Spring实战教程 | 第九篇:SpringAOP之入门
AOP的3个关键概念
切入点(Pointcut)
在介绍Pointcut之前先介绍Join Point(连接点)的概念。Join Point指程序运行中的某个阶段点,比如一个方法调用,异常抛出等。Pointcut就是Join Point的集合,它是程序中需要注入Advice的位置的集合,指明Advice在什么样的条件下才能被触发。
Pointcut.java源码
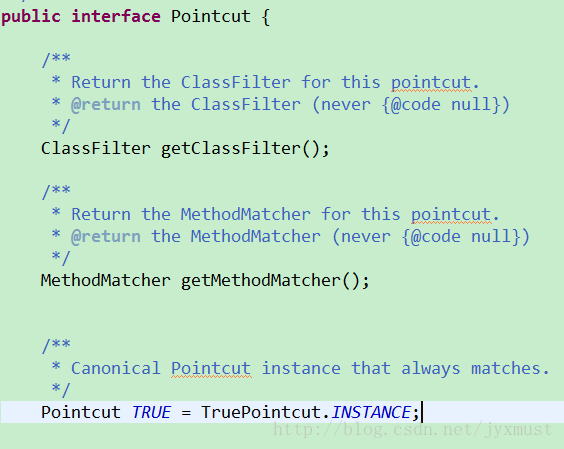
接口ClassFilter:用来将切入点限定在给定的目标类中
接口MethodMatcher:用来判断切入点是否匹配目标类给定的方法
通知(Advice)
Advice是某个连接点所采用的处理逻辑,也就是向连接点注入的代码。 在spring AOP中,它主要描述Spring AOP围绕方法调用而注入的切面行为。
Advisor
Advisor是Pointcut和Advice的配置器,它包括Pointcut和Advice,是将Advice注入程序中Pointcut位置的代码
Spring的3种切入点(Pointcut)实现
静态切入点
静态切入点只限于给定的方法和目标类,不考虑方法的参数。Spring在调用静态切入点时只在第一次的时候计算静态切入点的位置,然后把它缓存起来,以后不再需要再进行计算。使用org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcut实现静态切入点
<bean id="settersAndAbsquatulatePointcut"
class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcut">
<property name="patterns">
<list>
<value>.*save.*value>
<value>.*do.*value>
list>
property>
bean>
beans>.* save.* : 表示所有以save开头的方法都是切入点
.* do.* : 表示所有以do开头的方法都是切入点
动态切入点
动态切入点不仅限定于给定的方法和类,还可以指定方法的参数。因为参数的变化性,动态切入点不能缓存,需要每次调用的时候都进行计算,因为使用动态切入点有很大的性能损耗。
当切入点需要在执行时根据参数值来调用通知,就需要使用动态切入点。Spring提供了一个内建的动态切入点:控制流切入点。该切入点匹配基于当前线程的调用的堆栈,只有在当前线程执行时找到特定的类和方法才能返回true
自定义切入点
因为Spring中的切入点是Java类,所以可以定义自定义切入点
Spring的通知(Advice)
Spring提供5种Advice类型:
① Interception Around :在Join Point前后调用
② Before :在Join Point前调用
③ after Returning :在Join Point后调用
④ Throw :在Join Point抛出异常调用
⑤ Introduction :在Join Point调用完毕后调用
Interception Around通知
Interception Around 在在Join Point前后调用,也是Spring中最基本的通知类型,实现Interception Around的类需要实现接口MethodInterception
public class LogInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throw Throwable
{
System.out.println("开始...");
Object ravl=invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("结束...");
return rval;
}
}Before通知
Before 在Join Point前调用,需要实现接MethodBeforeAdvice
public class LogBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
public void before(Method m, Object[] arg1, Object target)
throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("开始...");
}
}
after Returning通知
after Returning 在在Join Point后调用,需要实现接口AfterReturningAdvice
public class LogAfterAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice{
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object arg0, Method arg1, Object[] arg2,
Object arg3) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("结束...");
}
}
Throw通知
Throw**在Join Point抛出异常**调用,需要实现接口ThrowsAdvice
public class LogThrowAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice{
public void afterThrowing(RemoteException e) throws Throwable
{
System.out.println(" 抛出异常,请检查..."+e);
}
}Introduction通知
Introduction 在Join Point调用完毕后调用,需要实现接口IntroductionAdvice和接口IntroductionInterceptor
用ProxyFactoryBean创建AOP代理
使用Spring提供的类org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean是创建AOP的最基本方式
使用ProxyFactoryBean代理目标类的所有方法
在Spring中,ProxyFactoryBean是在xml里配置的
<bean id="log" class="spring.aop.LogAfterAdvice">bean>
<bean id="timeBook" class="spring.aop.TimeBook">bean>
<bean id="logProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<value>spring.aop.TimeBookInterfacevalue>
property>
<property name="target">
<ref bean="timeBook"/>
property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>logvalue>
list>
property>
bean>id为log的Bean : 程序中的Advice
id为timeBook的Bean : ProxyFactoryBean要代理的目标类
id为logProxy的Bean : ProxyFactoryBean本身
ProxyFactoryBean的proxyInterfaces属性 : 指明要代理的接口
ProxyFactoryBean的target属性 : 指明要代理的目标类,这个目标类实现了上面proxyInterfaces属性指定的接口
ProxyFactoryBean的interceptorNames属性 : 指明要在代理的目标类中插入的Adivce
ProxyFactoryBean还有一个属性proxyTargetClass属性,如果属性设置为true,那proxyFactoryBean要使用CGLIB方式代理,而不是接口
使用ProxyFactoryBean代理目标类的指定方法
Advice会代理目标类的所有方法。使用Spring提供的org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor
<bean id="log" class="spring.aop.LogAfterAdvice">bean>
<bean id="timeBook" class="spring.aop.TimeBook">bean>
<bean id="logAdvisor"
class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice">
<ref bean="log" />
property>
<property name="patterns">
<value>.*doAuditing.*value>
property>
bean>
<bean id="logProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<value>spring.aop.TimeBookInterfacevalue>
property>
<property name="target">
<ref bean="timeBook" />
property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>logAdvisorvalue>
list>
property>
bean>1、在id为logAdvisor的Bean中设定Advice和指定的方法
2、把id为logProxy的Bean的interceptorNames属性值改为logAdvisor
3、logAdvisor的advice属性指定Advice
4、logAdvice的patterns属性指定要代理的方法。“.doAuditing”表示只有doAuditing()方法才能使用指定的Advice,patterns属性使用的是正则表达式(注意:因为要使用正则表达式,要引入jakarta-oro-2.0.8.jar)
正则表达式简介
正则表达式用于在一个文件中查找字符
1、“ . ” 可以用来匹配任何一个字符。比如:正则表达式为“ g.f ”,它就会匹配“ gaf ”、“ g*f ”、“ g&f ”等中间是任意字符的字符
2、“ [ ] ”只有[ ]里面指定的字符才能匹配。比如:正则表达式为“ g[ abc ]f ”,它只能匹配“ gaf ”、“ gbf ”、“ gcf ”,不会匹配“ g*f ”、“ g&f ”等
3、“ * ” 表示匹配次数,可以任意次,用来确定紧靠该符号左边的符号出现的次数。比如:正则表达式为“ g.*f ”,它只能匹配“ gaaaaaf ”、“ gf ”、“ g *f ”等
4、“ ? ” 可以匹配 0 或者 1 次,用来确定紧靠该符号左边的符号出现的次数。比如:正则表达式为“ g.?f ”,它只能匹配“ gaf ”、“ g f ”等
5、“ \ ” 是正则表达式的连续符 , 比如:正则表达式为“ g.-f ”,它只能匹配“ g-f ”、“ ga-f ”和“ g*-f ”等
上面的示例中,只对TimeBook类的doAuditing( )方法有效,如果要对TimeBook中所有以do开头的方法有效,可以这样设定“ .do. ”
<property name="patterns">
<value>.*do.*value>
property>如果要对TimeBook类中所有方法有效,可以这样设定“ .spring.aop.TimeBookInterface. ”
<property name="patterns">
<value> .*spring\.aop\.TimeBookInterface.*value>
property>注意:包的路径要用“ \ ”连接符来表示 “ . ”不是正则表达式的“ . ”
把输出日志的实例用Spring的AOP来实现
采用Interception Around通知的形式实现
Interception Around通知会在JointPoint的前后执行,实现Interception Around通知的类需要实现接口MethodInterception。
实现思路:
① 实现接口MethodInterception
② 在Invoke()方法里编写负责输出日志信息的代码,具体的业务逻辑还使用前面的接口TimeBookInterface和它的实现类TimeBook
③ 在Spring的配置文档中定义Pointcut
④ 编写测试类,执行
(1)负责输出日志信息的类LogAround,该类实现了MethodInterception,重写了Invoke()方法
public class LogAround implements MethodInterceptor {
private Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(this.getClass().getName());
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
logger.log(Level.INFO, invocation.getArguments()[0] + " 开始...");
try {
Object result = invocation.proceed();
//返回值即是被调用的方法的返回值
return result;
} finally {
// TODO: handle exception
logger.log(Level.INFO, invocation.getArguments()[0] + " 结束...");
}
}
}
<bean id="log" class="spring.aop.LogAround">bean>
<bean id="timeBook" class="spring.aop.TimeBook">bean>
<bean id="logProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<value>spring.aop.TimeBookInterfacevalue>
property>
<property name="target">
<ref bean="timeBook" />
property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>logvalue>
list>
property>
bean>public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
timeBookProxy.doAuditing("张三");
//通过ApplicationContext获取XML
ApplicationContext context=new
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:aop-config.xml");
TimeBookInterface timeBookProxy=(TimeBookInterface) context.getBean("logProxy");
timeBookProxy.doAuditing("CSDN");
}
}