skiplist及Java实现
一 序
在看《深入分布式缓存》的第7章,介绍redis的set的实现时候,提到了跳表skiplist.对应的整理下,主要分两篇吧,本篇先整理跳表及Java实现。后面在看Java的实现ConcurrentSkipListSet跟ConcurrentSkipListMap。
二 skiplist
2.1 名词
本节主要从wiki摘取:跳表由William Pugh 1989年发明。他在论文《Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees》中详细介绍了跳表的数据结构和插入删除等操作。论文是这么介绍跳表的:
Skip lists are a data structure that can be used in place of balanced trees.
Skip lists use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing and as a result the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees.
Skip list是一个“概率型”的数据结构,可以在很多应用场景中替代平衡树。Skip list算法与平衡树相比,有相似的渐进期望时间边界,但是它更简单,更快,使用更少的空间。
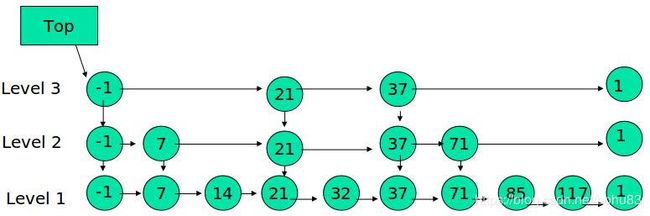
Skip list是一个分层结构多级链表,最下层是原始的链表,每个层级都是下一个层级的“高速跑道”。
图片来自wiki,完整介绍参见:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
如果对于上面说的不好理解,可以跟常见的结构做个比较。
有序数组。优点:是支持数据的随机访问,并且可以采用二分查找算法降低查找操作的复杂度。缺点:插入和删除数据时,为了保持元素的有序性,需要进行大量的移动数据的操作。
二叉查找树。 优点:既支持高效的二分查找算法,又能快速的进行插入和删除操作的数据结构。缺点:是在某些极端情况下,二叉查找树有可能变成一个线性链表。
平衡二叉树。对二叉树的缺点进行改进,引入了平衡的概念。根据平衡算法的不同,具体实现有AVL树 / B树(B-Tree) / B+树(B+Tree) / 红黑树 等等。但是平衡二叉树的实现多数比较复杂,较难理解。我自己有切身体会,平时业务搬砖头,拿出个白纸,来写写红黑树的实现,真写不出来。
所以对于跳表,性能接近,还是采用了空间换时间的思路。
| Algorithm | Average | Worst case | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Space | O(n) | O(n log n)[1] | |
| Search | O(log n) | O(n)[1] | |
| Insert | O(log n) | O(n) | |
| Delete | O(log n) | O(n) |
2.2 特性
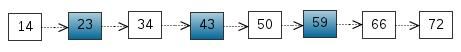
考虑一个有序表:
从该有序表中搜索元素 < 23, 43, 59 > ,需要比较的次数分别为 < 2, 4, 6 >,总共比较的次数
为 2 + 4 + 6 = 12 次。有没有优化的算法吗? 链表是有序的,但不能使用二分查找。类似二叉
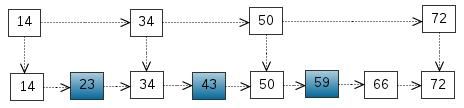
搜索树,我们把一些节点提取出来,作为索引。得到如下结构:
这里我们把 < 14, 34, 50, 72 > 提取出来作为一级索引,这样搜索的时候就可以减少比较次数了。
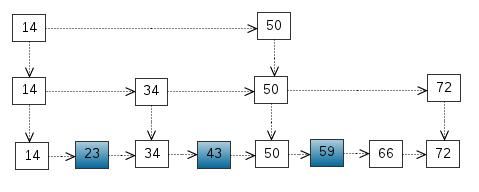
我们还可以再从一级索引提取一些元素出来,作为二级索引,变成如下结构:
这里元素不多,体现不出优势,如果元素足够多,这种索引结构就能体现出优势来了。
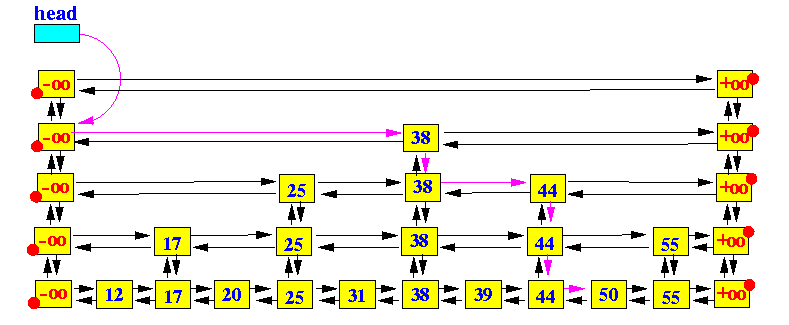
下图是一个跳表的例子
跳表具有如下性质:
(1) 由很多层结构组成
(2) 每一层都是一个有序的链表
(3) 最底层(Level 1)的链表包含所有元素
(4) 如果一个元素出现在 Level i 的链表中,则它在 Level i 之下的链表也都会出现。
(5) 每个节点包含两个指针,一个指向同一链表中的下一个元素,一个指向下面一层的元素。
2.3 原理
看了上面的,应该理解了跳表的由来及特性。本节就是来看对应的原理。
Skip List主要思想是将链表与二分查找相结合,它维护了一个多层级的链表结构(就是用空间换取时间)。常见的操作有:搜索、插入、删除。
对与一个目标元素的搜索:会从顶层链表的头部元素开始,然后遍历该链表,直到找到元素大于或等于目标元素的节点,如果当前元素正好等于目标,那么就直接返回它。如果当前元素小于目标元素,那么就垂直下降到下一层继续搜索,如果当前元素大于目标或到达链表尾部,则移动到前一个节点的位置,然后垂直下降到下一层。正因为Skip List的搜索过程会不断地从一层跳跃到下一层的,所以被称为跳跃表。
对于插入:
新节点和各层索引节点逐一比较,确定原链表的插入位置。O(logN)
把索引插入到原链表。O(1)
利用抛硬币的随机方式,决定新节点是否提升为上一级索引。是的话付继续上面的步骤。
跳表的设计者用“抛硬币”的方法选取节点是否提拔,也就是随机的方式,每个节点有50%概率会提拔。这样虽然不会让索引绝对均匀分布,但也会大体上是均匀的。
删除:
自上而下,查找第一次出现节点的索引,并逐层找到每一层对应的节点。O(logN)
删除每一层查找到的节点,如果该层只剩下1个节点,删除整个一层。
三 Java实现
本节主要参考emory大学的课程,搜了下还是美国的名校呢。估计下面的图大家看了很熟悉,但是转来转去的没标明出处。
http://www.mathcs.emory.edu
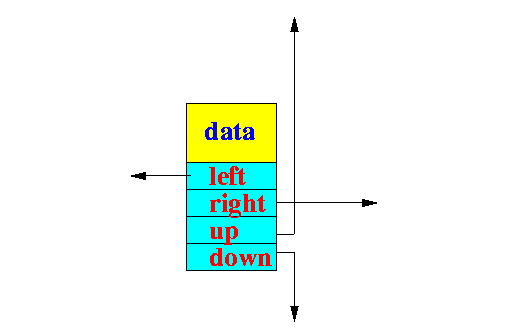
3.1 数据节点结构
data 就是具体的存储数据key,value 。 至于四个指针left,right,up,down,很好理解就是分别节点为了实现跳表的链接关系。
class SkipListEntry {
Integer key;
Integer value;
SkipListEntry right;
SkipListEntry left;
SkipListEntry down;
SkipListEntry up;
public SkipListEntry(Integer key, Integer value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public String toString()
{
return "(" + key + "," + value + ")";
}
public int pos;//与数据结构无关,只为输出方便
}3.2 跳表结构
public class SkipList {
// number of entries in the Skip List
public int n;
// height
public int h;
// 表头
private SkipListEntry head;
// 表尾
private SkipListEntry tail;
// 生成randomLevel用到的概率值
private Random r; list 有头尾的指针,还需要跳表的高度h,长度 n,随机数是模拟抛硬币随机高度的。
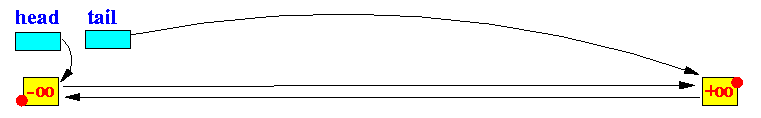
public SkipList() {
head = new SkipListEntry(Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
tail = new SkipListEntry(Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
head.right =tail;
tail.left = head;
n = 0;
h = 0;
r = new Random();
}
图上边界是“-∞”“∞”,有的为了演示方便,把key设置为String类型。这里就是integer的min,max来代替边界范围。
初始化两个首尾节点,并且链接指向。
3.3 实现map的基本操作
-
get(String key) : 根据key值查找某个元素
-
put(String key, Integer value) :插入一个新的元素,元素已存在时为修改操作
-
remove(String key): 根据key值删除某个元素
Notice that each basic operation must first find (search) the appropriate entry (using a key) before the operation can be completed.So we must learn how to search a Skip List for a given key first...就是上面的操作,都依赖于查找.所以先看查找实现方法。
查找:
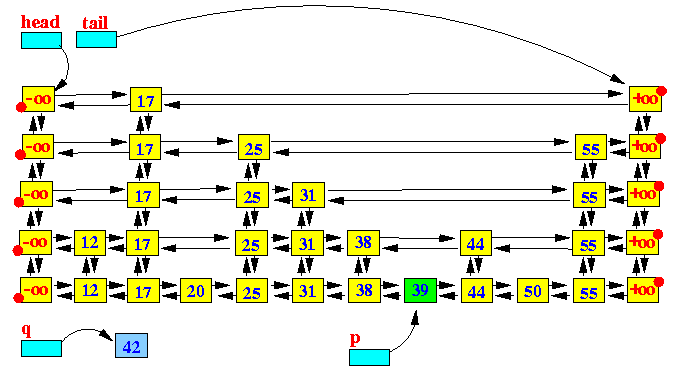
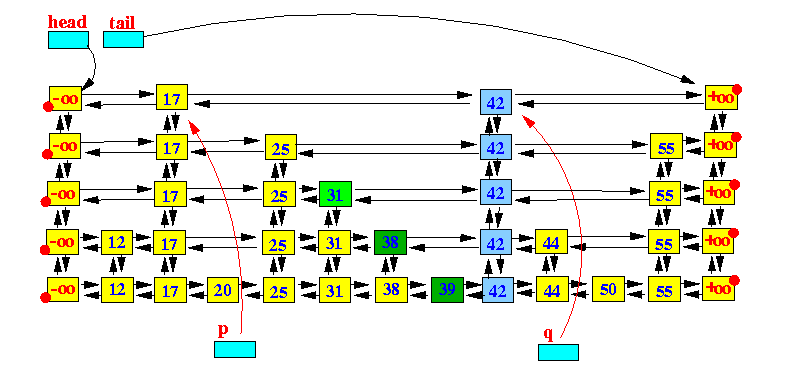
上面的图示使用紫色的箭头画出了在一个SkipList中查找key值50的过程。过程如下:
从head出发,因为head指向最顶层(top level)链表的开始节点,相当于从顶层开始查找;
移动到当前节点的右指针(right)指向的节点,直到右节点的key值大于要查找的key值时停止;
如果还有更低层次的链表,则移动到当前节点的下一层节点(down),如果已经处于最底层,则退出;
重复第2步 和 第3步,直到查找到key值所在的节点,或者不存在而退出查找;
java 实现代码如下:
/**
* 查找
* @param searchKey
* @return
*/
public SkipListEntry findEntry(Integer key)
{
SkipListEntry p;
/* -----------------
Start at "head"
----------------- */
p = head;
while ( true )
{
/* --------------------------------------------
Search RIGHT until you find a LARGER entry
E.g.: k = 34
10 ---> 20 ---> 30 ---> 40
^
|
p stops here
p.right.key = 40
-------------------------------------------- */
while ( p.right.key != Integer.MAX_VALUE && p.right.key< key )
{
p = p.right;
// System.out.println(">>>> " + p.key);
}
/* ---------------------------------
Go down one level if you can...
--------------------------------- */
if ( p.down != null )
{
p = p.down;
// System.out.println("vvvv " + p.key);
}
else
break; // We reached the LOWEST level... Exit...
}
return(p); // p.key <= k
}
public Integer get(int key) {
SkipListEntry p;
p = findEntry(key);
if(p.key ==key) {
return p.value;
} else {
return null;
}
}note:
|
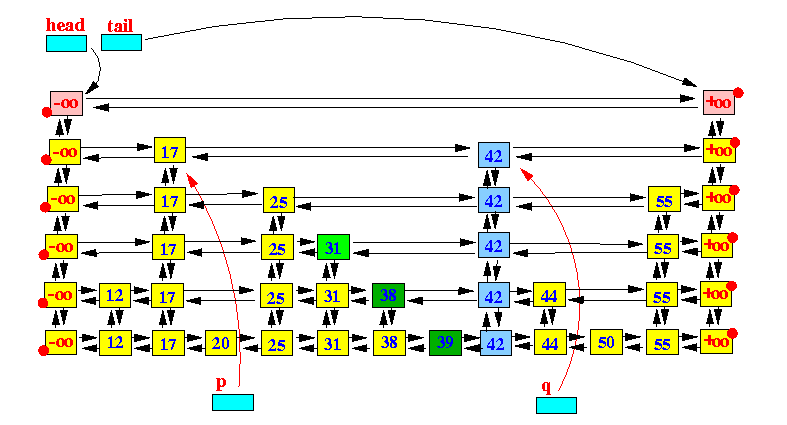
插入:实现put方法:
如果put的key值在跳跃表中存在,则进行修改操作;
如果put的key值在跳跃表中不存在,则需要进行新增节点的操作,并且需要由random随机数决定新加入的节点的高度(最大level);
当新添加的节点高度达到跳跃表的最大level,需要添加一个空白层(除了-oo和+oo没有别的节点)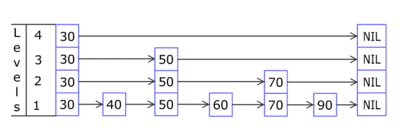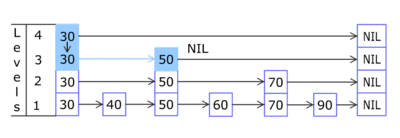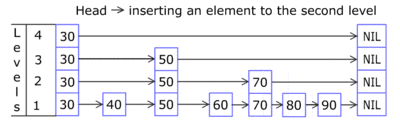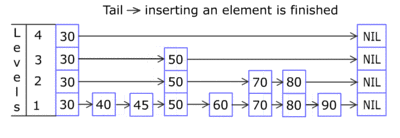
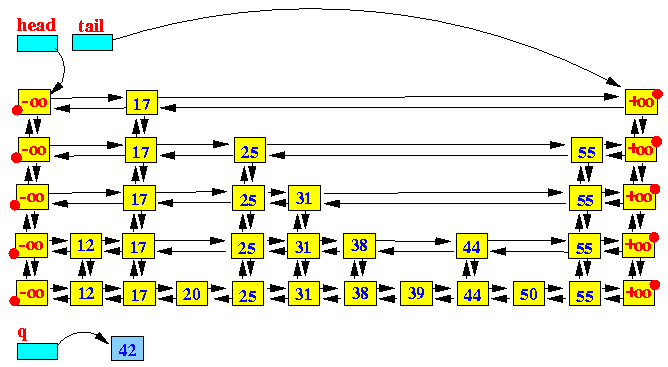
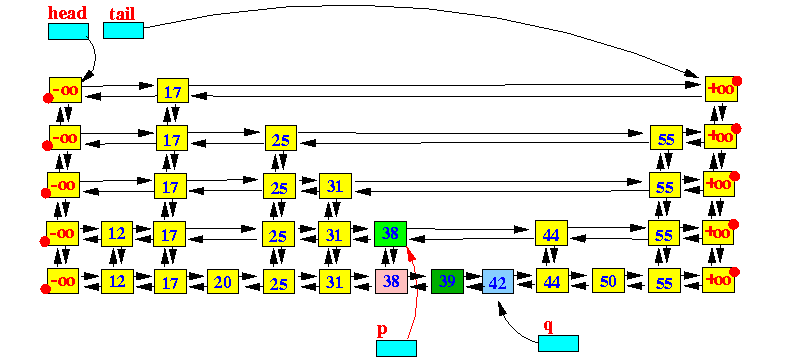
上面是个插入的动图,下面分布把图展示出来:
插入之前:
1,查找适合插入的位子
- p = findEntry(k)
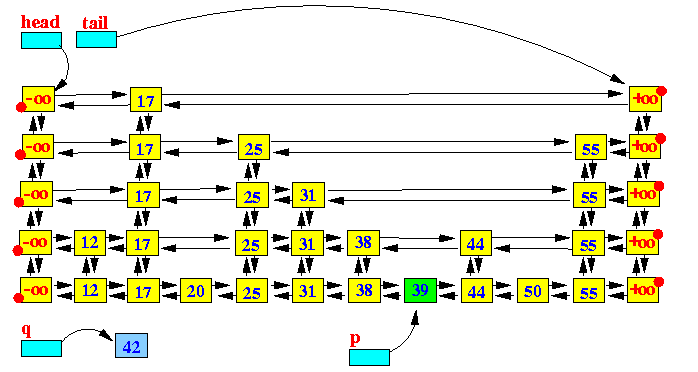
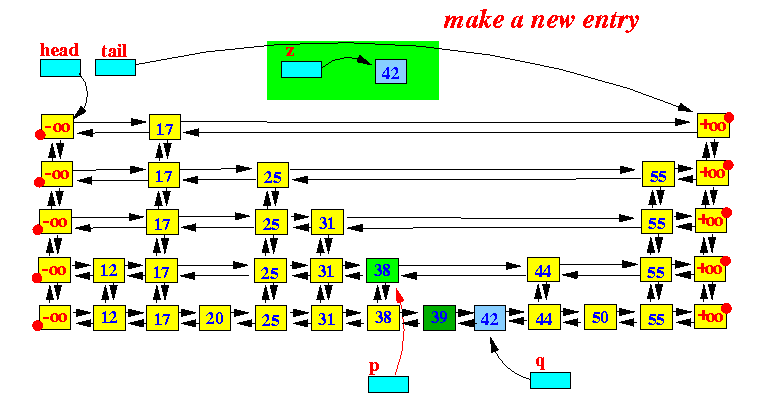
2 在查找到的p节点后面插入新增的节点q insert q after p:
3 Now make a column of random height: repeat these steps a random number of times
3.1 使用随机数决定新增节点的高度
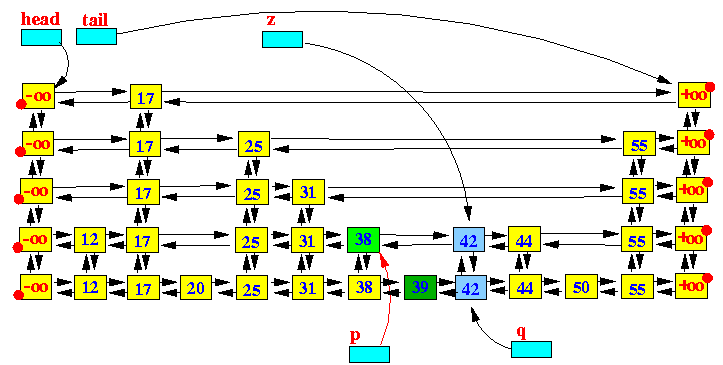
Starting at p, (using p to) scan left and find the first entry that has an up-entry: 向左找到第一个up不为空的节点
Make p point to the up-element 把p指向 向上的节点
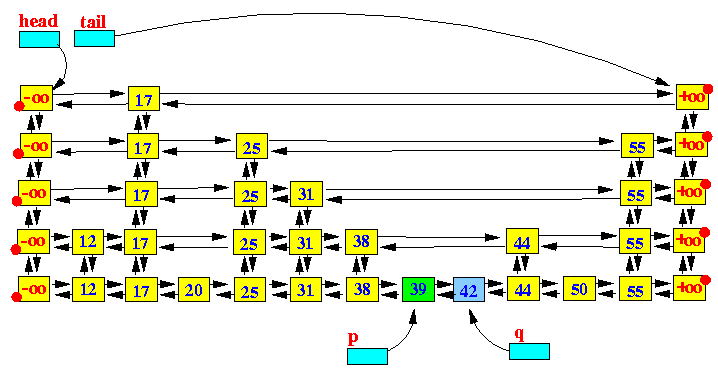
创建一个新的节点。(根插入节点key一样,value为空)
Insert the newly created entry: right of p and up from q: 插入新创建的节点。注意左右链接跟指向向下的节点。
Make q point to the newly inserted entry 把q指向新插入的节点
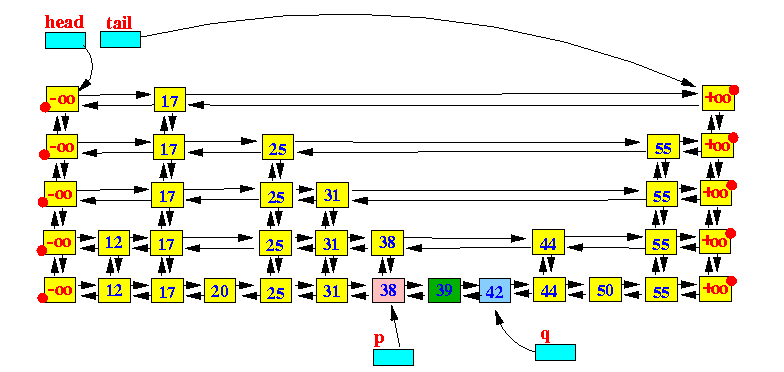
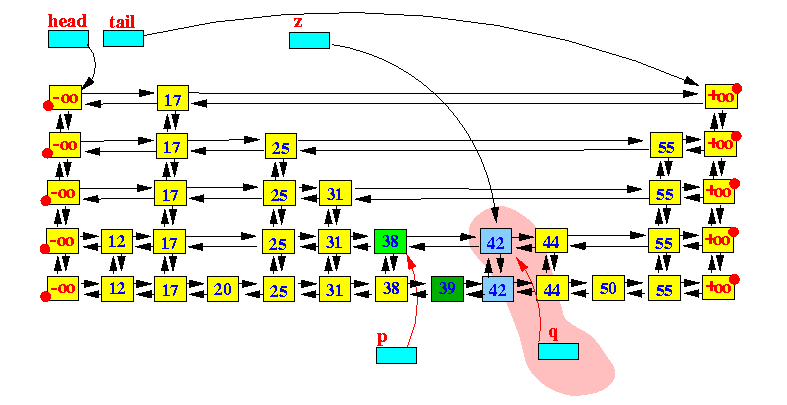
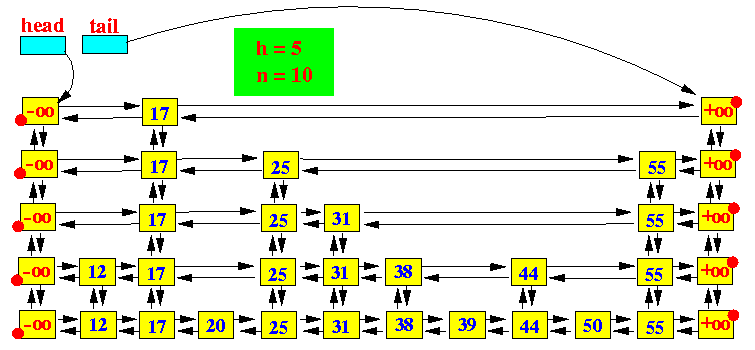
repeat the steps and show the effect of building a "tower":只要随机数满足条件,key=42的节点就会一直向上攀升,直到它的level等于跳跃表的高度(height)。这个时候我们需要在跳跃表的最顶层添加一个空白层,同时跳跃表的height+1,以满足下一次新增节点的操作。
Java 实现代码如下:
public Integer insert(int key, int value) {
SkipListEntry p, q;
int i = 0;
// 查找适合插入的位子
p = findEntry(key);
// 如果跳跃表中存在含有key值的节点,则进行value的修改操作即可完成
if(p.key ==key) {
Integer oldValue = p.value;
p.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
// 如果跳跃表中不存在含有key值的节点,则进行新增操作
q = new SkipListEntry(key, value);
/* --------------------------------------------------------------
Insert q into the lowest level after SkipListEntry p:
p put q here p q
| | | |
V V V V V
Lower level: [ ] <------> [ ] ==> [ ] <--> [ ] <--> [ ]
--------------------------------------------------------------- */
q.left = p;
q.right = p.right;
p.right.left = q;
p.right = q;
//本层操作完毕,看更高层操作
//抛硬币随机决定是否上层插入
while ( r.nextDouble() < 0.5 /* Coin toss */ )
{
if ( i >= h ) // We reached the top level !!!
{
//Create a new empty TOP layer
addEmptyLevel();
}
/* ------------------------------------
Find first element with an UP-link
------------------------------------ */
while ( p.up == null )
{
p = p.left;
}
/* --------------------------------
Make p point to this UP element
-------------------------------- */
p = p.up;
/* ---------------------------------------------------
Add one more (k,*) to the column
Schema for making the linkage:
p <--> e(k,*) <--> p.right
^
|
v
q
---------------------------------------------------- */
SkipListEntry e;
// 这里需要注意的是除底层节点之外的节点对象是不需要value值的
e = new SkipListEntry(key, null);
/* ---------------------------------------
Initialize links of e
--------------------------------------- */
e.left = p;
e.right = p.right;
e.down = q;
/* ---------------------------------------
Change the neighboring links..
--------------------------------------- */
p.right.left = e;
p.right = e;
q.up = e;
//把q执行新插入的节点:
q = e;
// level增加
i = i + 1;
}
n = n+1; //更新链表长度
return null;
}
private void addEmptyLevel() {
SkipListEntry p1, p2;
p1 = new SkipListEntry(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
p2 = new SkipListEntry(Integer.MAX_VALUE, null);
p1.right = p2;
p1.down = head;
p2.left = p1;
p2.down = tail;
head.up = p1;
tail.up = p2;
head = p1;
tail = p2;
h = h + 1;
}
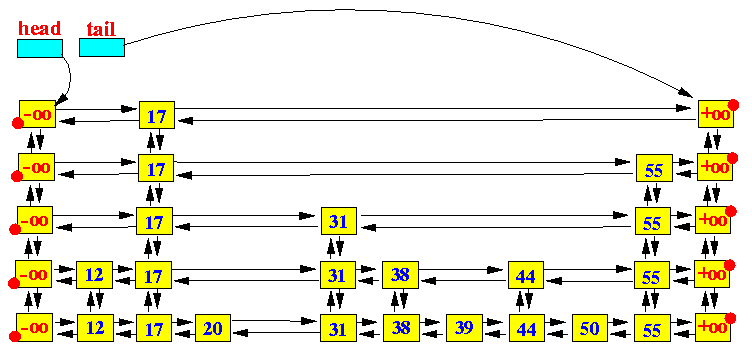
删除 Deleting an entry from a Skip List
删除25
删除节点的操作相对put就比较简单了,首先查找到包含key值的节点,将节点从链表中移除,接着如果有更高level的节点,则repeat这个操作即可。
public Integer remove(int key) {
SkipListEntry p, q;
p = findEntry(key);
if(!p.key.equals(key)) {
return null;
}
Integer oldValue = p.value;
while(p != null) {
q = p.up;
p.left.right = p.right;
p.right.left = p.left;
p = q;
}
return oldValue;
}还有需要说明的一点是:跳跃表每次运行的结果是不一样的,这就是为什么说跳跃表是属于随机化数据结构。
测试类:
public void printHorizontal()
{
String s = "";
int i;
SkipListEntry p;
/* ----------------------------------
Record the position of each entry
---------------------------------- */
p = head;
while ( p.down != null )
{
p = p.down;
}
i = 0;
while ( p != null )
{
p.pos = i++;
p = p.right;
}
/* -------------------
Print...
------------------- */
p = head;
while ( p != null )
{
s = getOneRow( p );
System.out.println(s);
p = p.down;
}
}
public String getOneRow( SkipListEntry p )
{
String s;
int a, b, i;
a = 0;
s = "" + p.key;
p = p.right;
while ( p != null )
{
SkipListEntry q;
q = p;
while (q.down != null)
q = q.down;
b = q.pos;
s = s + " <-";
for (i = a+1; i < b; i++)
s = s + "--------";
s = s + "> " + p.key;
a = b;
p = p.right;
}
return(s);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SkipList l = new SkipList();
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
int tmp = r.nextInt(100);
System.out.println("add:"+tmp);
l.insert( tmp, tmp );
l.printHorizontal();
}
System.out.println("over");
}输出:
add:8
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 2147483647
add:57
-2147483648 <-> 8 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 57 <-> 2147483647
add:32
-2147483648 <---------> 32 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 32 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 32 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 32 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 32 <-> 57 <-> 2147483647
add:54
-2147483648 <---------> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 32 <-> 54 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 8 <-> 32 <-> 54 <-> 57 <-> 2147483647
add:1
-2147483648 <-----------------> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-----------------> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 8 <-> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 32 <-> 54 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 32 <-> 54 <-> 57 <-> 2147483647
add:10
-2147483648 <-------------------------> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-------------------------> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 54 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 54 <-> 57 <-> 2147483647
add:34
-2147483648 <-------------------------> 32 <-------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-------------------------> 32 <-> 34 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-----------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-> 54 <---------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-> 54 <-> 57 <-> 2147483647
add:89
-2147483648 <-------------------------> 32 <---------------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-------------------------> 32 <-> 34 <-------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-> 54 <---------> 89 <-> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-> 54 <-> 57 <-> 89 <-> 2147483647
add:26
-2147483648 <---------------------------------> 32 <---------------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------------------------------> 32 <-> 34 <-------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 8 <-> 10 <---------> 32 <-> 34 <-------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <---------> 32 <-> 34 <-> 54 <---------> 89 <-> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 26 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-> 54 <-> 57 <-> 89 <-> 2147483647
add:41
-2147483648 <---------------------------------> 32 <-----------------------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------------------------------> 32 <-> 34 <---------------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <---------> 8 <-> 10 <---------> 32 <-> 34 <---------------------------------> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <---------> 32 <-> 34 <-> 41 <-> 54 <---------> 89 <-> 2147483647
-2147483648 <-> 1 <-> 8 <-> 10 <-> 26 <-> 32 <-> 34 <-> 41 <-> 54 <-> 57 <-> 89 <-> 2147483647
over
参考:
http://kenby.iteye.com/blog/1187303
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list