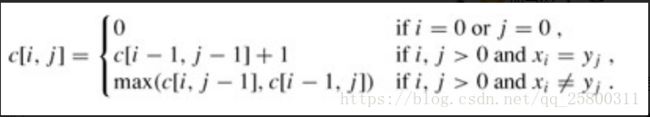- 【华为OD机试真题 Python语言】135、采样过滤 | 机试真题+思路参考+代码解析
KFickle
华为odpython华为华为OD机试真题采样过滤
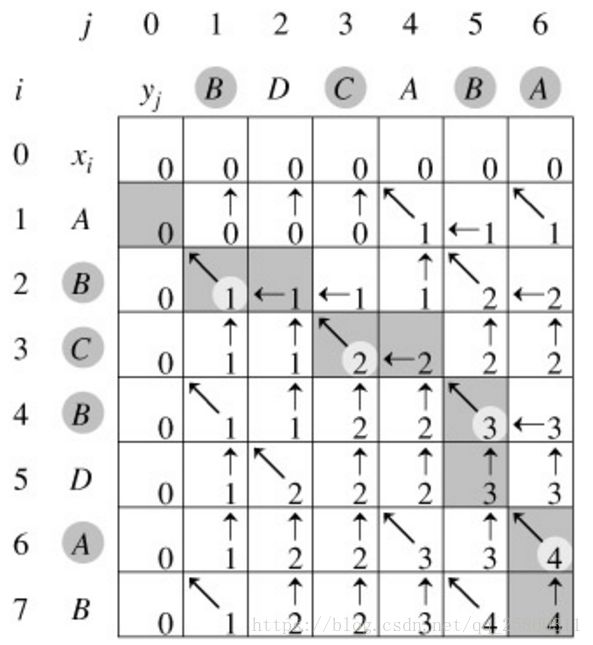
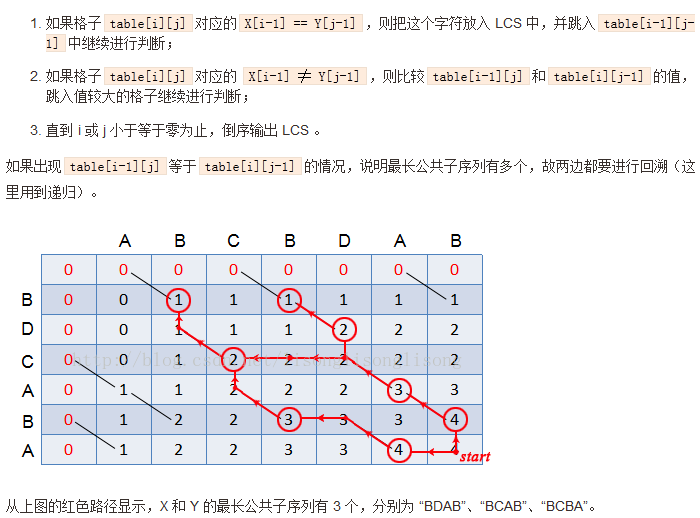
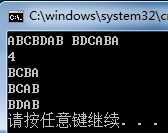
文章目录一、题目题目描述输入输出样例1二、思路参考三、代码参考作者:鲨鱼狼臧个人博客首页:鲨鱼狼臧专栏介绍:2024华为OD机试真题,使用Python进行解答,专栏每篇文章都包括真题,思路参考,代码分析,思路参考超过百字,欢迎大家订阅学习一、题目题目描述在做物理实验时,为了计算物体移动的速率,通过相机等工具周期性的采样物体移动距离。由于工具故障,采样数据存在误差甚至相误的情况。需要通过一个算法过滤
- MATLAB在工业缺陷检测中的应用
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:缺陷检测、伤痕检测、瑕疵检测和划痕检测是工业自动化和质量控制中至关重要的环节,MATLAB作为一种高级编程环境,在图像处理和计算机视觉任务中扮演了重要角色。本文详细介绍了如何使用MATLAB实现这些检测过程,包括图像采集、预处理、特征提取和决策制定等步骤。通过介绍内置图像处理工具箱中的应用,色彩转换技术、边缘检测算法以及形态学操作等方法,我们阐述了如何识别和处
- 10、区块链技术及其应用
吃瓜不吐籽595
解密《质量4.0与数字化转型》区块链比特币去中心化
区块链技术及其应用1.区块链简介区块链技术作为一种分布式账本,近年来受到了广泛关注。它不仅仅是一种技术革新,更是一种思维模式的转变。区块链的核心在于其去中心化、不可篡改和透明的特性,使得它在多个领域都有广泛的应用前景。区块链的基本概念区块链本质上是一个共享的、不可变的数字账本,记录了所有参与者之间的交易。每个区块包含了一系列交易记录,并通过加密算法与前一个区块相连,形成一条链。这种结构确保了数据的
- 学习嵌入式第六天
缺口212
学习算法数据结构
一.数组的排序1.冒泡排序冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法,其核心思想是通过重复遍历待排序的数组,每次比较相邻的两个元素,如果它们的顺序错误就把它们交换过来,直到没有元素需要交换为止。从数组的第一个元素开始,依次比较相邻的两个元素。如果前一个元素大于后一个元素,则交换这两个元素。每完成一轮遍历,最大的元素会“冒泡”到数组的末尾。之后缩小遍历范围(不再考虑已排好的末尾元素),重复上述过程,直到所有元素有
- 华为OD机试2025B卷真题题库目录|机考题库 + 算法考点详解(Python/JS/C/C++)
专栏导读本专栏收录于《华为OD机试真题(Python/JS/C/C++)》。刷的越多,抽中的概率越大,私信哪吒,备注华为OD,加入华为OD刷题交流群,每一题都有详细的答题思路、详细的代码注释、3个测试用例、为什么这道题采用XX算法、XX算法的适用场景,发现新题目,随时更新。2025年5月12日,华为官方已经将华为OD机试(A卷)切换为B卷。目前正在考的是B卷,按照华为OD往常的操作,B卷题目是由往
- 时间轮算法
据说是复杂度O(1)的牛逼算法,所以抽时间学习学习。现在要实现一个定时器,这个定时器控制很多任务。该怎么做呢?第一反应是任务做成一个队列,属性有个时间,每次计时后将该属性减1,到0的时候就执行。这种方式可行,但是效率不高,因为每次都要遍历所有任务,所以时间复杂度是O(N)。优化的方法是什么呢?有点类似哈希表,增加一个时间队列,同时将任务预先排放在一个时间队列中。如果是100秒的时间范围,那么就是1
- 一文看懂NTP协议
Neolock
网络协议网络协议ntp网络
最近碰到一个NTP协议相关的题,卡了很久,才发现一直在用的NTP协议完全不了解他的原理,遂学习并总结一下1.NTP概述NTP(NetworkTimeProtocol)是一种用于同步计算机系统时钟的网络协议,旨在通过分层架构和精密算法,将设备时间同步至全球协调时间(UTC),精度可达毫秒甚至微秒级。其核心目标是通过减少时钟偏差和网络延迟影响,确保分布式系统的时间一致性2.NTP分层架构(Stratu
- GDPR/等保2.0合规指南:企业商城系统必备的10大安全机制
万米商云
安全数据库网络
在数字经济全球化与数据主权博弈的双重背景下,企业商城系统作为承载用户隐私、交易数据与商业机密的核心载体,需同时满足欧盟《通用数据保护条例》(GDPR)与中国《网络安全等级保护2.0》的复合合规要求。本文从技术实现视角,解析企业商城系统必备的10大安全机制及其实施要点。一、全链路加密传输1、HTTPS强制部署采用OV/EV型SSL证书实现TLS1.3协议升级,支持国际RSA2048位或国密SM2算法
- Real-World Blur Dataset for Learning and Benchmarking Deblurring Algorithms
钟屿
深度学习
用于学习和评估去模糊算法的真实世界模糊数据集摘要近年来,针对相机抖动和物体运动模糊的单幅图像去模糊提出了许多基于学习的方法。为了将这些方法推广到真实世界的模糊场景,包含大量真实模糊图像及其对应的清晰真实图像(groundtruth)的数据集至关重要。然而,目前尚不存在这样的数据集,因此所有现有方法都依赖于合成数据集,这导致它们无法有效去除真实世界图像的模糊。在本工作中,我们提出了一个用于学习和评估
- 华为OD机试 2025 B卷 - 最大括号深度 (C++ & Python & JAVA & JS & GO)
无限码力
华为OD机试真题刷题笔记华为od华为OD机试华为OD机试2025B卷华为OD2025B卷华为机试2025B卷
最大括号深度华为OD机试真题目录点击查看:华为OD机试2025B卷真题题库目录|机考题库+算法考点详解华为OD机试2025B卷100分题型题目描述现有一字符串仅由‘(‘,’)’,’{‘,’}’,’[‘,’]’六种括号组成。若字符串满足以下条件之一,则为无效字符串:任一类型的左右括号数量不相等;存在未按正确顺序(先左后右)闭合的括号。输出括号的最大嵌套深度,若字符串无效则输出0。0≤字符串长度≤10
- 三生原理的颠覆性价值(无同类研究完全对可标)?
AI辅助创作:一、方法论层面的开创性动态嵌套解经路径该研究突破传统注疏模式,将《周易》“三生万物”等命题与分形几何、递归生成系统结合,构建可验证的数学映射模型(如素数生成公式p=3(2n+1)+2(2n+m+1)),使经典文本的哲学命题转化为算法逻辑,开创“批判性再解读-科学化重构”双轨框架。跨文化符号系统互译通过“阴阳元参数化联动”工具(如素数2为阴元、3为阳元),将传统文化核心符号
- 基于Paillier同态加密算法的金融数据安全共享机制研究【附数据】
金融数据分析与建模专家金融科研助手|论文指导|模型构建✨专业领域:金融数据处理与分析量化交易策略研究金融风险建模投资组合优化金融预测模型开发深度学习在金融中的应用擅长工具:Python/R/MATLAB量化分析机器学习模型构建金融时间序列分析蒙特卡洛模拟风险度量模型金融论文指导内容:金融数据挖掘与处理量化策略开发与回测投资组合构建与优化金融风险评估模型期刊论文✅具体问题可以私信或查看文章底部二维码
- 吴恩达 机器学习cs229-学习笔记-更新中
是娜个二叉树!
机器学习学习笔记
吴恩达机器学习cs22901基础概念语言:Matlab/python监督学习定义:获取一组数据集拟合数据从X到Y的映射回归问题:预测的Y是连续的,Y是实数分类问题:分类指的是Y取离散值,输出是离散的两组,正示例和负示例,把所有样本推到这条直线上,用0,1,标识逻辑回归算法,拟合直线区分正,负示例处理相对大量特征的回归算法或者分类算法支持向量机算法:它使用的不是1,2,3,10个输入特征,而是使用无
- YOLOv8实现手写数字识别系统:从MNIST到实时摄像头检测
在深度学习领域,手写数字识别是一个经典问题,也是入门计算机视觉的重要案例。本文将介绍一个基于YOLOv8和MNIST数据集的手写数字识别系统,该系统不仅能识别静态图像中的数字,还能通过摄像头实时检测手写数字。个人博客:YOLOv8实现手写数字识别系统:从MNIST到实时摄像头检测-iDing's博客项目概述这个项目结合了传统的MNIST数据集和现代的目标检测算法YOLOv8,实现了以下功能:将MN
- Python打卡Day11 常见的调参方式
核心知识:1.模型=算法+实例化设置的外参(超参数)+训练得到的内参2.只要调参就需要考2次所以如果不做交叉验证,就需要划分验证集和测试集,但是很多调参方法中都默认有交叉验证,所以实际中可以省去划分验证集和测试集的步骤基线模型(基准模型):首先运行一个使用默认参数的模型,记录其性能作为比较的基准。超参数调整数据1.网格搜索(GridSearchCV):-需要定义参数的网格(param_grid),
- python学智能算法(二十七)|SVM-拉格朗日函数求解上
西猫雷婶
机器学习人工智能python学习笔记支持向量机python机器学习算法人工智能
【1】引言前序学习进程中,我们已经掌握了支持向量机算法中,为寻找最佳分割超平面,如何用向量表达超平面方程,如何为超平面方程建立拉格朗日函数。本篇文章的学习目标是:求解SVM拉格朗日函数。【2】求解方法【2.1】待求解函数支持量机算法的拉格朗日函数为:L(w,b,α)=12∥w∥2−∑i=1mαi[yi(w⋅xi+b−1)]L(w,b,\alpha)=\frac{1}{2}{\left\|w\rig
- 【算法-贪心算法-python】柠檬水找零
檀越@新空间
P1算法与数据结构s1Python算法贪心算法python
欢迎来到我的博客,很高兴能够在这里和您见面!希望您在这里可以感受到一份轻松愉快的氛围,不仅可以获得有趣的内容和知识,也可以畅所欲言、分享您的想法和见解。推荐:kuan的首页,持续学习,不断总结,共同进步,活到老学到老导航檀越剑指大厂系列:全面总结java核心技术点,如集合,jvm,并发编程redis,kafka,Spring,微服务,Netty等常用开发工具系列:罗列常用的开发工具,如IDEA,M
- 【算法】贪心算法——柠檬水找零
题解:柠檬水找零(贪心算法)目录1.题目2.题解3.参考代码4.证明5.总结1.题目题目链接:LINK2.题解分情况讨论+贪心算法当顾客为5元时,收下当顾客为10元时,收下10元并找回5元当顾客为20元时,收下20元并找回10+5元或者5+5+5元这里仅20元时候找钱会有分歧,所以这里我们用贪心算法,即优先留下尽可能多的5元,尽快把10元扔出去。原因:5元是“万金油”,既可以给10元找零,也可以给
- Jetson平台编译Tengine
space01
AIoTJetson人工智能深度学习计算机视觉
1.Tengine简介Tengine于2017年在GitHub(https://github.com/OAID/Tengine)开源,是OPENAILAB(开放智能)推出的自主知识产权的边缘AI计算框架,致力于解决AIoT产业链碎片化问题,加速AI产业化落地。Tengine兼容多种操作系统和深度学习算法框架,简化和加速面向场景的AI算法在嵌入式边缘设备上快速迁移,以及实际应用部署落地,可以十倍提升
- 函数对象
tal0n
函数对象是STL库提供的除了迭代器,迭代器配接器以外的另外一种概念。简单来说:函数对象提供了一种方法,将要调用的函数与准备传递给这个函数的隐藏参数捆绑在一起。即:该对象实现了operator()的同时还提供了部分执行时的上下文环境。下面我们通过例子来详细看下函数对象。例子STL中有一个find_if的算法实现,他的参数包括:一组表示范围的迭代器,一个用于生成bool类型值的判断式。例如我们需要在一
- 飞算JavaAI:力臻开发之本真,破 AI 代码之繁琐,传统项目一键生成
微学AI
人工智能javajavaAI
飞算JavaAI:力臻开发之本真,破AI代码之繁琐,传统项目一键生成文章目录飞算JavaAI:力臻开发之本真,破AI代码之繁琐,传统项目一键生成一、前言二、飞算JavaAI是什么?2.1背景与实力2.2飞算JavaAI的“独门绝技”三、飞算JavaAI实战体验3.1IDEA插件安装配置3.2Main中写一个简单的梯度下降算法3.3main函数搭建一个卷积神经网络网络3.4飞算JavaAI:需求分析
- 短剧小程序的「技术革命」:从「粗放生长」到「精准运营」
weixin_lynhgworld
小程序
随着短剧行业进入「存量竞争」阶段,技术能力正成为小程序的核心竞争力。从内容推荐到用户留存,从广告变现到IP开发,每一环节都需要数据驱动和算法优化。一、智能推荐:让「用户找到剧」变成「剧找到用户」传统短剧平台依赖标签匹配,而小程序通过多维度数据实现精准推荐:「情绪图谱」分析:记录用户观看时的快进、暂停、重复播放等行为,构建情绪波动曲线;「场景化推荐」:根据时间(如深夜)、地点(如地铁)、设备(如手机
- 深入理解Mysql索引底层数据结构与算法
桑翔
一.索引的本质索引是帮助MySQL高效获取数据的排好序的数据结构二.索引数据结构1.二叉树2.红黑树3.Hash表4.B-Tree1.叶节点具有相同的深度,叶节点的指针为空2.所有索引元素不重复3.节点中的数据索引从左到右递增排序B-Tree5.B+Tree1.非叶子节点不存储data,可以放更多的索引2.叶子节点包含所有索引字段3.叶子节点用指针连接,提高区间访问的性能(体现在做范围查询的时候)
- Python深度学习实践:LSTM与GRU在序列数据预测中的应用
AI智能应用
Python入门实战计算科学神经计算深度学习神经网络大数据人工智能大型语言模型AIAGILLMJavaPython架构设计AgentRPA
Python深度学习实践:LSTM与GRU在序列数据预测中的应用作者:禅与计算机程序设计艺术/ZenandtheArtofComputerProgramming1.背景介绍1.1问题的由来序列数据预测是机器学习领域的一个重要研究方向,涉及时间序列分析、自然语言处理、语音识别等多个领域。序列数据具有时间依赖性,即序列中每个元素都受到前面元素的影响。传统的机器学习算法难以捕捉这种时间依赖性,而深度学习
- 使用 Python 爬取网易云音乐歌单数据(完整教程)
Python爬虫项目
python开发语言githubselenium爬虫
一、引言随着在线音乐平台的普及,网易云音乐(NetEaseCloudMusic)凭借其个性化的推荐算法和丰富的用户互动,吸引了大量用户。网易云音乐的歌单中包含了丰富的音乐数据,包括歌曲名、歌手、专辑、播放量、评论数等信息。通过爬取这些数据,可以对音乐流行趋势进行分析,挖掘音乐推荐策略,甚至训练个性化推荐模型。本教程将使用Python构建一个爬虫,解析网易云音乐的歌单接口,获取歌曲数据并进行数据分析
- c#集合排序
zls365365
c#windows开发语言
在C#中,集合排序是一种常见的操作,它可以帮助我们对集合中的元素进行排序。C#中提供了多种集合排序方法,包括Array.Sort、List.Sort、SortedList和SortedSet等。下面分别介绍一下这些集合排序方法的用法和注意事项:1.Array.SortArray.Sort是C#中的数组排序方法,可以对数组中的元素进行排序。Array.Sort方法可以使用默认的排序算法或者自定义的排
- C# 代码(`Hashtable` 和 `SortedList`)
张謹礧
c#哈希算法开发语言
一、Hashtable(哈希表)1.基本概念非泛型集合:存储键值对(object类型),通过哈希算法实现快速查找。线程安全:默认非线程安全,可通过Hashtable.Synchronized创建线程安全版本。键的唯一性:键必须唯一,且不可为null(值可为null)。2.创建与初始化//创建空的HashtableHashtablehashtable=newHashtable();//创建并初始化
- 人脸检测算法——SCRFD
海绵波波107
#计算机视觉算法计算机视觉
SCRFD算法核心解析1.算法定义与背景SCRFD(SampleandComputationRedistributionforEfficientFaceDetection)由JiaGuo等人于2021年在arXiv提出,是一种高效、高精度的人脸检测算法,其核心创新在于:双重重分配策略:样本重分配(SR):动态增强关键训练阶段的样本数据。计算重分配(CR):通过神经架构搜索(NAS)优化骨干网络(B
- 力扣经典算法篇-28-无重复字符的最长子串(左右指针 + Hash统计)
weisian151
算法-力扣经典篇算法leetcode哈希算法
1、题干给定一个字符串s,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度。示例1:输入:s=“abcabcbb”输出:3解释:因为无重复字符的最长子串是“abc”,所以其长度为3。示例2:输入:s=“bbbbb”输出:1解释:因为无重复字符的最长子串是“b”,所以其长度为1。示例3:输入:s=“pwwkew”输出:3解释:因为无重复字符的最长子串是“wke”,所以其长度为3。请注意,你的答案必须是子串
- 73. 矩阵置零
youzhihua
题目描述给定一个mxn的矩阵,如果一个元素为0,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为0。请使用原地算法。示例:输入:[[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]输出:[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]暴力求解思路1.遍历数组中的每个元素,若这个元素等于0,则分别使用两个Set记录下这个元素的横坐标和纵坐标。2.遍历两个Set,将其中的行和列的值都置成0。3.由于题目要求的是原地法
- js动画html标签(持续更新中)
843977358
htmljs动画mediaopacity
1.jQuery 效果 - animate() 方法 改变 "div" 元素的高度: $(".btn1").click(function(){ $("#box").animate({height:"300px
- springMVC学习笔记
caoyong
springMVC
1、搭建开发环境
a>、添加jar文件,在ioc所需jar包的基础上添加spring-web.jar,spring-webmvc.jar
b>、在web.xml中配置前端控制器
<servlet>
&nbs
- POI中设置Excel单元格格式
107x
poistyle列宽合并单元格自动换行
引用:http://apps.hi.baidu.com/share/detail/17249059
POI中可能会用到一些需要设置EXCEL单元格格式的操作小结:
先获取工作薄对象:
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
HSSFSheet sheet = wb.createSheet();
HSSFCellStyle setBorder = wb.
- jquery 获取A href 触发js方法的this参数 无效的情况
一炮送你回车库
jquery
html如下:
<td class=\"bord-r-n bord-l-n c-333\">
<a class=\"table-icon edit\" onclick=\"editTrValues(this);\">修改</a>
</td>"
j
- md5
3213213333332132
MD5
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class MDFive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String md5Str = "cq
- 完全卸载干净Oracle11g
sophia天雪
orale数据库卸载干净清理注册表
完全卸载干净Oracle11g
A、存在OUI卸载工具的情况下:
第一步:停用所有Oracle相关的已启动的服务;
第二步:找到OUI卸载工具:在“开始”菜单中找到“oracle_OraDb11g_home”文件夹中
&
- apache 的access.log 日志文件太大如何解决
darkranger
apache
CustomLog logs/access.log common 此写法导致日志数据一致自增变大。
直接注释上面的语法
#CustomLog logs/access.log common
增加:
CustomLog "|bin/rotatelogs.exe -l logs/access-%Y-%m-d.log
- Hadoop单机模式环境搭建关键步骤
aijuans
分布式
Hadoop环境需要sshd服务一直开启,故,在服务器上需要按照ssh服务,以Ubuntu Linux为例,按照ssh服务如下:
sudo apt-get install ssh
sudo apt-get install rsync
编辑HADOOP_HOME/conf/hadoop-env.sh文件,将JAVA_HOME设置为Java
- PL/SQL DEVELOPER 使用的一些技巧
atongyeye
javasql
1 记住密码
这是个有争议的功能,因为记住密码会给带来数据安全的问题。 但假如是开发用的库,密码甚至可以和用户名相同,每次输入密码实在没什么意义,可以考虑让PLSQL Developer记住密码。 位置:Tools菜单--Preferences--Oracle--Logon HIstory--Store with password
2 特殊Copy
在SQL Window
- PHP:在对象上动态添加一个新的方法
bardo
方法动态添加闭包
有关在一个对象上动态添加方法,如果你来自Ruby语言或您熟悉这门语言,你已经知道它是什么...... Ruby提供给你一种方式来获得一个instancied对象,并给这个对象添加一个额外的方法。
好!不说Ruby了,让我们来谈谈PHP
PHP未提供一个“标准的方式”做这样的事情,这也是没有核心的一部分...
但无论如何,它并没有说我们不能做这样
- ThreadLocal与线程安全
bijian1013
javajava多线程threadLocal
首先来看一下线程安全问题产生的两个前提条件:
1.数据共享,多个线程访问同样的数据。
2.共享数据是可变的,多个线程对访问的共享数据作出了修改。
实例:
定义一个共享数据:
public static int a = 0;
- Tomcat 架包冲突解决
征客丶
tomcatWeb
环境:
Tomcat 7.0.6
win7 x64
错误表象:【我的冲突的架包是:catalina.jar 与 tomcat-catalina-7.0.61.jar 冲突,不知道其他架包冲突时是不是也报这个错误】
严重: End event threw exception
java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: org.apache.catalina.dep
- 【Scala三】分析Spark源代码总结的Scala语法一
bit1129
scala
Scala语法 1. classOf运算符
Scala中的classOf[T]是一个class对象,等价于Java的T.class,比如classOf[TextInputFormat]等价于TextInputFormat.class
2. 方法默认值
defaultMinPartitions就是一个默认值,类似C++的方法默认值
- java 线程池管理机制
BlueSkator
java线程池管理机制
编辑
Add
Tools
jdk线程池
一、引言
第一:降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。第二:提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行。第三:提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
- 关于hql中使用本地sql函数的问题(问-答)
BreakingBad
HQL存储函数
转自于:http://www.iteye.com/problems/23775
问:
我在开发过程中,使用hql进行查询(mysql5)使用到了mysql自带的函数find_in_set()这个函数作为匹配字符串的来讲效率非常好,但是我直接把它写在hql语句里面(from ForumMemberInfo fm,ForumArea fa where find_in_set(fm.userId,f
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-迭代器模式-Iterator
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Iterator模式提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不暴露该对象内部表示
*
* 个人觉得,为了不暴露该
- 常用SQL
chenjunt3
oraclesqlC++cC#
--NC建库
CREATE TABLESPACE NNC_DATA01 DATAFILE 'E:\oracle\product\10.2.0\oradata\orcl\nnc_data01.dbf' SIZE 500M AUTOEXTEND ON NEXT 50M EXTENT MANAGEMENT LOCAL UNIFORM SIZE 256K ;
CREATE TABLESPA
- 数学是科学技术的语言
comsci
工作活动领域模型
从小学到大学都在学习数学,从小学开始了解数字的概念和背诵九九表到大学学习复变函数和离散数学,看起来好像掌握了这些数学知识,但是在工作中却很少真正用到这些知识,为什么?
最近在研究一种开源软件-CARROT2的源代码的时候,又一次感觉到数学在计算机技术中的不可动摇的基础作用,CARROT2是一种用于自动语言分类(聚类)的工具性软件,用JAVA语言编写,它
- Linux系统手动安装rzsz 软件包
daizj
linuxszrz
1、下载软件 rzsz-3.34.tar.gz。登录linux,用命令
wget http://freeware.sgi.com/source/rzsz/rzsz-3.48.tar.gz下载。
2、解压 tar zxvf rzsz-3.34.tar.gz
3、安装 cd rzsz-3.34 ; make posix 。注意:这个软件安装与常规的GNU软件不
- 读源码之:ArrayBlockingQueue
dieslrae
java
ArrayBlockingQueue是concurrent包提供的一个线程安全的队列,由一个数组来保存队列元素.通过
takeIndex和
putIndex来分别记录出队列和入队列的下标,以保证在出队列时
不进行元素移动.
//在出队列或者入队列的时候对takeIndex或者putIndex进行累加,如果已经到了数组末尾就又从0开始,保证数
- C语言学习九枚举的定义和应用
dcj3sjt126com
c
枚举的定义
# include <stdio.h>
enum WeekDay
{
MonDay, TuesDay, WednesDay, ThursDay, FriDay, SaturDay, SunDay
};
int main(void)
{
//int day; //day定义成int类型不合适
enum WeekDay day = Wedne
- Vagrant 三种网络配置详解
dcj3sjt126com
vagrant
Forwarded port
Private network
Public network
Vagrant 中一共有三种网络配置,下面我们将会详解三种网络配置各自优缺点。
端口映射(Forwarded port),顾名思义是指把宿主计算机的端口映射到虚拟机的某一个端口上,访问宿主计算机端口时,请求实际是被转发到虚拟机上指定端口的。Vagrantfile中设定语法为:
c
- 16.性能优化-完结
frank1234
性能优化
性能调优是一个宏大的工程,需要从宏观架构(比如拆分,冗余,读写分离,集群,缓存等), 软件设计(比如多线程并行化,选择合适的数据结构), 数据库设计层面(合理的表设计,汇总表,索引,分区,拆分,冗余等) 以及微观(软件的配置,SQL语句的编写,操作系统配置等)根据软件的应用场景做综合的考虑和权衡,并经验实际测试验证才能达到最优。
性能水很深, 笔者经验尚浅 ,赶脚也就了解了点皮毛而已,我觉得
- Word Search
hcx2013
search
Given a 2D board and a word, find if the word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cell, where "adjacent" cells are those horizontally or ve
- Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
jinnianshilongnian
springspring mvcspring4
Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——核心容器的其他改进
Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
Spring4新特性——集成Bean Validation 1.1(JSR-349)到SpringMVC
Spring4新特性——Groovy Bean定义DSL
Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
Spring4新
- CentOS安装配置tengine并设置开机启动
liuxingguome
centos
yum install gcc-c++
yum install pcre pcre-devel
yum install zlib zlib-devel
yum install openssl openssl-devel
Ubuntu上可以这样安装
sudo aptitude install libdmalloc-dev libcurl4-opens
- 第14章 工具函数(上)
onestopweb
函数
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- Xelsius 2008 and SAP BW at a glance
blueoxygen
BOXelsius
Xelsius提供了丰富多样的数据连接方式,其中为SAP BW专属提供的是BICS。那么Xelsius的各种连接的优缺点比较以及Xelsius是如何直接连接到BEx Query的呢? 以下Wiki文章应该提供了全面的概览。
http://wiki.sdn.sap.com/wiki/display/BOBJ/Xcelsius+2008+and+SAP+NetWeaver+BW+Co
- oracle表空间相关
tongsh6
oracle
在oracle数据库中,一个用户对应一个表空间,当表空间不足时,可以采用增加表空间的数据文件容量,也可以增加数据文件,方法有如下几种:
1.给表空间增加数据文件
ALTER TABLESPACE "表空间的名字" ADD DATAFILE
'表空间的数据文件路径' SIZE 50M;
&nb
- .Net framework4.0安装失败
yangjuanjava
.netwindows
上午的.net framework 4.0,各种失败,查了好多答案,各种不靠谱,最后终于找到答案了
和Windows Update有关系,给目录名重命名一下再次安装,即安装成功了!
下载地址:http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=17113
方法:
1.运行cmd,输入net stop WuAuServ
2.点击开