outOfBoundsMsg:我们经常看见的越界的错误信息就是这个地方定义抛出的错误。
整个ArrayList的源码实现,实际上还是有很多内容的,我只是浅显理解,然后把自己的理解转化成可以便于理解的文字,ArrayList在实际的开发中利用是极其广泛的,深入理解ArrayList的源码还是对日常的开发工作是有很多很大好处。
这里只是介绍了一部分内容,在迭代器这块没有任何涉及,如有错误请指正,谢谢!我将积极更正。
最后附上ArrayList的源码,源码来自于开源平台,这里只提供下载,不做其他用途。
https://download.csdn.net/download/la859962513/10681442,好像不可以设置免费。