1、ALDL
AIDL(Android Interface Define Language)是IPC进程间通信的一种方式,用于生成可以在Android设备上两个进程之间进行进程间通信(interprocess communication, IPC)的代码.
2、默认支持的数据类型
- 基本数据类型(int、long、char、boolean、double等)
- String,CharSequence
- List(只支持ArrayList,里面的每个元素都必须被AIDL支持)
- Map(只支持HashMap, 里面的每个元素都必须被AIDL支持,包括key和value)
- Parcelable(所有实现了Parcelable接口的对象)
- AIDL接口:所有的AIDL接口本身也可以在AIDL文件中使用。
自定义的Parceable对象和AIDL对象必须要显式的import进来,不管它们是否和当前的AIDL文件在同一个包中。如果AIDL文件用到了自定义的Parcelable对象,那么必须新建一个和它同名的AIDL文件,并在其中声明它为Parcelable类型。除此之外,AIDL除了基本类型,其他类型的参数都必须标上方向:in、out或者inout,in标上输入型参数,out表示输出型参数,inout表示输入输出型参数
3、AIDL和Messager的区别
- Messager以串行的方式来处理客户端发来的消息,如果有大量的消息同时发送到服务端,服务端仍然只能一个一个的去处理;故Messager不适用大量并发的请求
- Messenger主要是为了传递消息:对于需要跨进程调用服务端的方法,这种情景不适用Messenger。
- Messenger的底层实现是AIDL,系统为我们做了封装从而方便上层的调用。
- AIDL适用于大量并发的请求,以及涉及到服务端方法调用的情况
4、AIDL使用步骤
1、新建一个项目作为服务端AIDLService,在项目中新建AIDL文件;然后build生成ICalculateInterface.aidl文件
package com.wuc.aidltest;
interface ICalculateInterface {
//计算两个数的和
int addNum(int num1,int num2);
}
2、新建一个IRemoteService
package com.wuc.aidltest;
public class IRemoteService extends Service {
private IBinder mIBinder = new ICalculateInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public int addNum(int num1, int num2) throws RemoteException {
return num1 + num2;
}
};
//客户端绑定service时会执行
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mIBinder;
}
}
我在测试过程中报错,错误信息为
java.lang.SecurityException: Not allowed to bind to service Intent { cmp=com.wuc.aidltest/.IRemoteService }
错误原因是没有配置 android:exported="true"这个属性;它的主要作用是:是否支持其它应用调用当前组件。 默认值:如果包含有intent-filter 默认值为true; 没有intent-filter默认值为false。
3、新建一个客户端AIDLClient,把服务端AIDLService里的AIDL文件拷贝到客户端AIDLClient(包名要一致);然后build工程。然后在Activity中绑定服务
package com.wuc.aidlclient;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private AppCompatEditText mEdt_num1;
private AppCompatEditText mEdt_num2;
private AppCompatButton mBtn_calculate;
private AppCompatTextView mTxt_result;
private ICalculateInterface mICalculateInterface;
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//判断Binder是否死忙
//boolean binderAlive = service.isBinderAlive();
//用于将服务端的Binder对象转换为客户端需要的AIDL接口类型的对象
mICalculateInterface = ICalculateInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
//给binder设置死忙代理,当Binder死忙时就可以收到通知
service.linkToDeath(mDeathRecipient, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
//连接断开,释放AIDL Binder对象
mICalculateInterface = null;
Log.d(TAG, "binder died");
}
};
private IBinder.DeathRecipient mDeathRecipient = new IBinder.DeathRecipient() {
@Override
public void binderDied() {
if (mICalculateInterface == null) {
return;
}
//移除之前绑定的代理并重新绑定远程服务
mICalculateInterface.asBinder().unlinkToDeath(mDeathRecipient, 0);
mICalculateInterface = null;
bindService();
}
};
@SuppressLint("CutPasteId")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mEdt_num1 = findViewById(R.id.edt_num1);
mEdt_num2 = findViewById(R.id.edt_num2);
mTxt_result = findViewById(R.id.txt_result);
mBtn_calculate = findViewById(R.id.btn_calculate);
mBtn_calculate.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(mEdt_num1.getText().toString());
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(mEdt_num2.getText().toString());
try {
int num = mICalculateInterface.addNum(num1, num2);
mTxt_result.setText("结果:" + num);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
mTxt_result.setText("计算错误");
}
}
});
bindService();
}
private void bindService() {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.wuc.aidltest",
"com.wuc.aidltest.IRemoteService"));
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unbindService(conn);
}
}
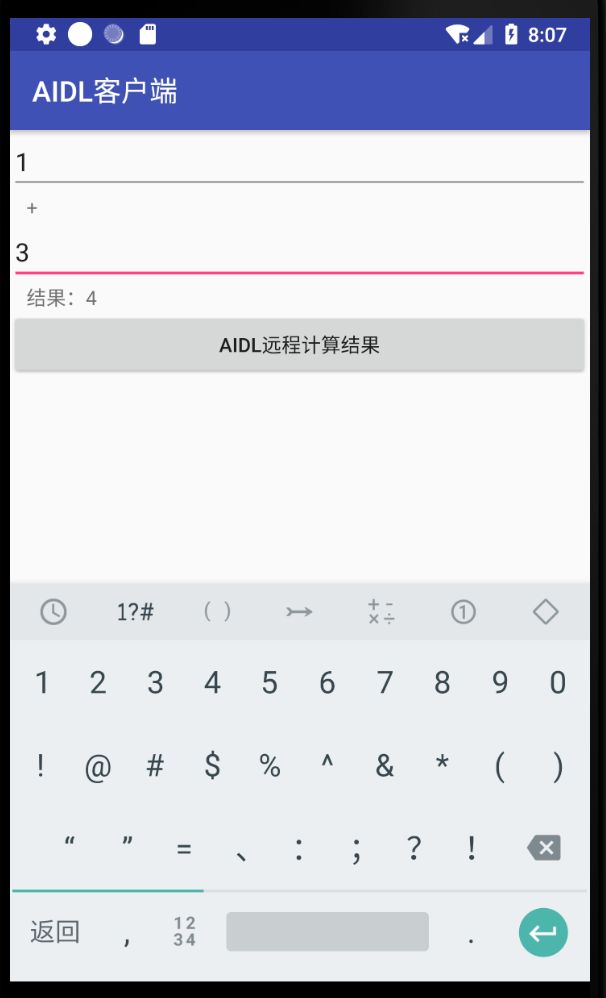
显示界面如下图:
4、自定义类型
4.1 自定义类型要实现Parcelable接口,下面代码中创建一个Person类并实现了Parcelable接口
package com.wuc.aidltest;
public class Person implements Parcelable {
public static final Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
@Override
public Person createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new Person(in);
}
@Override
public Person[] newArray(int size) {
return new Person[size];
}
};
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
protected Person(Parcel in) {
name = in.readString();
age = in.readInt();
}
public String getName() {
return name == null ? "" : name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeInt(age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + ":" + age;
}
}
4.2 接下来新建一个同名的Person.aidl文件,在Person.aidl中申明自定义的类型和它的完整包名,注意这边parcelable是小写的,不是Parcelable接口,一个自定类型需要一个这样同名的AIDL文件;Person.aidl文件的内容如下:
//Person.aidl
package com.wuc.aidltest;
parcelable Person;
4.3 在ICalculateInterface及入口中导入AIDL类型
如:import com.wuc.aidltest.Person;
package com.wuc.aidltest;
import com.wuc.aidltest.Person;
interface ICalculateInterface {
//计算两个数的和
int addNum(int num1,int num2);
List addPerson(in Person person);
}
4.4 定义接口方法,build后在Service中做具体实现
package com.wuc.aidltest;
public class IRemoteService extends Service {
/**
* CopyOnWriteArrayList支持并发读写,AIDL方法是在服务端的Binder线程池中执行的,因此当多个客户端同时连接的时候,
* 会存在多个线程同时访问的情形,所以我们要在AIDL方法中处理线程同步,这里使用CopyOnWriteArrayList来进行自动的线程同步
*
* 因为AIDL中所支持的是抽象的List,二List只是一个接口,因此虽然服务端返回的是CopyOnWriteArrayList,但是在Binder中
* 会按照List的规范去访问数据并最终形成一个新的ArrayList传递给客户端,所以采用CopyOnWriteArrayList是可以的,类似的
* 还有ConcurrentHashMap
*/
private CopyOnWriteArrayList mPersonList;
private IBinder mIBinder = new ICalculateInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public int addNum(int num1, int num2) throws RemoteException {
return num1 + num2;
}
@Override
public List addPerson(Person person) throws RemoteException {
mPersonList.add(person);
return mPersonList;
}
};
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
mPersonList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
return mIBinder;
}
}
最后将我们的AIDL文件和自定义类型的java一并拷贝到AIDLClient中,注意包名都要一样
然后在Activity中使用自定义类型的AIDL接口
package com.wuc.aidlclient;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private AppCompatButton mBtn_calculate;
private ICalculateInterface mICalculateInterface;
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//用于将服务端的Binder对象转换为客户端需要的AIDL接口类型的对象
mICalculateInterface = ICalculateInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
@SuppressLint("CutPasteId")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mBtn_calculate = findViewById(R.id.btn_calculate);
mBtn_calculate.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
try {
List personList = mICalculateInterface.addPerson(new Person("wuc", 22));
Log.d("aidl", personList.toString());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
bindService();
}
private void bindService() {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.wuc.aidltest",
"com.wuc.aidltest.IRemoteService"));
bindService(intent, conn, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unbindService(conn);
}
}
效果图如下:
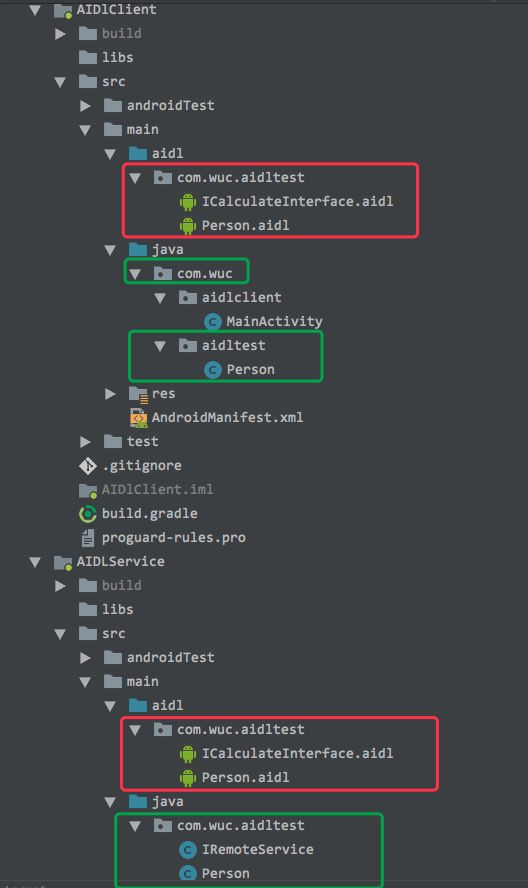
下图是客户端和服务端的目录结构图;(注意包名的一致)