go语言快速入门:IPC之Socket(9)
多进程之间的通信常见的手段有管道/信号量/共享内存/Socket等,在上篇文章中介绍了管道的使用方法。管道在多进程通信中使用方便但是也具局限性,当通信双方在不同的机器上的时候通信方式更多采用Socket方式。在这篇文章中我们将会继续探索如何使用go所提供的net包等实现TCP和UDP方式的Socket通信。
传输层协议
OSI模型
OSI七层模型,简单来说,下三层主要负责数据通信,而上三层主要负责数据处理。处于第四层的传输层是通信子网和资源子网的接口和桥梁,整体起到承上启下的作用。而TCP和UDP则是传输层的协议。
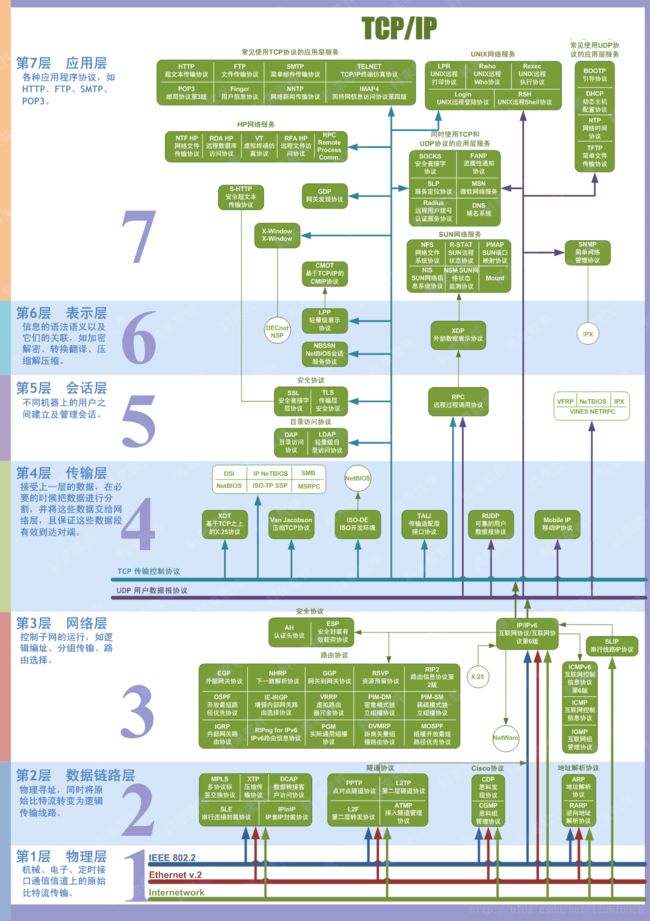
TCP和UDP的区别
TCP和UDP最大的区别在于是否是面向连接的协议,作为面向连接的TCP协议,以此决定了在本质上是否是安全可靠的特性。

TCP通信
无论TCP方式还是UDP方式,常见的场景应用会分为服务器端和客户端的类型。作为面向连接的TCP方式,服务器端的应用一般会绑定到某一端口,然后再此端口上进行监听,当其受到客户端的连接时便会进行交互。
Server端实现
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# cat basic-tcp-server.go
package main
import "fmt"
import "os"
import "net"
import "time"
func main() {
//get a tcp address
tcp_address, err := net.ResolveTCPAddr("tcp4", ":8848")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when getting a tcp address...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//listen to the tcp address
tcp_listener, err := net.ListenTCP("tcp", tcp_address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when listening to the tcp address...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//greeting words
str_header := "Hello, this is information from tcp server , and current time is : "
//main loop of tcp server
for {
//waiting connection from client
tcp_connection, err := tcp_listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
continue
}
//get the current time infor
str_time := time.Now().String()
//set greeting words for client connection
str_greetings := str_header + str_time
//send information to client
tcp_connection.Write([]byte(str_greetings))
tcp_connection.Close()
}
}
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#客户端实现
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# cat basic-tcp-client.go
package main
import "fmt"
import "io/ioutil"
import "os"
import "net"
func main() {
//usage of client application
if len(os.Args) != 2 {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "Usage: %s host:port ", os.Args[0])
os.Exit(1)
}
//get a tcp address
arg_address := os.Args[1]
tcp_address, err := net.ResolveTCPAddr("tcp4", arg_address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when getting a tcp address...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//connect to a tcp server
tcp_connection, err := net.DialTCP("tcp", nil, tcp_address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when connecting a tcp server...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//read information from tcp server
str_greeting, err := ioutil.ReadAll(tcp_connection)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when reading from the tcp server...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//display the information
fmt.Println(string(str_greeting))
os.Exit(0)
}
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#执行确认
首先将server端运行起来,等待client端的连接
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-tcp-server.go运行client端,可以得到从server端发过的信息
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-tcp-client.go 192.168.32.123:8848
Hello, this is information from tcp server , and current time is : 2017-01-31 10:56:48.590783817 -0500 EST
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-tcp-client.go 192.168.32.123:8848
Hello, this is information from tcp server , and current time is : 2017-01-31 10:56:54.969361975 -0500 EST
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-tcp-client.go 192.168.32.123:8848
Hello, this is information from tcp server , and current time is : 2017-01-31 10:57:08.226263371 -0500 EST
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#UDP方式
通过上述例子,可以了解到TCP方式的简单实现。接下来看一下UDP方式。UDP作为无连接的传输层协议的实现,在go所提供的API可以看到,形式已经非常类似。
Server端实现
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# cat basic-udp_server.go
package main
import "fmt"
import "os"
import "net"
import "time"
func main() {
//get a udp address
udp_address, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp4", ":9848")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when getting a udp address...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//listen to the udp address
udp_connection, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", udp_address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when listening to the udp address...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//greeting words
str_header := "Hello, this is information from udp server , and current time is : "
//main loop of udp server
for {
//read information from client
var udp_buffer [1024]byte
_, address, err := udp_connection.ReadFromUDP(udp_buffer[0:])
if err != nil {
continue
}
//get the current time infor
str_time := time.Now().String()
//set greeting words for client connection
str_greetings := str_header + str_time
//send information to client
udp_connection.WriteToUDP([]byte(str_greetings), address)
}
}
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#客户端实现
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# cat basic-udp_client.go
package main
import "fmt"
import "os"
import "net"
func main() {
//usage of client application
if len(os.Args) != 2 {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "Usage: %s host:port ", os.Args[0])
os.Exit(1)
}
//get a udp address
arg_address := os.Args[1]
udp_address, err := net.ResolveUDPAddr("udp4", arg_address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when getting a udp address...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//connect to a udp server
udp_connection, err := net.DialUDP("udp", nil, udp_address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when connecting a udp server...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//send information to udp server
_, err = udp_connection.Write([]byte("hello"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when sending message to the udp server...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//udp buffer
var udp_buffer [1024]byte
//read information from udp server
num, err := udp_connection.Read(udp_buffer[0:])
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error happened when reading from the tcp server...", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
//display the information
fmt.Println(string(udp_buffer[0:num]))
os.Exit(0)
}
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#执行确认
首先将server端运行起来,等待client端的连接
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-udp_server.go运行client端,可以得到从server端发过的信息
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-udp_client.go 192.168.32.123:9848
Hello, this is information from udp server , and current time is : 2017-01-31 11:25:03.274881649 -0500 EST
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-udp_client.go 192.168.32.123:9848
Hello, this is information from udp server , and current time is : 2017-01-31 11:25:05.895074805 -0500 EST
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#
[root@liumiaocn goprj]# go run basic-udp_client.go 192.168.32.123:9848
Hello, this is information from udp server , and current time is : 2017-01-31 11:25:09.886004761 -0500 EST
[root@liumiaocn goprj]#总结
在这篇文章中,我们继续讨论了go语言中Socket通信的两个简单实例,通过这两个例子,实现了TCP和UDP的服务器和客户端的交互。虽然在实际中的应用还有很远一段距离,比如并发的控制上述简单的例子没有涉及到,但是通过这两个例子,已经能看出多进程通信的go的实现方式。