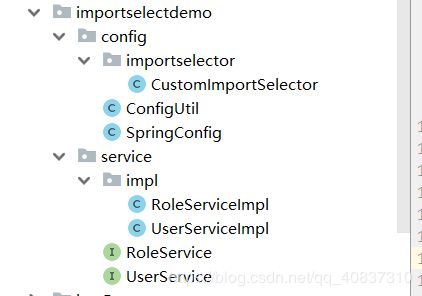
Spring高级之注解@Import注解、ImportSelector、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar详解(超详细)
定义/作用
@Import注解只能作用在类上,一种使用场景是在spring注解驱动开发环境下与配置类配合使用的,其作用是引用其他配置类。使得我们可以和早起的基于XML配置文件开发那样。使用不同的配置类配置不同的内容,比如Mysql数据源配置用一个配置类。Redis数据源配置用一个配置类等。然后使用在注解在一个主配置类中引入这些从配置类,使得配置更加清晰。被引入的类可以不使用@Configuration、@Component注解。
另一种使用 场景是该注解也是一种注册bean的方案。可以在配置类中使用Import注册组件。可以配合ImportSelector、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar按一定规则进行组件的批量注册。
源码:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Import {
/**
* 要引入的配置类,也可以引入ImportSelector、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar过滤器和注册器
* 按照一定的规则进行组件的引入。
*/
Class<?>[] value();
}
使用方式:
不成功的情况:
/**
* @author YeHaocong
* @decription 主配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
}
/**
* @author YeHaocong
* @decription Mysql数据源配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class MysqlConfig {
@Bean
public DruidDataSource dataSource() throws IOException {
//创建druid数据源
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
//加载配置文件,作为数据源的初始化属性
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("daoconfig/datasource-config.properties");
dataSource.setConnectProperties(properties);
//返回dataSource,spring会把他注册到IOC容器中。
return dataSource;
}
//.....
}
//测试类
public class ImportDemoTest {
//引入主配置类创建容器
private AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
@Test
public void testImportDemo(){
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) context.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
}
配置文件:
执行结果:
![]()
分析:因为容器是引入主配置类创建,而没有引入mysql数据源配置类,所以不会扫描创建数据源。
使用Import注解解决:
/**
* @author YeHaocong
* @decription 主配置文件
*/
@Configuration
//使用import注解,把其他从配置类引入
@Import({MysqlConfig.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
/**
* @author YeHaocong
* @decription Mysql数据源配置文件
*/
//从配置类可以不使用@Configuration和Component等注解。
public class MysqlConfig {
@Bean
public DruidDataSource dataSource() throws IOException {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
//加载配置文件,作为数据源的初始化属性
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("daoconfig/datasource-config.properties");
dataSource.setConnectProperties(properties);
//返回dataSource,spring会把他注册到IOC容器中。
return dataSource;
}
//.....
}
被引入的类会被注册到spring的IOC容器中,并且组件id为类的全限定名称,比如上面的:
public class ImportDemoTest {
private AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
@Test
public void testImportDemo(){
//获取MysqlConfig配置组件
MysqlConfig mysqlConfig = context.getBean(MysqlConfig.class);
System.out.println(mysqlConfig);
//获取注解中所有的组件名称
String[] beanNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName:beanNames)
System.out.println(beanName);
}
}
ImportSelector和ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
我们注册bean的方式有很多种。
比如:
- 我们自己写的类,可以使用@Component及其衍生类进行注册。
- 到导入第三方库时,可以使用@Bean注解和@Import注解进行注册。
但是,当要注册的类很多时,每个类上加注解,写Bean方法注册,用Import方法导入大量的Bean时,会显得很繁琐,此时可以使用自定义ImportSelector和ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar来实现组件的批量注册。spring boot有很多EnableXXX的注解,绝大多数多借助了ImportSelector和ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar。
共同点:
- 他们都用于动态注册bean对象到容器中,并且支持大批量的bean导入。
区别:
- ImportSelector是一个接口,我们在使用时需要提供自己的实现类,实现类中重写的方法返回要注册的bean的全限定名数组。然后ConfigurationClassParser类中的precessImports方法注册bean对象。
- ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar也是一个接口,需要我们自己提供实现类,在实现类中手动注册bean到容器中。
注意事项:实现了ImportSelector和ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的类不会被解析成一个bean添加到容器中。
ImportSelector
/**
* @author YeHaocong
* @decription 自定义的ImportSelector,导入选择器。
* 1. 通过AspectJ表达式进行类型筛选。
* 2. 当使用该选择器的配置类没有使用@ComponentScan注解指定扫描包时,会扫描该配置类所在包及其子包。
*/
public class CustomImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
//AspectJ表达式
private String expression;
public CustomImportSelector() throws IOException {
try {
//载入配置文件,创建一个Properties对象
Properties props = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("import/custom-import-selector.properties");
//获取配置文件配置的键为 expression的值,并赋值给expression变量
expression = props.getProperty("expression");
if (expression == null || expression.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("配置文件import/custom-import-selector.properties 的expression 不存在");
}
}
catch (RuntimeException e){
throw e;
}
}
/**
*
* @param importingClassMetadata 参数是被Import注解作用的配置类的注解元信息
* @return 返回的是要注册的组件的类的全限定名数组。
*/
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
//定义要扫描的基础包
String[] basePackages = null;
//获取ComponentScan注解的全限定名称。
String ComponentScanName = ComponentScan.class.getName();
//判断被Import注解作用的类上是否有@ComponentScan注解
if (importingClassMetadata.hasAnnotation(ComponentScanName)){
//有@ComponentScan注解,获取该注解上的属性配置,封装成Map对象。
Map<String,Object> attributes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ComponentScanName);
//获取@ComponentScan注解的value属性或者basePackages属性,因为他们是互为别名,所以获取其中一个即可。
basePackages = (String[]) attributes.get("basePackages");
}
//判断是否有ComponentScan注解或者ComponentScan注解是否有指定扫描包。
//当basePackages为null时,表示没有ComponentScan注解。
//当basePackages.length等于0时,表示有basePackages注解,但是没有指定扫描的包。
if (basePackages == null || basePackages.length == 0){
//如果@Import注解作用的配置类上没有ComponentScan注解或者有ComponentScan注解但是没有指定扫描包的情况下。
//我们就扫描该配置类所在包及其子包。
String basePackage = null;
//获取被Import注解作用的配置类所在的包。
try {
basePackage = Class.forName(importingClassMetadata.getClass().getName()).getPackage().getName();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//把包名设置到basePackages中。
basePackages = new String[]{basePackage};
}
//创建类路径扫描器,参数的含义是不使用默认的过滤规则,与@ComponentScan注解的 useDefaultFilters属性一样。
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = new ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider(false);
//创建类型过滤器,此处使用AspectJ类型过滤器。传入参数是AspectJ表达式和类加载器对象
TypeFilter typeFilter = new AspectJTypeFilter(expression,CustomImportSelector.class.getClassLoader());
//类型过滤器添加到扫描器中。添加的是包含扫描器。
scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter);
//定义要扫描类的全限定类名的集合
Set<String> classes = new HashSet<>();
//遍历基础扫描类数组,得到要扫描的类的全限定名,并添加到集合中
for (String basePackage: basePackages){
//扫描基础包,获取扫描到的BeanDefinition集合
Set<BeanDefinition> candidateComponents = scanner.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
//遍历。获取全限定名添加到集合中。
for (BeanDefinition beanDefinition: candidateComponents){
classes.add(beanDefinition.getBeanClassName());
}
}
//返回集合
return classes.toArray(new String[classes.size()]);
}
}
/**
*配置类
*/
@Configuration
@Import({CustomImportSelector.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
//还有两个业务接口和两个业务接口实现类和一个ConfigUtil,这两个业务实现类和ConfigUtil类都是要注册的组件。这里不再贴出,可以看上面包结构。
public class TestImportSelector {
private AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
@Test
public void TestImportSelector(){
//根据类型获取bean
try {
ConfigUtil configUtil = (ConfigUtil) context.getBean(ConfigUtil.class);
System.out.println(configUtil);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {
RoleService roleService = (RoleService) context.getBean(RoleService.class);
System.out.println(roleService);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean(UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
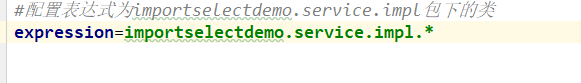
配置文件:
执行结果:
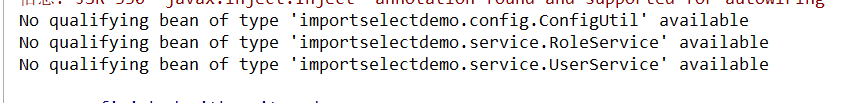
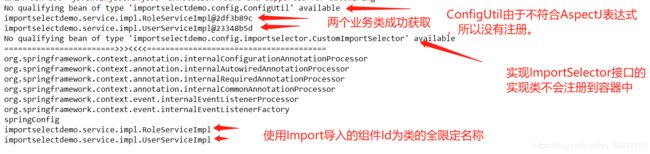
分析:一个bean都没有注册成功,原因是:
配置类SpringConfig上没有使用@ComponentScan或者使用了但是没有配置扫描包。所以会扫描配置类所在包及其子包,看上面包结果。明显没有扫描到service包。所以两个业务实现类没有被注册到容器中。而ConfigUtil虽然被扫描到了,但是由于不符合AspectJ表达式而没有被添加到选择器中。
接下来我们使用@ComponentScan扫描指定包。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "importselectdemo")
@Import({CustomImportSelector.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
/**
*测试类
*/
public class TestImportSelector {
private AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
@Test
public void TestImportSelector(){
//根据类型获取bean
try {
ConfigUtil configUtil = (ConfigUtil) context.getBean(ConfigUtil.class);
System.out.println(configUtil);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {
RoleService roleService = (RoleService) context.getBean(RoleService.class);
System.out.println(roleService);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean(UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {
CustomImportSelector selector = (CustomImportSelector) context.getBean(CustomImportSelector.class);
System.out.println(selector);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
String[] beanNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName:beanNames){
System.out.println(beanName);
}
}
}
注意:不能导入配置类自身,因为,这样会导致报错。
将表达式设置为: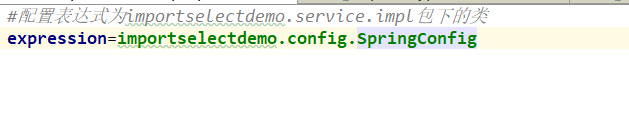
结果:
org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.BeanDefinitionParsingException: Configuration problem: A circular @Import has been detected: Illegal attempt by @Configuration class 'SpringConfig' to import class 'SpringConfig' as 'SpringConfig' is already present in the current import stack [SpringConfig->SpringConfig]
Offending resource: importselectdemo.config.SpringConfig
使用上述方法只要符合CustomImportSelector规则,即使不使用@Component等注解也会注册到容器中。
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
这个注册器不会把扫描到的类返回,而是把扫描到的类直接就在这里注册了。
demo(扫描逻辑与上面的CustomImportSelector一样):
/**
* @author YeHaocong
* @decription 自定义的ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,导入注册器。
* 1. 通过AspectJ表达式进行类型筛选。
* 2. 当使用该选择器的配置类没有使用@ComponentScan注解指定扫描包时,会扫描该配置类所在包及其子包。
* 3. CustomImportDefinitionRegistrar会扫描指定包里,符合AspectJ表达式的组件的类进行注册
*/
public class CustomImportDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
//AspectJ表达式
private String expression;
public CustomImportDefinitionRegistrar() throws IOException {
try {
//载入配置文件,创建一个Properties对象
Properties props = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("import/custom-import-selector.properties");
//获取配置文件配置的键为 expression的值,并赋值给expression变量
expression = props.getProperty("expression");
if (expression == null || expression.isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("配置文件import/custom-import-selector.properties 的expression 不存在");
}
}
catch (RuntimeException e){
throw e;
}
}
/**
*
* @param importingClassMetadata 参数是被Import注解作用的配置类的注解元信息
* @param registry BeanDefinition注册器,会将扫描到的类直接使用该注册器进行注册
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//定义要扫描的基础包
String[] basePackages = null;
//获取ComponentScan注解的全限定名称。
String ComponentScanName = ComponentScan.class.getName();
//判断被Import注解作用的类上是否有@ComponentScan注解
if (importingClassMetadata.hasAnnotation(ComponentScanName)){
//有@ComponentScan注解,获取该注解上的属性配置,封装成Map对象。
Map<String,Object> attributes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(ComponentScanName);
//获取@ComponentScan注解的value属性或者basePackages属性,因为他们是互为别名,所以获取其中一个即可。
basePackages = (String[]) attributes.get("basePackages");
}
//判断是否有ComponentScan注解或者ComponentScan注解是否有指定扫描包。
//当basePackages为null时,表示没有ComponentScan注解。
//当basePackages.length等于0时,表示有basePackages注解,但是没有指定扫描的包。
if (basePackages == null || basePackages.length == 0){
//如果@Import注解作用的配置类上没有ComponentScan注解或者有ComponentScan注解但是没有指定扫描包的情况下。
//我们就扫描该配置类所在包及其子包。
String basePackage = null;
//获取被Import注解作用的配置类所在的包。
try {
basePackage = Class.forName(importingClassMetadata.getClass().getName()).getPackage().getName();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//把包名设置到basePackages中。
basePackages = new String[]{basePackage};
}
//创建类路径扫描器ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,参数的含义是不使用默认的过滤规则,与@ComponentScan注解的 useDefaultFilters属性一样。
//registry参数是将扫描到的类使用指定的registry注册器注册
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(registry,false);
//创建类型过滤器,此处使用AspectJ类型过滤器。传入参数是AspectJ表达式和类加载器对象
TypeFilter typeFilter = new AspectJTypeFilter(expression,CustomImportSelector.class.getClassLoader());
//类型过滤器添加到扫描器中。添加的是包含扫描器。
scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter);
//进行扫描
scanner.scan(basePackages);
}
}
//配置类:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "importselectdemo")
//使用CustomImportDefinitionRegistrar
@Import({CustomImportDefinitionRegistrar.class})
public class SpringConfig {
}
- ConfigUtil不符合AspectJ表达式规则,所以没有注册。
- 业务类注册成功。
- 实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口的类不会被添加到容器中。
- 因为使用的是BeanDefinitionRegistry注册器,所以注册的bean id 默认是类的名字第一个转小写。而不是全限定名称。
使用上述方法只要符合CustomImportDefinitionRegistrar规则,即使不使用@Component等注解也会注册到容器中。