linux auditd审计的简单使用和理解
Linux审计主要用于查看系统改动的信息,如系统密码修改,用户的新建,主要用于保障系统的安全,下面简单介绍审计如何使用
1启动审计进程:
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo service auditd start
2查看当前审计规则
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo auditctl -l
[sudo] passwordfor tommy:
LIST_RULES:exit,always watch=/etc/passwd perm=rwxa
我这里已经新建了一条规则,默认是no rules
3新建临时规则
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo auditctl -w /etc/passwd -p rxwa
参数说明
-w :审计监视的路径
-p:目录或者文件的权限 ,rxwa分别是读、执行、写、属性
在输入命令
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo auditctl -l
就能看到添加的一条规则,这里是对/etc/passwd这个密码文件的监视,如果这个文件发生修改那么就会在审计日志中被记录下来
说明:sudo auditctl -w /etc/passwd -p rxwa这条命令只是新建一条临时规则,如果服务重启或者系统重启,那么这条命令会被清空,如果要让其成为永久的规则,必须修改audit.rules文件,如下
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo vi /etc/audit/audit.rules
[sudo] passwordfor tommy:
# This filecontains the auditctl rules that are loaded
# whenever theaudit daemon is started via the initscripts.
# The rules aresimply the parameters that would be passed
# to auditctl.
# First rule -delete all
-D
# Increase thebuffers to survive stress events.
# Make thisbigger for busy systems
-b 320
# Feel free toadd below this line. See auditctl man page
-w /etc/passwd -p rwxa
上面红色的语句就是添加的规则
4下面来测试passwd文件改动的审计信息
新建一个用户和设置密码
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo useradd lily
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo passwd lily
输入用户密码:
再次输入密码:
然后通过ausearch工具查看审计日志,通过useradd筛选出刚才添加用户的审计信息
[tommy@xie-test log]$ sudo ausearch -f/etc/passwd | grep useradd
type=SYSCALLmsg=audit(1504005888.886:16996): arch=c000003e syscall=2 success=yes exit=4a0=7fceac18869a a1=80000 a2=1b6 a3=0 items=3 ppid=27342 pid=27343 auid=503uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0 tty=pts1 ses=2416comm="useradd" exe="/usr/sbin/useradd" key=(null)
type=SYSCALLmsg=audit(1504005888.887:16997): arch=c000003e syscall=2 success=yes exit=5a0=7fceb3434ce0 a1=2 a2=1b6 a3=0 items=3 ppid=27342 pid=27343 auid=503 uid=0gid=0 euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0 tty=pts1 ses=2416 comm="useradd" exe="/usr/sbin/useradd"key=(null)
type=SYSCALLmsg=audit(1504005888.899:16998): arch=c000003e syscall=2 success=yes exit=9a0=7fceac18869a a1=80000 a2=1b6 a3=0 items=3 ppid=27342 pid=27343 auid=503uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0 tty=pts1 ses=2416comm="useradd" exe="/usr/sbin/useradd" key=(null)
type=SYSCALLmsg=audit(1504005888.900:17000): arch=c000003e syscall=2 success=yes exit=10a0=7fceac18869a a1=80000 a2=1b6 a3=0 items=3 ppid=27342 pid=27343 auid=503uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0 tty=pts1 ses=2416comm="useradd" exe="/usr/sbin/useradd" key=(null)
type=SYSCALLmsg=audit(1504005889.008:17004): arch=c000003e syscall=82 success=yes exit=0a0=7fff8135ec40 a1=7fceb3434ce0 a2=7fff8135eb00 a3=0 items=13 ppid=27342pid=27343 auid=503 uid=0 gid=0 euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=0 sgid=0 fsgid=0tty=pts1 ses=2416 comm="useradd" exe="/usr/sbin/useradd"key=(null)
参数说明:
time :审计时间。
•name :审计对象
•cwd :当前路径
•syscall :相关的系统调用
•auid :审计用户ID
•uid和 gid :访问文件的用户ID和用户组ID
•comm :用户访问文件的命令
•exe :上面命令的可执行文件路径
通过aureport查看生成的审计报告
[tommy@xie-testlog]$ sudo aureport
Summary Report
======================
Range of time inlogs: 2017年08月29日 19:23:12.160 - 2017年08月29日 19:50:57.654
Selected time forreport: 2017年08月29日 19:23:12 - 2017年08月29日 19:50:57.654
Number ofchanges in configuration: 3
Number ofchanges to accounts, groups, or roles: 6
Number oflogins: 0
Number of failedlogins: 0
Number ofauthentications: 3
Number of failedauthentications: 1
Number of users:3
Number ofterminals: 5
Number of hostnames: 1
Number ofexecutables: 9
Number of files:6
Number of AVC's:0
Number of MACevents: 0
Number of failedsyscalls: 0
Number ofanomaly events: 0
Number ofresponses to anomaly events: 0
Number of cryptoevents: 0
Number of keys:0
Number ofprocess IDs: 47
Number ofevents: 505
这里看到了错误的认证fail authentications是1,因为我在刚才使用sudo命令的时候提示输入用户密码输入错了一次,所以被记录了下来
注意:auditd的审计日志是在/var/log/audit/audit.log这里,如果设置的rules较多,日志会很大,所以要定期删除日志,在删除日志的时候注意要重启auditd服务
对auditd.conf文件的分析
这里说明一下几个关键的参数:
log_file:审计日志文件的位置
num_logs:审计日志文件的数量
max_log_file:审计日志文件的容量
max_log_file_action:当审计日志文件超过容量大小时候的操作,这里是rotate,会循环原来的日志文件
对audit.log日志文件的分析
msg=audit后面那串数字冒号前面的是linux系统的时间,我们需要用工具把它转换为我们熟悉的时间格式,这里使用这个网站的工具,输入这个时间就能看到
网址:tool.chinaz.com/Tools/unixtime.aspx
输入后可以看到相应的时间
addr:就是进行上述操作(sshd)的主机地址
2018-05-22补充说明
查看audit.log的时候发觉日志很多,能找到对应操作如useradd操作,但是却碰到一个难题,并不知道这个操作对应是哪个IP的,探讨了一天,下面以/etc/passwd这个文件的审计为例子,在此对这个问题进行分析:
为了方便观察,我用工具把/var/log/audit.log这个文件先拷出来,然后用notepad++把审计日志打开,因为在一开始我使用了useradd lily 和passwd等操作,我首先输入comm快速定位到有useradd或者passwd操作命令记录的日志位置
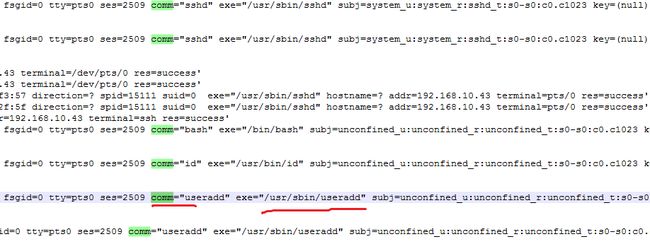
可以看到我画红线的部分,已经定位到useradd这个增加用户的操作记录,然后在这条记录的左手面,可以找到“ppid”这个字
眼,注意,这个是父进程,非常关键,这个就是对应那个ip登录的重要信息,如下图
![]()
可以看到我画红线的ppid是15111
然后我们根据这个15111,再在文件中查看15111这个数字,知道找到有详细的IP出现的位置,有惊喜发现!
![]()
可以看到我找到了user id=15111,ip为192.168.10.43这个IP主机,这个user id和刚才的ppid是对应的,所以就说明是
192.168.10.43这个IP的主机进行了刚才的useradd操作!