Nodejs开发grpc
nodejs开发grpc示例
Nodejs开发grpc有两种方式(与其他语言开发方式不同)
- 静态代码生成:与传统方式一样,提前编译生成好js源码,开发时就可以应用生成js文件中源码。
- 动态代码生成:不需要提前由.proto文件(IDL文件)生成js代码,而是通过提前指定好IDL文件的位置,运行时再生成对应的源码文件。
哪个好,哪个不好?没有明确规则,但是一个最佳实践:要么全部动态生成、要么全部静态生成,不然容易错乱。
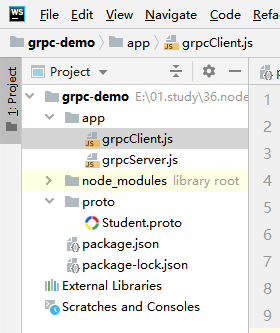
开发nodejs,工程路径没有严格要求,这里在工程根目录下:
- 创建app文件存放我们开发的js源码
- 创建proto文件存放IDL文件
- 由于nodejs是异步框架,所以编写nodejs代码绝大多数都是通过回调、通知、事件的方式获取对端的响应
一、动态代码生成
可见,代码中仅仅指定了IDL文件的路径,通过对应的gprc的load方法加载这个文件,全程没有用到grpc的编译工具生成相关代码。
工程结构:
这里是一个grpc的nodejs客户端与服务端实现,首先是服务端代码
//定义一个常量指定proto文件路径
var PROTO_FILE_PATH = 'E:\\01.study\\36.nodejs\\workspace\\grpc-demo\\proto\\Student.proto';
//引入GRPC库
var grpc = require('grpc');
//找到我们在IDL文件中定义的service:StudentService
var grpcService = grpc.load(PROTO_FILE_PATH).com.mzj.netty.ssy._08_grpc;
//定义服务端
var server = new grpc.Server();
server.addService(grpcService.StudentService.service,{
//添加测试的rpc方法,服务名:服务对应调用方法
getRealNameByUsername: getRealNameByUsername1,
// 添加其他rpc方法
getStudentsByAge: getStudentsByAge1,
getStudentsWrapperByAges: getStudentsWrapperByAges1,
biTalk: biTalk1,
})
//绑定端口,并设置不是用ssl安全加密
server.bind('localhost:8899',grpc.ServerCredentials.createInsecure());
//启动服务器
server.start();
//实现rpc服务调用处理函数:参数1call:请求对象,参数2callback:回调函数
function getRealNameByUsername1(call,callback) {
console.log("username : " + call.request.username);//打印请求对象
/**
* 定义回调函数
*/
callback(null,{realname: 'mazhongjia'});//参数1:错误对象,这里不进行设置,参数2:返回给客户端的结果对象,这里的属性名对应IDL中声明的属性名
}
function getStudentsByAge1(){
}
function getStudentsWrapperByAges1(){
}
function biTalk1(){
}
然后是客户端代码:
//--------------动态代码生成的方式:--------------
//1、定义grpc的IDL文件位置
var PROTO_FILE_PATH = 'E:\\01.study\\36.nodejs\\workspace\\grpc-demo\\proto\\Student.proto';
//2、引入grpc库,nodejs中,引入库用require方法
var grpc = require('grpc');
//3、定义grpc服务
//找到我们在IDL文件中定义的service:StudentService
var grpcService = grpc.load(PROTO_FILE_PATH).com.mzj.netty.ssy._08_grpc;
//4、定义nodejs客户端
var client = new grpcService.StudentService('localhost:8899',grpc.credentials.createInsecure());
//grpc.credentials.createInsecure():创建的是一个不安全的、不是用ssl证书加密的通道,与java如下代码等价:
//.usePlaintext(true).
//调用rpc方法,其中方法首字母转小写
client.getRealNameByUsername({username:'lisi'},function (error,respData) {
console.log(respData);
})
grpc的IDL文件:
syntax = "proto3";
package com.mzj.netty.ssy._08_grpc;
option java_package = "com.mzj.netty.ssy._08_grpc";
option java_outer_classname = "StudentProto";
option java_multiple_files = true;
service StudentService{
//gRpc支持的四种调用形式示例:
rpc GetRealNameByUsername(MyRequest) returns (MyResponse){}//种类1:普通输入参数与返回值
rpc GetStudentsByAge(StudentRequest) returns (stream StudentResponse){}//种类2:服务端rpc方法返回值是stream形式,参数是普通对象
rpc GetStudentsWrapperByAges(stream StudentRequest) returns (StudentResponseList){}//种类3:客户端输入参数是stream形式,返回是一个普通对象
rpc BiTalk(stream StreamRequest) returns (stream StreamResponse){}//种类4:双向的流式的数据传递(客户端发送请求/服务端返回结果都是流式)
//从IDL的定义上,四种调用形式区别体现在rpc定义时方法参数、返回值的message前面是否有stream关键字
//rpc方法的参数与返回值类型都是IDL中定义的message类型,而不能是string、int32等变量类型,这一点跟thrift不同,即使只有一个属性,也得定义成message
}
message MyRequest{
string username = 1;
}
message MyResponse{
string realname = 2;
}
message StudentRequest{
int32 age = 1;
}
message StudentResponse{
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
string city = 3;
}
message StudentResponseList{
//protobuf中集合用repeated表示
repeated StudentResponse studentResponse = 1;//repeated表示集合类型,这里表示服务器端向客户端返回的是一个集合类型,集合中元素是StudentResponse
}
message StreamRequest{
string request_info = 1;
}
message StreamResponse{
string response_info = 1;
}分别运行服务端、客户端代码。
二、静态代码生成
1、说明:通过grpc编译器protoc预先生成js源码,然后编码过程中显示调用。
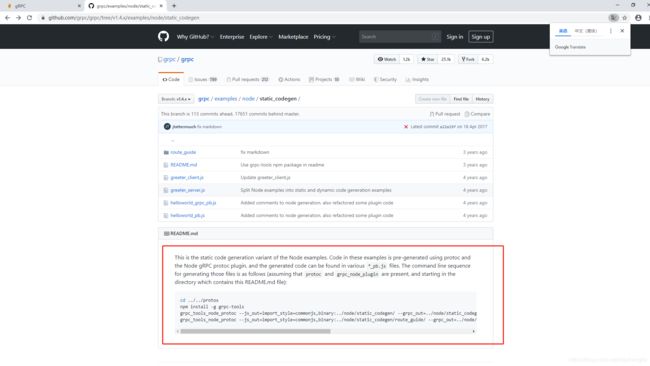
2、具体操作方式:按照官网示例
https://github.com/grpc/grpc/tree/v1.4.x/examples/node/static_codegen
下面内容参考的是上面网址的README.md文件
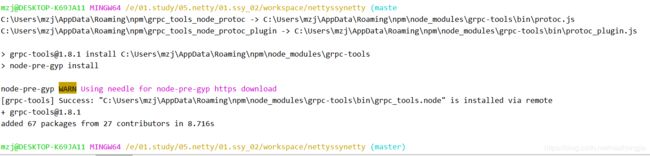
步骤1:安装grpc-tools,通过nodejs的npm包管理工具按照grpc-tools插件
npm install -g grpc-tools步骤2:通过编译器生成对应nodejs源码:
下面是readme文件中原始命令,需要进行修改
grpc_tools_node_protoc --js_out=import_style=commonjs,binary:../node/static_codegen/ --grpc_out=../node/static_codegen --plugin=protoc-gen-grpc=`which grpc_tools_node_protoc_plugin` helloworld.proto修改后实际执行的为:
grpc_tools_node_protoc --js_out=import_style=commonjs,binary:static_codegen/ --grpc_out=static_codegen --plugin=protoc-gen-grpc=/c/Users/mzj/AppData/Roaming/npm/grpc_tools_node_protoc_plugin.cmd proto/Student.proto其中两个路径分别是生成的消息源码路径和grpc通信源码路径,我们修改成生成到相同的路径
其中/c/Users/mzj/AppData/Roaming/npm/grpc_tools_node_protoc_plugin是通过执行原始命令中which grpc_tools_node_protoc_plugin得到的,但是后面需要加上.cmd:
执行后出错:
提示没有这个目录,手工创建后再执行,则OK
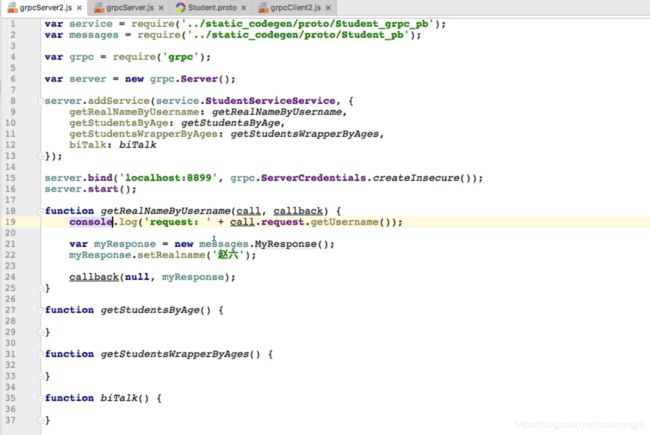
生成代码如下:
其中这两个文件:Student_pb.js是消息相关源码,Student_grpc_pb.js是grpc相关通信代码(与java生成源码类似,也是消息+grpc通信两部分)
编写客户端代码:
//1、定义service,service位于Student_grpc_pb.js中
var service = require('../static_codegen/proto/Student_grpc_pb.js');
//2、定义消息
var message = require('../static_codegen/proto/Student_pb.js');
//3、引入grpc库
var grpc = require('grpc');
//4、定义客户端
var client = new service.StudentServiceClient('localhost:8899',grpc.credentials.createInsecure());
//5、定义请求message(与动态生成方式不同)
var request = new message.MyRequest();
request.setUsername('huna');
//6、调用rpc方法
client.getRealNameByUsername(request,function (error,respData) {
//静态调用方式是以方法调用的方式获取返回结果,因为rpc的返回值在编译期可见,而动态方式rpc返回值编辑期不可见、是通过属性的方式获取结果
console.log(respData.getRealname());//打印返回结果
})测试:启动动态代码生成编写的服务端、启动静态代码生成的客户端。
静态代码生成方式编写的服务端:
总结动态与静态代码生成方式优缺点:
- 静态与动态方式使用场景,到底使用哪种(视频31_30分钟)
- 动态方式好处:不需要预先生成源码文件
- 动态方式缺陷:编写代码阶段无法获取具体有哪些属性,只能自己保证编写代码属性的正确性,无法在编译期保证正确性,同时可读性不好
- 静态方式好处:每一个对象有什么方法,编写代码阶段都能看到,代码可读性好
- 静态方式缺点:较动态方式麻烦
- 我推荐使用静态代码生成的方式:因为代码编写过程中一些代码编写提示与可读性更重要,而自动生成代码可以通过编写脚步实现自动化。