第32天(就业班) hibernate框架概述、ORM概念、hibernate第一个实例、api讲解、查询方式、主配置文件、映射配置、主键映射
SSH框架:基于mvc模式的应用层框架技术
Hibernate:基于持久层的框架(数据访问层的使用)
Dao代码
- 操作XML数据
- 使用Jdbc技术
原始的jdbc操作, Connection/Statement/ResultSet
自定义一个持久层框架, 封装了dao的通用方法
DbUtils组件, 轻量级的dao的组件;
Hibernate技术 【hibernate最终执行的也是jdbc代码!】
JDBC操作
List users = new ArrayList();
User user ;
try {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select * from users ");
while(resultSet.next()){
user = new User();
user.setId(resultSet.getInt(1));
//省略其他赋值方法
...
users.add(User);
}
statement.close();JDBC缺点:
l 开发效率低
l 代码冗余
• pstmt的setXX方法
• 方法参数冗余的getXX方法
• 如果POJO的属性很多,代码增加
l 重复性工作多
1. ORM概念理解
ORM(对象关系映射)概念
O,object对象
R,relation 关系型数据库,MySQL,oracle
M,Mapping 映射
Hibernate简介
l Hibernate作者——Gavin King
• Hibernate创始人
• 《 Hibernate in action 》作者
• 参加了XDoclet和Middlegen的开发
• 2003年9月加入JBoss,全职进行Hibernate开发
l Hibernate
• 一个开发源代码的对象关系映射框架
• 对JDBC进行了非常轻量级的对象封装
• 将JavaBean对象和数据库的表建立对应关系
ORM,解决什么问题?
存储: 能否把对象的数据直接保存到数据库?
获取: 能否直接从数据库拿到一个对象?
想做到上面2点,必须要有映射!
Hibernate与ORM的关系?Hibernate是ORM的实现!
Hibernate3架构体验
l 简化了JDBC或C3P0和DBUtils实现的dao层体系
l 主配置文件hibernate.cfg.xml src路径下(引入映射文件)
l 持久化类映射文件User.hbm.xml 类路径或src路径
l CRUD均是基于对象(查询是基于HQL)
l SessionFactory、Session等API类
l 思考:如何学习Hibernate3这样的持久层框架呢?
# 主配置和映射配置文件
# Hibernate提供的API类
2. hibernate第一个案例helloword
搭建一个hibernate环境,开发步骤
1)下载源码:
hibernate-distribution-3.6.0.Final-dist
2) 引入jar文件
hibernate3.jar核心 + required必须引入的(6个) + jpa 目录 + 数据库驱动包

3)写对象以及对象的映射
Employee.java 对象
package com.xp.a_hello;
import java.util.Date;
public class Employee {
private int empId;
private String empName;
private Date workDate;
public int getEmpId() {
return empId;
}
public void setEmpId(int empId) {
this.empId = empId;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public Date getWorkDate() {
return workDate;
}
public void setWorkDate(Date workDate) {
this.workDate = workDate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [empId=" + empId + ", empName=" + empName + "]";
}
}
Employee.hbm.xml 对象的映射
4)src/hibernate.cfg.xml在etc文件夹中导入此文件
hibernate.cfg.xml 主配置文件
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql:///hib_demo
root
xiongpan
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
true
true
update
none
5)第一个hibernate案例
App.java测试类
package com.xp.a_hello;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
public class App {
@Test
public void testHello() throws Exception
{
// 对象
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setEmpName("班长");
emp.setWorkDate(new Date());
// 获取加载配置文件的管理类对象
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.configure(); // 默认加载src/hibenrate.cfg.xml文件
// 创建session的工厂对象
SessionFactory sf = config.buildSessionFactory();
// 创建session (代表一个会话,与数据库连接的会话)
Session session = sf.openSession();
// 开启事务
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
//保存-数据库
session.save(emp);
// 提交事务
tx.commit();
// 关闭
session.close();
sf.close();
}
} Configuration类负责管理Hibernate的配置信息。包括如下内容:
• Hibernate运行的底层信息:数据库的URL、用户名、密码、JDBC驱动类,数据库Dialect,数据库连接池等
(对应 hibernate.cfg.xml 文件)。
• 持久化类与数据表的映射关系(*.hbm.xml 文件)
创建Configuration 的两种方式
• 属性文件(hibernate.properties):
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
• Xml文件(hibernate.cfg.xml)
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
|-- Configuration 配置管理类对象
config.configure(); 加载主配置文件的方法(hibernate.cfg.xml)
默认加载src/hibernate.cfg.xml
config.configure(“cn/config/hibernate.cfg.xml”); 加载指定路径下指定名称的主配置文件
config.buildSessionFactory(); 创建session的工厂对象
Hibernate3核心API-SchemaExport类
SchemaExport类主要负责根据类或者hbm文件映射生成持久化类对应的表结构:
• create(boolean script, boolean export)
参数1:是否生成脚本 参数2:是否导出到数据库
创建SchemaExport的方式
• SchemaExport schema = new SchemaExport(config);
Hibernate3核心API-SessionFactory接口
Configuration对象根据当前的配置信息生成 SessionFactory 对象。SessionFactory 对象一旦构造完毕,即被赋予特定的配置信息(SessionFactory 对象中保存了当前的数据库配置信息和所有映射关系以及预定义的SQL语句。同时,SessionFactory还负责维护Hibernate的二级缓存)。
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
是线程安全的。
SessionFactory是生成Session的工厂:
Session session = sf.openSession();
构造SessionFactory很消耗资源,一般情况下一个应用中只初始化一个 SessionFactory对象。
|-- SessionFactory session的工厂(或者说代表了这个hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件)
sf.openSession(); 创建一个sesison对象
sf.getCurrentSession(); 创建session或取出session对象
Hibernate3核心API-Session接口
Session是应用程序与数据库之间交互操作的一个单线程对象,是 Hibernate 运作的中心,所有持久化对象必须在 session 的管理下才可以进行持久化操作。此对象的生命周期很短。Session 对象有一个一级缓存,显式执行 flush 之前,所有的持久层操作的数据都缓存在 session 对象处。相当于 JDBC 中的 Connection。
持久化类与 Session 关联起来后就具有了持久化的能力。
是线程不安全的
Session 类的方法:
• 取得持久化对象的方法: get() load()
• 持久化对象都得保存,更新和删除:save(),update(),saveOrUpdate(),delete()
• 开启事务: beginTransaction().
• 管理 Session 的方法:isOpen(),flush(), clear(), evict(), close()等
|--Session session对象维护了一个连接(Connection), 代表了与数据库连接的会话。
Hibernate最重要的对象: 只用使用hibernate与数据库操作,都用到这个对象
session.beginTransaction(); 开启一个事务; hibernate要求所有的与数据库的操作必须有事务的环境,否则报错!
更新:
session.save(obj); 保存一个对象
session.update(emp); 更新一个对象
session.saveOrUpdate(emp); 保存或者更新的方法:
没有设置主键,执行保存;
有设置主键,执行更新操作;
如果设置主键不存在报错!
主键查询:
session.get(Employee.class, 1); 主键查询
session.load(Employee.class, 1); 主键查询 (支持懒加载)
App2.java
package com.xp.a_hello;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
public class App2 {
private static SessionFactory sf;
static {
/*
* //1. 创建配置管理类对象 Configuration config = new Configuration(); // 加载配置文件
* (默认加载src/hibernate.cfg.xml) config.configure(); //2.
* 根据加载的配置管理类对象,创建SessionFactory对象 sf = config.buildSessionFactory();
*/
// 创建sf对象
sf = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
}
// 1. 保存对象
@Test
public void testSave() throws Exception {
// 对象
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setEmpName("张三123");
emp.setWorkDate(new Date());
// 根据session的工厂,创建session对象
Session session = sf.openSession();
// 开启事务
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
// -----执行操作-----
session.save(emp);
// 提交事务/ 关闭
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
// 更新
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
// 对象
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setEmpId(1000000);
emp.setEmpName("张三3");
// 创建session
Session session = sf.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
// -------执行操作-------
// 没有设置主键,执行保存;有设置主键,执行更新操作; 如果设置主键不存在报错!
session.saveOrUpdate(emp);
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
5.hibernate提供的查询各种方式(概述)
HQL查询:
HQL查询与SQL查询区别:
SQL: (结构化查询语句)查询的是表以及字段; 不区分大小写。
HQL: hibernate query language 即hibernate提供的面向对象的查询语言
查询的是对象以及对象的属性。
区分大小写。
Criteria查询:
完全面向对象的查询。
本地SQL查询:
复杂的查询,就要使用原生态的sql查询,也可以,就是本地sql查询的支持!
(缺点: 不能跨数据库平台!)
package com.xp.a_hello;
import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.SQLQuery;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.List;
public class App3 {
private static SessionFactory sf;
static {
// 创建sf对象
sf = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
}
//HQL查询 【适合有数据库基础的】
@Test
public void testQuery() throws Exception {
Session session = sf.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
// 主键查询
//Employee emp = (Employee) session.get(Employee.class, 1);
// HQL查询,查询全部
Query q = session.createQuery("from Employee where empId=1 or empId=2");
List list = q.list();
System.out.println(list);
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
//QBC查询 , query by criteria 完全面向对象的查询
@Test
public void testQBC() throws Exception {
Session session = sf.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Employee.class);
// 条件
criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("empId", 1));
// 查询全部
List list = criteria.list();
System.out.println(list);
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
//sQL
@Test
public void testSQL() throws Exception {
Session session = sf.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
// 把每一行记录封装为对象数组,再添加到list集合
// SQLQuery sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery("select * from employee");
// 把每一行记录封装为 指定的对象类型
SQLQuery sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery("select * from employee")
.addEntity(Employee.class);
List list = sqlQuery.list();
System.out.println(list);
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
Hibernate3核心API简介-Transaction接口
代表一次原子操作,它具有数据库事务的概念。所有持久层都应该在事务管理下进行,即使是只读操作。
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
常用方法:
• commit():提交相关联的session实例
• rollback():撤销事务操作
• wasCommitted():检查事务是否提交
|-- Transaction hibernate事务对象
共性问题1:
ClassNotFoundException…., 缺少jar文件!
问题2:
如果程序执行程序,hibernate也有生成sql语句,但数据没有结果影响。
问题一般是事务忘记提交…….
遇到问题,一定看错误提示 从后看到前
6.crud综合案例
package com.xp.b_crud;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import com.xp.a_hello.Employee;
public interface IEmployeeDao {
void save(Employee emp);
void update(Employee emp);
Employee findById(Serializable id);
List getAll();
List getAll(String employeeName);
List getAll(int index, int count);
void delete(Serializable id);
}
package com.xp.utils;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class HibernateUtils {
private static SessionFactory sf;
static {
// 加载主配置文件, 并创建Session的工厂
sf = new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
}
// 创建Session对象
public static Session getSession(){
return sf.openSession();
}
}
package com.xp.b_crud;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.xp.a_hello.Employee;
import com.xp.utils.HibernateUtils;
public class EmployeeDaoImpl implements IEmployeeDao {
@Override
public Employee findById(Serializable id) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 获取Session
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
// 开启事务
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// 主键查询
return (Employee) session.get(Employee.class, id);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
@Override
public List getAll() {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// HQL查询
Query q = session.createQuery("from Employee");
return q.list();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
@Override
public List getAll(String employeeName) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Query q =session.createQuery("from Employee where empName=?");
// 注意:参数索引从0开始
q.setParameter(0, employeeName);
// 执行查询
return q.list();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
@Override
public List getAll(int index, int count) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Query q = session.createQuery("from Employee");
// 设置分页参数
q.setFirstResult(index); // 查询的其实行
q.setMaxResults(count); // 查询返回的行数
List list = q.list();
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
@Override
public void save(Employee emp) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// 执行保存操作
session.save(emp);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
@Override
public void update(Employee emp) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.update(emp);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
@Override
public void delete(Serializable id) {
Session session = null;
Transaction tx = null;
try {
session = HibernateUtils.getSession();
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// 先根据id查询对象,再判断删除
Object obj = session.get(Employee.class, id);
if (obj != null) {
session.delete(obj);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
}
测试案例App.java
package com.xp.b_crud;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.xp.a_hello.Employee;
public class App {
private EmployeeDaoImpl empDao = new EmployeeDaoImpl();
@Test
public void testFindById() {
System.out.println(empDao.findById(1));
}
@Test
public void testGetAll() {
System.out.println(empDao.getAll());
}
@Test
public void testGetAllString() {
System.out.println(empDao.getAll("张三3"));
}
@Test
public void testGetAllIntInt() {
System.out.println(empDao.getAll(4, 2));
}
@Test
public void testSave() {
empDao.save(new Employee());
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setEmpId(23);
emp.setEmpName("new jack");
empDao.update(emp);
}
@Test
public void testDelete() {
empDao.delete(23);
}
}
7.主配置文件
Hibernate.cfg.xml
主配置文件中主要配置:数据库连接信息、其他参数、映射信息!
常用配置查看源码:
hibernate-distribution-3.6.0.Final\project\etc\hibernate.properties
数据库连接参数配置
例如:
## MySQL
#hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
#hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect
#hibernate.dialect org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLMyISAMDialect
#hibernate.connection.driver_class com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#hibernate.connection.url jdbc:mysql:///test
#hibernate.connection.username gavin
#hibernate.connection.password
自动建表
Hibernate.properties
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create-drop 每次在创建sessionFactory时候执行创建表;
当调用sesisonFactory的close方法的时候,删除表!
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto create 每次都重新建表; 如果表已经存在就先删除再创建
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto update 如果表不存在就创建; 表存在就不创建;
#hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto validate (生成环境时候) 执行验证: 当映射文件的内容与数据库表结构不一样的时候就报错!
package com.xp.b_crud;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.tool.hbm2ddl.SchemaExport;
import org.junit.Test;
public class App_ddl {
// 自动建表
@Test
public void testCreate() throws Exception {
// 创建配置管理类对象
Configuration config = new Configuration();
// 加载主配置文件
config.configure();
// 创建工具类对象
SchemaExport export = new SchemaExport(config);
// 建表
// 第一个参数: 是否在控制台打印建表语句
// 第二个参数: 是否执行脚本
export.create(true, true);
}
}
8.映射配置
1. 普通字段类型
2. 主键映射
单列主键映射
多列作为主键映射 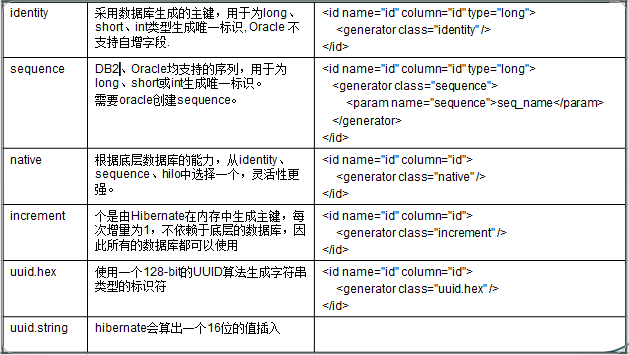
主键生成策略,查看api: 5.1.2.2.1. Various additional generators
数据库:
一个表能否有多个主键? 不能。
为什么要设置主键? 数据库存储的数据都是有效的,必须保持唯一。
(为什么把id作为主键?)
因为表中通常找不到合适的列作为唯一列即主键,所以为了方法用id列,因为id是数据库系统维护可以保证唯一,所以就把这列作为主键!
联合/复合主键
如果找不到合适的列作为主键,出来用id列以外,我们一般用联合主键,即多列的值作为一个主键,从而确保记录的唯一性。
App2.java
package com.xp.c_hbm_config;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
public class App2 {
private static SessionFactory sf;
static {
// 创建sf对象
sf = new Configuration()
.configure()
.addClass(Employee.class) //(测试) 会自动加载映射文件:Employee.hbm.xml
.buildSessionFactory();
}
//1. 保存对象
@Test
public void testSave() throws Exception {
// 对象
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setEmpName("张三");
emp.setWorkDate(new Date());
emp.setDesc("描述");
Session session = sf.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.save(emp);
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}Hibernate3映射数据类型

1. 在实际开发中需要在hbm文件中使用的type属性值是指定的类型。那
么指定的类型一般的是基于hibernate的类型。
2. 当然在实际过程中也可以在hbm文件中指定java类型。

l 流类型
FileInputStream in = newFileInputStream(new File("测试文档.txt"));
int length = in.available();
byte[] b = new byte[length];
in.read(b);
l 时间戳类型
newTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis())
l 查询的排序
session.createQuery("fromDataType as d order by d.id asc");
l 分页
query.setFirstResult(2); query.setMaxResults(2);
l 方法比较
list()/iterator()的区别
package com.xp.d_compositeKey;
public class User {
// 名字跟地址,不会重复
private CompositeKeys keys;
private int age;
public CompositeKeys getKeys() {
return keys;
}
public void setKeys(CompositeKeys keys) {
this.keys = keys;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.xp.d_compositeKey;
import java.io.Serializable;
//复合主键类
public class CompositeKeys implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String userName;
private String address;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
package com.xp.d_compositeKey;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
public class App2 {
private static SessionFactory sf;
static {
// 创建sf对象
sf = new Configuration()
.configure()
.addClass(User.class) //(测试) 会自动加载映射文件:Employee.hbm.xml
.buildSessionFactory();
}
//1. 保存对象
@Test
public void testSave() throws Exception {
Session session = sf.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
// 对象
CompositeKeys keys = new CompositeKeys();
keys.setAddress("广州棠东");
keys.setUserName("Jack");
User user = new User();
user.setAge(20);
user.setKeys(keys);
// 保存
session.save(user);
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
@Test
public void testGet() throws Exception {
Session session = sf.openSession();
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
//构建主键再查询
CompositeKeys keys = new CompositeKeys();
keys.setAddress("广州棠东");
keys.setUserName("Jack");
// 主键查询
User user = (User) session.get(User.class, keys);
// 测试输出
if (user != null){
System.out.println(user.getKeys().getUserName());
System.out.println(user.getKeys().getAddress());
System.out.println(user.getAge());
}
tx.commit();
session.close();
}
}
User.hbm.xml
Hibernate3运行原理
Hibernate的运行过程如下:
1、应用程序先调用Configuration类,该类读取Hibernate配置文件及映射文件中的信息,
2、并用这些信息生成一个SessionFactory对象,
3、然后从SessionFactory对象生成一个Session对象,
4、并用Session对象生成Transaction对象;
A、可通过Session对象的get(),load(),save(),update(),delete()
和saveOrUpdate()等方法对PO进行加载、保存、更新、删除、
等操作;
B、在查询的情况下,可通过Session对象生成一个Query对象,然后
利用Query对象执行查询操作;如果没有异常,Transaction对象将
提交这些操作到数据库中。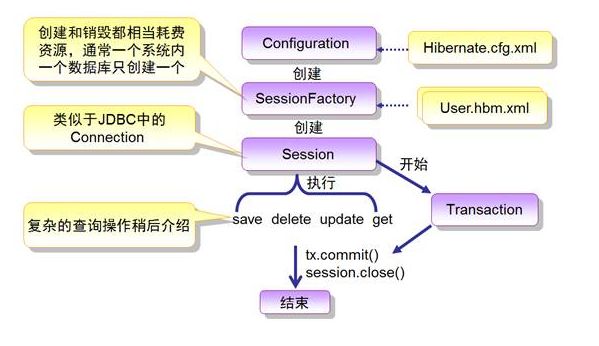
Hibernate3新手容易犯错的地方
1. 错误
hibernate.cfg.xml报错
No suitable driver found for12jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate
2. 错误
cn.itcast.hibernate.apis.HibernateTest is not mapped
3. 错误
Could not determinetype for: String, at table: hibernate_test, for columns

1. 练习:Query对象在获取表的所有的数据的时候,使用list()和 iterator()有什么区别?
# 编写代码的方式不同 list()和iterator()
# 底层发送的SQL语句不同
list()直接一次性获取到所有持久化类的对象
iterator()先获取的是所有的数据的id值。当真正的遍历使用数据的
时候再发送select语句。因此该方法一定要处于session会话中。
# list发送的查询语句只有1条。Iterator发送多条查询语句,因此
iterator的效率低下。懒汉式(iterator) 饿汉式(list)