rapidxml库生成xml小例子及需注意的问题
结论:rapidxml和pugixml在生成xml方面,我建议使用pugixml,优点很多,不用关心string的生命周期,像函数一样使用添加节点,属性,很方便;而且效率高,个人测试了下:生成300个xml文件,pugixml用时6s,rapidxml用时60+s,效率差了10倍
如果你工作必须使用rapidxml或者换起来麻烦,那么继续往下看,有关写xml需要注意的一些问题
rapidxml 下载:
在官网上下载即可,
http://rapidxml.sourceforge.net/
https://sourceforge.net/projects/rapidxml/
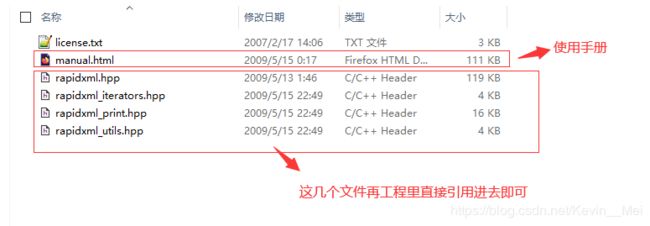
得到的压缩包里有文件如下:
读取或者解析xml,这篇大佬写的比较全面:
https://blog.csdn.net/v_xchen_v/article/details/75634273
这里补充下生成xml方面需要注意的问题:
1. 字符串的生命周期问题:每次添加节点,string需要使用rapidxml的内存申请函数
如果给节点赋值的是一个局部变量string或者char*,如果局部变量的生命周期,那么节点的值就会为空,建议使用rapidxml自带的allocate_string方法来申请字符串内存,这样它的生命周期和节点的值必然是一致的了;
2. 节点包含中文的情况(这部分个人理解,如有不对,恳请斧正)
先说我们要写的xml文件如下:
小王子
一般写的话,还有,这是我们常见的,同样有 等,编码格式声明;
使用rapidxml,写入字符串,有char *和wchar_t *的区别,默认是char *
// char * 方式
rapidxml::xml_node<>* rot = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_pi, xml_doc.allocate_string("xml version='1.0' encoding='gbk'"));
// wchar_t * 方式
rapidxml::xml_node* rot = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_pi, xml_doc.allocate_string(L"xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'"));
如果你用的是char*,然后节点包含中文,这时候声明为:,那么生成的xml文件在浏览器里会报错,如下所示:

所以这里建议:如果你用的是char*,然后节点包含中文,使用这个声明;
当然最好的,是用wchar_t *,节点包含中文,就可以使用声明,不用担心编码解析问题
3. 节点写入int,float等类型的值
int, float,bool需要转换成char*字符串再写入节点,这里觉得使用不方便,不过还是提供下转换的函数如下,具体见下面代码里的Convert函数
char *方式创建一个包含中文格式的xml文件
#include
#include
#include "rapidxml.hpp"
#include "rapidxml_utils.hpp"
#include "rapidxml_print.hpp"
// int , float, double等类型 转为 std::string
// bool 类型会解析成 false:0, true :1
template
std::string Convert(const T value)
{
using namespace std;
ostringstream oss;
oss << value;
string str(oss.str());
return str;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
rapidxml::xml_document<> xml_doc;
//生成
//创建指向上述节点位置的节点对象
rapidxml::xml_node<>* rot = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_pi, xml_doc.allocate_string("xml version='1.0' encoding='gbk'"));
xml_doc.append_node(rot);
rapidxml::xml_node<>* root_node = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_element, xml_doc.allocate_string("book"));
// 写入int, float等值需要先转成string类型再写入
int count = 10;
char *pageNum_str = xml_doc.allocate_string(Convert(count).c_str());
rapidxml::xml_attribute<>* attr_pageNum = xml_doc.allocate_attribute(xml_doc.allocate_string("PageNumber"), pageNum_str);
root_node->append_attribute(attr_pageNum);
rapidxml::xml_node<>* name_node = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_element, xml_doc.allocate_string("name"), xml_doc.allocate_string("小王子"));
root_node->append_node(name_node);
xml_doc.append_node(root_node);
// 先得到
std::string sOut;
rapidxml::print(std::back_inserter(sOut), xml_doc, 0);
std::cout << sOut << std::endl;
// 保存xml文件
std::string file_name("rapidxml_example.xml");
// C++ 流式写入文件
std::ofstream pagefile(file_name);
pagefile << sOut;
pagefile.close();
return 0;
}
wchar_t方式创建一个包含中文格式的xml文件
#include
#include
#include "rapidxml.hpp"
#include "rapidxml_utils.hpp"
#include "rapidxml_print.hpp"
template
std::wstring Convert(const T Num)
{
using namespace std;
wostringstream oss;
oss << Num;
wstring str(oss.str());
return str;
}
// std::wstring 转 std::string
std::string ws2s(const std::wstring &ws)
{
size_t i;
std::string curLocale = setlocale(LC_ALL, NULL);
setlocale(LC_ALL, "chs");
const wchar_t* _source = ws.c_str();
size_t _dsize = 2 * ws.size() + 1;
std::unique_ptr< char[] > buff(new char[_dsize]);
memset(buff.get(), 0x0, _dsize);
wcstombs_s(&i, buff.get(), _dsize, _source, _dsize);
std::string result = buff.get();
setlocale(LC_ALL, curLocale.c_str());
return result;
}
// std::string 转 std::wstring
std::wstring s2ws(const std::string &s)
{
size_t i;
std::string curLocale = setlocale(LC_ALL, NULL);
setlocale(LC_ALL, "chs");
const char* _source = s.c_str();
size_t _dsize = s.size() + 1;
std::unique_ptr< wchar_t[] > buff(new wchar_t[_dsize]);
wmemset(buff.get(), 0x0, _dsize);
mbstowcs_s(&i, buff.get(), _dsize, _source, _dsize);
std::wstring result = buff.get();
setlocale(LC_ALL, curLocale.c_str());
return result;
}
// using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
rapidxml::xml_document xml_doc;
//生成
//创建指向上述节点位置的节点对象
rapidxml::xml_node* rot = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_pi, xml_doc.allocate_string(L"xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'"));
xml_doc.append_node(rot);
rapidxml::xml_node* root_node = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_element, xml_doc.allocate_string(L"book"));
// 写入int, float等值需要先转成string类型再写入
int count = 10;
wchar_t *pageNum_str = xml_doc.allocate_string(Convert(count).c_str());
rapidxml::xml_attribute* attr_pageNum = xml_doc.allocate_attribute(xml_doc.allocate_string(L"PageNumber"), pageNum_str);
root_node->append_attribute(attr_pageNum);
rapidxml::xml_node* name_node = xml_doc.allocate_node(rapidxml::node_element, xml_doc.allocate_string(L"name"), xml_doc.allocate_string(L"小王子"));
root_node->append_node(name_node);
xml_doc.append_node(root_node);
// 先得到
std::wstring sOut;
rapidxml::print(std::back_inserter(sOut), xml_doc, 0);
std::wcout.imbue(std::locale("chs"));
std::wcout << sOut << std::endl;
// 保存xml文件
std::string file_name("rapidxml_wchar_example.xml");
// C 库函数写入文件,可以确保文件编码为utf-8
std::wstring wfilename = s2ws(file_name);
FILE * fp = _wfsopen(wfilename.c_str(), L"a+,ccs=UTF-8", _SH_DENYNO);
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("err\n");
}
int num = fwprintf_s(fp, L"%s", sOut.c_str());
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}