Spring注解驱动开发之生命周期
回顾
Spring注解驱动开发之组件注册
介绍
bean的生命周期: bean的创建----初始化----销毁
Spring容器为我们管理了该周期, 但是我们也可以自定义该周期, 容器中的bean在进行到相对应的阶段时则调用我们自定义的方法.
3种初始化方法以及1种初始化前后的拦截方法
1. 通过@Bean指定自定义的初始化方法和自定义的销毁方法
① 创建一个Car类
public class Car {
public Car() {
System.out.println("Car对象被创建...");
}
/**
* 自定义一个初始化对象方法
*/
public void init(){
System.out.println("Car对象被初始化...");
}
/**
* 自定义一个销毁对象方法
*/
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Car对象被销毁...");
}
}② 创建一个配置类MyConfigOfLifeCycle
@Configuration
public class MyConfigOfLifeCycle {
@Bean(initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy")//指定初始化方法和销毁方法
public Car car(){
return new Car();
}
}③ 测试
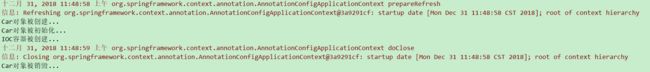
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfigOfLifeCycle.class);
System.out.println("IOC容器被创建..."); //此时会创建并初始化所有的单例对象
applicationContext.close();
}④ 结果如下
ps: 如果是多实例的, 则会在调用的时候对象才会被创建和初始化, 且容器不再管理这些多例的对象, 所有当关闭容器时无法销毁该对象
⑤ 修改为多例
@Configuration
public class MyConfigOfLifeCycle {
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean(initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy")//指定初始化方法和销毁方法
public Car car(){
return new Car();
}
}⑥ 再测试
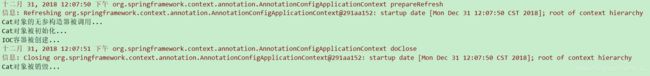
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfigOfLifeCycle.class);
System.out.println("IOC容器被创建..."); //此时会创建并初始化所有的单例对象
applicationContext.getBean("car");
applicationContext.close();
}⑦ 结果如下
2. 通过让bean实现接口InitializingBean来实现初始化逻辑, 同理, 通过让bean实现接口DisposableBean来实现销毁逻辑
① 创建一个Cat类, 并使用组件注解
@Component
public class Cat implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Cat() {
System.out.println("Cat对象的无参构造器被调用...");
}
/**
* 销毁方法, 在容器关闭时被调用
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Cat对象被销毁...");
}
/**
* 初始化方法, 在对象创建并设置完所有属性后被调用
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Cat对象被初始化...");
}
}② 使用组件扫描注解将组件注入容器中
@ComponentScan("com.spring.annotation.bean")
@Configuration
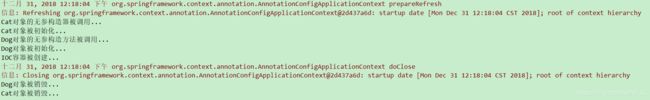
public class MyConfigOfLifeCycle {...}③ 测试, 结果如下
3. 使用JSR250规范定义的注解@PostConstruct和注解@PreDestroy
@PostConstruct
在bean创建并属性赋值完成后调用该注解下的方法
@PreDestroy
在bean被销毁之前通知该注解下的方法
创建一个Dog对象并标上相应的注解
@Component
public class Dog {
public Dog() {
System.out.println("Dog对象的无参构造方法被调用...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Dog对象被初始化...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Dog对象被销毁...");
}
}测试结果如下
4. bean的后置处理器, BeanPostProcessor接口, 用于初始化前后的拦截操作
创建一个实现BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类MyBeanPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* @param bean 刚创建还未初始化的实例
* @param beanName bean的名称
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(beanName+"初始化之前==>"+bean);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(beanName+"初始化之后==>"+bean);
return bean;
}
}测试结果如下
Spring注解驱动的生命周期部分整理完了, 接下来会写自动装配部分.