UEFI实战——如何在OS下获取UEFI变量
说明
UEFI变量在BIOS启动过程中创建。
它们有不同的类型,可以直接看属性:
///
/// Attributes of variable.
///
#define EFI_VARIABLE_NON_VOLATILE 0x00000001
#define EFI_VARIABLE_BOOTSERVICE_ACCESS 0x00000002
#define EFI_VARIABLE_RUNTIME_ACCESS 0x00000004并不是所有的变量都可以在OS下获取到,比如EFI_VARIABLE_BOOTSERVICE_ACCESS类型的变量当在UEFI下调用了ExitBootServices()之后就不能再使用了。
在《UEFI Spec》中有如下的章节:"Globally Defined Variables",它介绍了UEFI下定义的变量,它们都包含了EFI_VARIABLE_RUNTIME_ACCESS这个属性,因此可以在OS下访问到。
各个变量的使用方式见《UEFI Spec》。
Windows下访问UEFI变量
MSDN中有介绍UEFI变量访问的接口,主要是如下几个:
GetFirmwareEnvironmentVariable
GetFirmwareEnvironmentVariableEx
SetFirmwareEnvironmentVariable
SetFirmwareEnvironmentVariableEx
下面是一个示例:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "windows.h"
#include "tchar.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#define EFI_GLOBAL_VARIABLE "{8BE4DF61-93CA-11D2-AA0D-00E098032B8C}"
#define ConOut "ConOut"
#define MAX_SIZE 200
BOOL AdjustToken();
int _tmain (int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
DWORD dwRet;
PVOID pBuffer;
DWORD nSize;
DWORD index;
dwRet = ERROR_SUCCESS;
nSize = MAX_SIZE;
pBuffer = malloc (nSize);
AdjustToken ();
//
// 首先使用空(Dummy)的变量,来确定是否是在Legacy BIOS上安装的Windows;
//
dwRet = GetFirmwareEnvironmentVariable (
_T (""),
_T ("{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}"),
pBuffer,
nSize
);
if (0 == dwRet)
{
//
// 返回值是变量的大小,0表示的是没有获取到;
//
if (GetLastError () == ERROR_INVALID_FUNCTION)
{
//
// 如果Windows是装在Legacy BIOS上,返回值是ERROR_INVALID_FUNCTION;
//
printf ("Windows was installed using legacy BIOS.\n");
}
else
{
//
// 如果返回998(ERROR_NOACCESS)表示没有这个GUID的变量,这也是正常的,因为访问的是空的变量;
//
printf ("ErrCode = %ld.\n", GetLastError ());
printf ("Windows was installed using UEFI BIOS.\n");
dwRet = GetFirmwareEnvironmentVariable (
_T (ConOut),
_T (EFI_GLOBAL_VARIABLE),
pBuffer,
100
);
if (0 == dwRet)
{
printf ("ErrCode = %ld.\n", GetLastError ());
}
else
{
printf ("Variable size: %d.\n", dwRet);
for (index = 0; index < dwRet; index++)
{
printf ("%02x ", *((BYTE *)pBuffer + index));
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
free (pBuffer);
return ERROR_SUCCESS;
}这里有几点说明:
1. 上述代码在VS2107 commnity上编译和使用,系统环境是Windows10,运行结果如下:
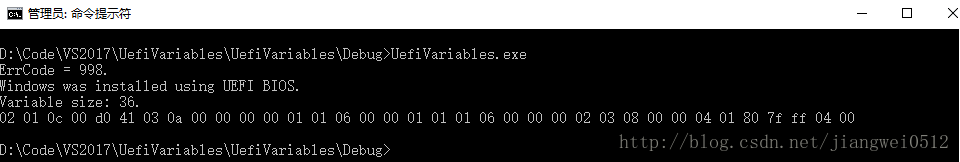
2. 需要在Administrator打开命令行并运行,这里是一个权限的问题;
3. 这里还需要一个函数AdjustToken(),也是用来处理权限的,代码来自下面的网址:
http://blog.csdn.net/youyudexiaowangzi/article/details/48245309
Linux下访问UEFI变量
要了解Linux下如何获取变量,可以从efibootmgr这个命令开始,下面是一个例子:
efibootmgr命令用来调整UEFI启动顺序,它就是通过操作UEFI变量来完成的。
efibootmgr的源代码可以在https://github.com/rhboot/efibootmgr下载到。
查看源代码就会注意到里面操作变量的接口,下面是efibootmgr中读取启动项顺序的函数:
static int
read_order(const char *name, var_entry_t **order)
{
int rc;
var_entry_t *new = NULL, *bo = NULL;
if (*order == NULL) {
new = calloc(1, sizeof (**order));
if (!new) {
efi_error("calloc(1, %zd) failed",
sizeof (**order));
return -1;
}
*order = bo = new;
} else {
bo = *order;
}
rc = efi_get_variable(EFI_GLOBAL_GUID, name,
&bo->data, &bo->data_size, &bo->attributes);
if (rc < 0 && new != NULL) {
efi_error("efi_get_variable failed");
free(new);
*order = NULL;
bo = NULL;
}
if (bo) {
/* latest apple firmware sets high bit which appears invalid
* to the linux kernel if we write it back so lets zero it out
* if it is set since it would be invalid to set it anyway */
bo->attributes = bo->attributes & ~(1 << 31);
}
return rc;
}里面可以看到读取UEFI变量的接口:efi_get_variable。
它的声明在头文件
https://github.com/rhboot/efivar
具体的实现和例子就不用多说了,主要还是要看代码。
