基于HTML5 画布功能canvas的绘画板:画线、画圆、画矩形、橡皮、改变线条
写在前面
试看链接: https://yyywwwqqq.coding.me/draw
项目下载地址:https://coding.net/u/yyywwwqqq/p/draw
希望您能点个fork 点个关注 点个收藏!
有问题请留言!
代码实现
1.HTML内容
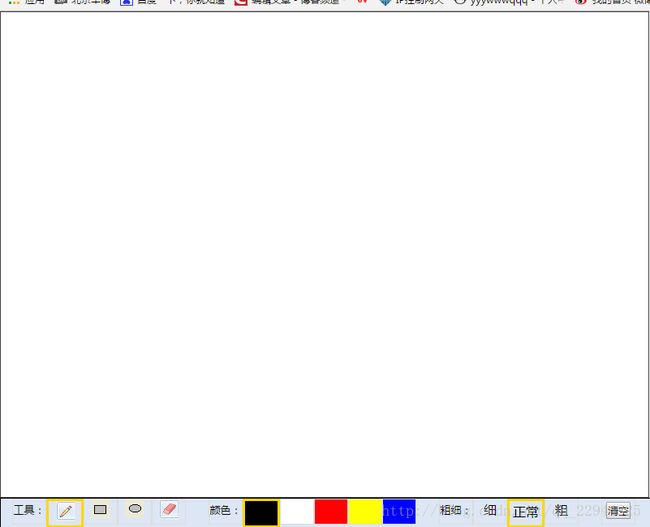
上面是一个div 800*600,里面放了两张画布,相同大小,相互覆盖,因为画布默认是透明的,所以你在哪一个画布上绘画,你都可以在屏幕中看到。
下面是四个ul列表,分别对应工具、颜色、粗细、清空。记得给每一个li选项添加一个class区分。
以下是body里面的内容:
<div id="div1">
<canvas id="c" width="800px" height="600px" style="">canvas>
<canvas id="c2" width="800px" height="600px" >canvas>
div>
<div id="div2" >
<ul>
<li style="font-size: 13px;">工具:li>
<li id="qianbi" class="choice"><img src="img/qianbi.png"/>li>
<li id="juxing"><img src="img/juxing.png"/>li>
<li id="yuanxing"><img src="img/yuanxing.png"/>li>
<li id="xiangpi"><img src="img/xiangpi.png"/>li>
ul>
<ul>
<li style="font-size: 13px;">颜色:li>
<li class="black choice">li>
<li class="white" >li>
<li class="red">li>
<li class="yellow">li>
<li class="blue">li>
ul>
<ul>
<li style="font-size: 13px;">粗细:li>
<li class="small" >细li>
<li class="normol choice" >正常li>
<li class="big">粗li>
ul>
<ul>
<li class="cleardraw" ><button>清空button>li>
ul>
div>2.CSS
写完body里面的内容之后,接下来我们来设置一下样式。
主要注意的内容有两点:
1.两张画布要重叠放在一起,所以需要调整一下它们的位置
2.ul下的li是块级元素,每一个会占一行,让它们在一行展示
以下是css代码:
body
{
margin: 0px;
}
canvas
{
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
right: 0px;
/*background-color: transparent */
}
#div1
{
width: 800px;
height: 600px;
position: relative;
border: 1px solid black;
}
#div2
{
width: 800px;
height: 36px;
border: 1px solid black;
background-color:rgb(220,230,244) ;
}
ul
{
background-color: rgb(220,230,244);
text-align: center;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 30px;
float: left;
margin-left: 14px;
margin-right: 14px;
}
ul>li
{
float: left;
border: 1px solid gainsboro;
width: 40px;
line-height: 25px;
display: inline-block;
height: inherit;
}
button
{
padding: 0px;
}
.red
{
background-color: red;
}
.black
{
background-color: black;
}
.white
{
background-color: white;
}
.blue
{
background-color: blue;
}
.yellow
{
background-color: yellow;
}
.choice
{
border: 3px solid gold;
}3.JS
说一下我的实现思路,定义三个变量 style、mywidth、mycolor分别代表工具类型、粗细和颜色。所以首先写的是ul下li的点击事件,并且给每一个点击的li添加一个choice类(有一个黑色的粗边框),用来表示其被选状态;
以下点击事件的代码:
var style = 0;
var mycolor = "black";
var mywidth = 2.5;
$(function(){
//添加选中样式
$("li").click(function(){
$(".cleardraw").removeClass("choice");
//如果点的是那几个小标题是没有反应的
if ($(this).prop("className") == "firstli") {
} else{
//先把父元素下的其他元素的选中状态移除。
$(this).parent().children().removeClass("choice");
$(this).addClass("choice");
}
})
$(".small").click(function(){
mywidth = 1;
})
$(".normol").click(function(){
mywidth = 2.5;
})
$(".big").click(function(){
mywidth = 5;
})
$("#qianbi").click(function(){
style=0;
})
$("#juxing").click(function(){
style=1;
})
$("#yuanxing").click(function(){
style=2;
})
$("#xiangpi").click(function(){
style=3;
})
$(".red").click(function(){
mycolor = "red";
})
$(".black").click(function(){
mycolor = "black";
})
$(".white").click(function(){
mycolor = "white";
})
$(".yellow").click(function(){
mycolor = "yellow";
})
$(".blue").click(function(){
mycolor = "blue";
})
$(".cleardraw").click(function(){
ctx.clearRect(0,0,800,600);
})
})这样就把click事件基本上写完了,下面来实现绘画功能,主要涉及到mousedown mousemove mouseup 三个事件
说一下我的思路,鼠标点下的时候触发mousedown函数,switch一下style,判断是铅笔还是橡皮,还是矩形或者圆~
先说铅笔,记录一下mousedown的坐标beginx和beginy,每一次鼠标move的时候,取一下这时候的event.pageX和event.pageY变量,然后在这两点之间画出线,并且修改下一次mousemove画线的起点应该是上一次的终点。也就是说,每次移动的之后都要beginx =event.pageX,beginy =event.pageY
注意:mousemove事件并不会随着你的鼠标抬起而clear,即使你把他写在了mousedown事件下,所以我用了一个lock,点击的时候lock = true 打开,mouseup的时候,lock = false锁上。后来发现更简单的方法,就是用 bind和unbind方法!
$("#div1").mousedown(function(event){
beginx =event.pageX;
beginy =event.pageY;
console.log("我点下来的时候:",beginx,beginy);
switch(style)
{
//铅笔状态
case 0:
console.log("我选的是铅笔");
lock0 = true;
//console.log("我点下来的时候:",beginx,beginy);
$("#div1").bind('mousemove',function(event){
if(lock0)
{
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(beginx,beginy);
ctx.lineTo(event.pageX,event.pageY);
ctx.strokeStyle = mycolor;
ctx.lineWidth = mywidth;
ctx.stroke();
beginx =event.pageX;
beginy =event.pageY;
}
})
break;
}
}
})橡皮的思路和铅笔一样,只不过要把颜色设置成白色固定!
case 3:
console.log("我选的是橡皮");
lock3 = true;
//console.log("我点下来的时候:",beginx,beginy);
$("#div1").bind('mousemove',function(event){
if(lock3)
{
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(beginx,beginy);
ctx.lineTo(event.pageX,event.pageY);
ctx.strokeStyle = "white";
ctx.lineWidth = mywidth*3;
ctx.stroke();
beginx =event.pageX;
beginy =event.pageY;
}
})
break;然后是画矩形,这时候就用到了声明的第二个画布,我们可以把它看做成一个缓冲区,在mousemove下鼠标每次移动,先清空这个缓冲区,然后画到缓冲区里面一个矩形。mouseup的时候,也清空以下缓冲区,然后在第一张画布里根据位置声明一个一样的矩形。
代码如下:
case 1:
lock1 = true;
console.log("画个矩形吧!");
$("#div1").bind('mousemove',function(event){
if(lock1)
{
ctx2.clearRect(0,0,800,600);
xx=event.pageX-beginx;
yy=event.pageY-beginy;
ctx2.beginPath();
ctx2.rect(beginx,beginy,xx,yy);
ctx2.strokeStyle = mycolor;
ctx2.lineWidth = mywidth;
ctx2.stroke();
}
})
break;画圆的话,和画矩形局相似了,我就不赘述了。
下面是画圆的代码:
case 2 :
lock2=true;
console.log("画个圆吧 !")
$("#div1").bind('mousemove',function(event){
if(lock2)
{
ctx2.clearRect(0,0,800,600);
xx=event.pageX-beginx;
yy=event.pageY-beginy;
r = Math.sqrt(xx*xx+yy*yy)/2;
centerx = (event.pageX+beginx)/2;
centery = (event.pageY+beginy)/2;
console.log(xx,yy,centerx,centery,r);
ctx2.beginPath();
ctx2.arc(centerx,centery,r,0,2*Math.PI,true);
ctx2.strokeStyle = mycolor;
ctx.lineWidth = mywidth;
ctx2.stroke();
}
})
break;最后把鼠标抬起的事件贴一下,下面是代码:
$("#div1").mouseup(function(){
switch(style)
{
//铅笔状态
case 0:
break;
//矩形状态
case 1:
ctx2.clearRect(0,0,800,600);
xx=event.pageX-beginx;
yy=event.pageY-beginy;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.rect(beginx,beginy,xx,yy);
ctx.strokeStyle = mycolor;
ctx.lineWidth = mywidth;
ctx.stroke();
break;
//画圆状态
case 2:
ctx2.clearRect(0,0,800,600);
xx=event.pageX-beginx;
yy=event.pageY-beginy;
console.log(event.pageX,event.pageY);
r = Math.sqrt(xx*xx+yy*yy)/2;
centerx = (event.pageX+beginx)/2;
centery = (event.pageY+beginy)/2;
console.log(xx,yy,centerx,centery,r);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(centerx,centery,r,0,2*Math.PI,true);
ctx.strokeStyle = mycolor;
ctx.lineWidth = mywidth;
ctx.stroke();
break;
case 3:
break;
}
$("#div1").unbind("mousemove");
//lock0=false;
//lock1=false;
// lock2=false;
// lock3=false;
});