8. 随机超参搜索(The caret package)
1. 简介(The caret package )
2. 可视化(The caret package)
3. 预处理(The caret package)
4. 数据分割(The caret package)
5. 模型训练和调参(The caret package)
6. 可用模型(The caret package )
7. train的模型标签
8. 随机超参搜索
在train中优化参数的默认方法是使用网格搜索。这种方法通常是有效的,但是,在有很多参数要调整的时候,他可能不那么有效。另一种方法是用参数组合的随机选择来遍历参数空间。
有很多模型,用这种方法在相对短的时间内找到参数的合理值。然而,有一些模型,在小的搜索区域中能抵消其他的优化。例如,在caret包中的一些模型使用“子模型技巧”,在这“子模型技巧”中M个参数组合被估计,但是可能需要的拟合估计远小于这M个模型。当使用一个简单的网格搜索时,这种方法是最好的原型。由于这个原因,对于下列模型方法,用随机搜索可能不那么有效:
ada, AdaBag, AdaBoost.M1, bagEarth, blackboost, blasso, BstLm, bstSm, bstTree, C5.0, C5.0Cost, cubist, earth, enet, foba, gamboost, gbm, glmboost, glmnet, kernelpls, lars, lars2, lasso, lda2, leapBackward, leapForward, leapSeq, LogitBoost, pam, partDSA, pcr, PenalizedLDA, pls, relaxo, rfRules, rotationForest, rotationForestCp, rpart, rpart2, rpartCost, simpls, spikeslab, superpc, widekernelpls, xgbTree.
最终,由train包装的许多模型有很少的参数,平均参数有1.8个。
要使用随机搜索方法,另一个选择,即trainControl中的search是可以使用的。这个参数的可能取值为grid和random。caret包内置的模型包含一些代码去产生随机参数的组合。总的不同组合的数量有train中的参数tuneLength`设定。
再一次我们使用Sonar数据,通过查看30个参数组合来描述规则判别分析。
library(mlbench)
data(Sonar)
library(caret)
set.seed(998)
inTraining <- createDataPartition(Sonar$Class, p = .75, list = FALSE)
training <- Sonar[ inTraining,]
testing <- Sonar[-inTraining,]
fitControl <- trainControl(method = "repeatedcv",
number = 10,
repeats = 10,
classProbs = TRUE,
summaryFunction = twoClassSummary,
search = "random")
set.seed(825)
rda_fit <- train(Class ~ ., data = training,
method = "rda",
metric = "ROC",
tuneLength = 30,
trControl = fitControl)
rda_fit
## Regularized Discriminant Analysis
##
## 157 samples
## 60 predictor
## 2 classes: 'M', 'R'
##
## No pre-processing
## Resampling: Cross-Validated (10 fold, repeated 10 times)
## Summary of sample sizes: 142, 142, 140, 142, 142, 141, ...
## Resampling results across tuning parameters:
##
## gamma lambda ROC Sens Spec
## 0.03989739 0.90079034 0.8876811 0.8459722 0.7667857
## 0.04968076 0.92570716 0.8816245 0.8425000 0.7610714
## 0.07268784 0.24747192 0.9153125 0.8893056 0.8107143
## 0.15727695 0.92403079 0.8842262 0.8636111 0.7696429
## 0.18095571 0.19419752 0.9138318 0.8895833 0.7907143
## 0.25251704 0.59742978 0.9184152 0.9254167 0.7891071
## 0.29954232 0.63759620 0.9133681 0.9169444 0.7710714
## 0.31520463 0.96521251 0.8743998 0.8511111 0.7773214
## 0.33009668 0.81815445 0.8950967 0.8937500 0.7746429
## 0.36085613 0.75063821 0.8999231 0.9056944 0.7658929
## 0.36447104 0.04755168 0.8947321 0.8726389 0.7500000
## 0.38014796 0.81490324 0.8939087 0.8901389 0.7648214
## 0.42198667 0.94140042 0.8776984 0.8508333 0.7801786
## 0.42208259 0.20124965 0.9042262 0.8863889 0.7526786
## 0.43249714 0.41644166 0.9075818 0.8958333 0.7641071
## 0.43342775 0.24999664 0.9047173 0.8898611 0.7598214
## 0.49307138 0.20539733 0.8989608 0.8897222 0.7503571
## 0.50624038 0.06571280 0.8952133 0.8794444 0.7444643
## 0.51244277 0.52918233 0.9032813 0.9000000 0.7444643
## 0.54605138 0.44369088 0.9007292 0.8916667 0.7428571
## 0.56784496 0.37966361 0.8992882 0.8931944 0.7419643
## 0.58229517 0.15112209 0.8933135 0.8776389 0.7423214
## 0.69886586 0.18057206 0.8876314 0.8825000 0.7244643
## 0.70747426 0.02153708 0.8836111 0.8740278 0.7232143
## 0.70986464 0.02730106 0.8839286 0.8752778 0.7217857
## 0.71609215 0.98811552 0.8544147 0.7781944 0.7617857
## 0.74102544 0.88861156 0.8634003 0.8097222 0.7433929
## 0.77714849 0.94955834 0.8504812 0.7794444 0.7433929
## 0.89569896 0.81051218 0.8287773 0.7795833 0.7067857
## 0.93822474 0.10278451 0.8341741 0.8397222 0.6810714
##
## ROC was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
## The final values used for the model were gamma = 0.252517 and lambda
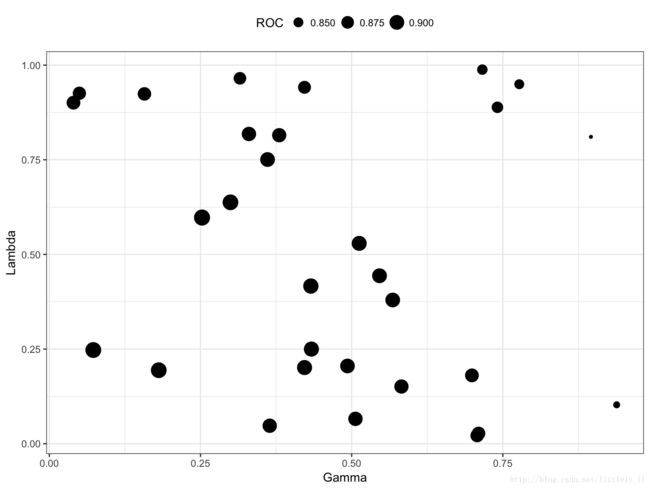
## = 0.5974298.这儿仅有一个ggplot方法,带有随机搜索的函数的结果依赖于参数的个数和类型。在这个例子中,它生成了一个连续参数的散点图。
ggplot(rda_fit) + theme(legend.position = "top")