Spring5 事件驱动模型分析
目录
- 简介
- 概念
- 核心组成
- Spring中事件驱动模型核心组成
- 案例说明
- 原理分析
- 事件广播器初始化
- 事件对象ApplicationContextEvent分析
- 注册监听事件
- 事件发布和事件监听器执行
- 相关
- 参考
- 源码
简介
事件驱动模型,也即是我们通常说的观察者设计模式的一种实现方式。
概念
定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生变化时,所有依赖它的对象都得到通知并自动更新。
核心组成
- 事件源:负责产生事件的对象。比如我们常见的按钮,按钮就是一个事件源,能够产生“点击”这个事件
- 事件监听器/事件处理器:负责处理事件的对象
- 事件:或者称为事件对象,是事件源和事件监听器之间的信息桥梁。是整个事件模型驱动的核心
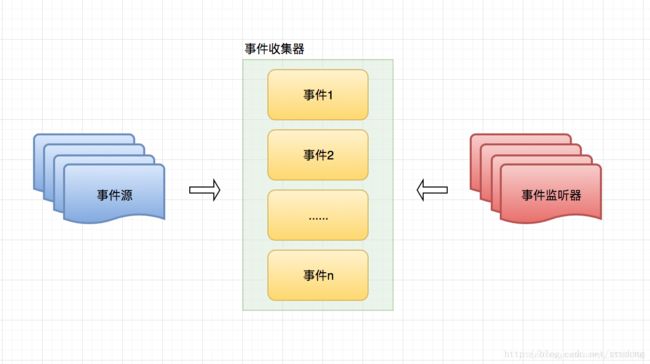
图片引自:https://blog.csdn.net/zrudong/article/details/78567473
Spring中事件驱动模型核心组成
- 事件对象:ApplicationContextEvent
- 事件源:AbstractApplicationContext
- 事件监听器/事件处理器:ApplicationListener的实现类
- 事件发布者:ApplicationEventPublisher
- 事件广播器:ApplicationEventMulticaster
案例说明
用户注册功能需要实现:
- 注册用户
- 加积分
- 发确认邮件
- 如果是游戏帐户,可能赠送游戏大礼包
- 索引用户数据
以下案例通过使用Spring事件监听机制实现注册核心功能和辅助业务解耦
部分核心代码如下:
// 事件本身
public class RegisterEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
// User对象为事件源
public RegisterEvent(User user) {
super(user);
}
}
-----
// 监听用户注册事件,异步发送邮件
@Component
public class EmailRegisterListener implements ApplicationListener<RegisterEvent> {
// 异步执行
@Async
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(final RegisterEvent event) {
System.out.println("注册成功,发送确认邮件给:" + ((User)event.getSource()).getUsername());
}
}
------
// 监听用户注册事件,索引用户信息
@Component
public class
IndexRegisterListener implements ApplicationListener<RegisterEvent> {
@Async
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(final RegisterEvent event) {
System.out.println("注册成功,索引用户信息:" + ((User)event.getSource()).getUsername());
}
}
---------
@Service
public class RegisterService {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public void register(String username, String password) {
System.out.println(username + "注册成功!");
// 发布事件
publishRegisterEvent(new User(username, password));
}
private void publishRegisterEvent(User user) {
applicationContext.publishEvent(new RegisterEvent(user));
}
}
--------
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过配置文件方式初始化上下文
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-config-register.xml");
RegisterService registerService = context.getBean(RegisterService.class);
registerService.register("long", "123");
}
-----------------------
<context:component-scan base-package="com.sishuok"/>
<!-- 任务调度器 -->
<task:scheduler id="scheduler" pool-size="10"/>
<!-- 任务执行器 -->
<task:executor id="executor" pool-size="10"/>
<!--开启注解调度支持 @Async @Scheduled-->
<task:annotation-driven executor="executor" scheduler="scheduler" proxy-target-class="true"/>
测试输出如下:
long注册成功!
注册成功,发送确认邮件给:long
注册成功,索引用户信息:long
注册成功,赠送游戏大礼包给:long
注册成功,赠送积分给:long
案例核心
- 事件源 :User 对象
- 事件类型 :注册事件RegisterEvent
- 事件监听器 : IndexRegisterListener 、EmailRegisterListener
- 事件发布: …ApplicationContext 继承了ApplicationEventPublisher,具有事件发布的能力
- 异步执行注解: @Async
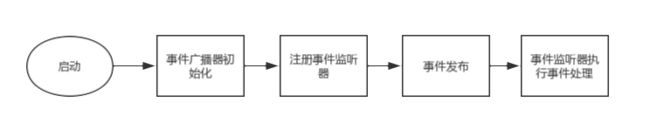
原理分析
事件广播器初始化
// org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
// 事件广播器初始化
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
// 注册事件监听器
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
初始化核心代码
public static final String APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME = "applicationEventMulticaster";
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
// 判断是否已加载bean:applicationEventMulticaster
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 已加载,applicationEventMulticaster 赋值
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
// 未加载,创建SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象并赋值
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
// 注册bean
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
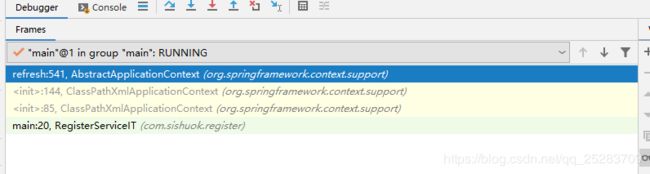
- 由
AbstractApplicationContext类图可知,AbstractApplicationContext本身具有事件发布的功能 - 事件广播器初始化过程完成了事件创博对象的创建、注册和注入到具有事件发布功能的AbstractApplicationContext``中。
事件对象ApplicationContextEvent分析
先说下EventObject对象,java中所有事件对象均为EventObject子类。类声明和注释如下:
/**
*
* 从中派生所有事件状态对象的根类。
* The root class from which all event state objects shall be derived.
*
* All Events are constructed with a reference to the object, the "source",
* that is logically deemed to be the object upon which the Event in question
* initially occurred upon.
*
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public class EventObject implements java.io.Serializable {
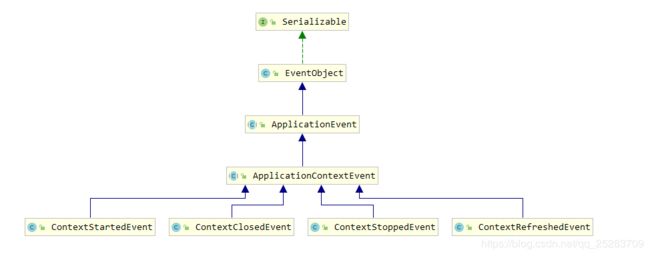
- ApplicationContextEvent也不例外,也为EventObject的派生类。
- 由ApplicationContextEvent派生出四个和应用上下文相关的事件
- ContextStartedEvent:容器启动后触发的事件。
- ContextRefreshedEvent:容器初始化或者刷新完成后触发的事件。
- ContextStopedEvent:容器停止后触发的事件。
- ContextClosedEvent:容器关闭后触发的事件。
源码如下:
public abstract class ApplicationContextEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
/**
* Create a new ContextStartedEvent.
* @param source the {@code ApplicationContext} that the event is raised for
* (must not be {@code null})
*/
public ApplicationContextEvent(ApplicationContext source) { //1
super(source);
}
/**
* Get the {@code ApplicationContext} that the event was raised for.
*/
public final ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { //2
return (ApplicationContext) getSource();
}
}
1.构造函数,声明事件源对象ApplicationContext。查看源码可知,由ApplicationContextEvent 派生出的四个应用上下文事件,事件源对象也为ApplicationContext,eg:
public class ContextClosedEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
/**
* Creates a new ContextClosedEvent.
* @param source the {@code ApplicationContext} that has been closed
* (must not be {@code null})
*/
public ContextClosedEvent(ApplicationContext source) {
super(source);
}
}
2.获取事件源对象方法,即获取应用上下文对象。
注册监听事件
核心代码如下
// org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#registerListeners()
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
//首先注册静态指定的侦听器。 --- Spring本身的事件监听器
for (ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
// 注册到时间广播器中
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
// 获取ApplicationListeners实现类
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
// 注册到时间广播器中
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
事件发布和事件监听器执行
// org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType)
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
// 转成spring事件
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
// 通过事件广播器发布事件
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
发布事件方法详情如下
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 获取注册到事件广播器中监听指定事件类型的事件集合,遍历执行对应事件监听器
//type:org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent
//type:com.sishuok.register.RegisterEvent
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
// taskExecutor属性存在,异步执行监听事件
// eg-1: 使用@Async
// eg-2:
// 相关
参考
- https://blog.csdn.net/zrudong/article/details/78567473
- https://www.iteye.com/blog/jinnianshilongnian-1902886
源码
https://github.com/hdlxt/event