ssh-ssh整合(Struts2+Spring+Hibernate)
在之前呢我们已经讲解过ssm以及ssm2的整合开发,今天我们进行ssh的整合,在之前已经有一篇整合ssh的文章,那是基于注解开发的,今天讲解的为基于配置文件注入方式进行开发。
思路:Spring管理hibernate相关会话工厂的创建以及负责管理hibernate的事务,同时spring容器管理service层的实现以及struts2的action,话不多说,我们进入正题。
同样的,我们以一个用户登录的案例进行讲解。
开发软件:
Eclipse neon
Tomcat7.0
Jdk1.7
Struts2.3
Spring2.5
Hiberbate3.0
项目结构如下所示:
项目源码下载:点击下载
在线演示:点击观看
ssh的开发我们同样的分为标准的三层进行开发,首先我们进行Model层的开发。
Model
1、首先我们编写po对象-User.java
package com.sw.domain;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年4月27日
*@Explain:用户表po对象
*id:编号
*username:用户名
*password:密码
*/
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}2、编写对应的hibernate映射文件-User.hbm.xml
3、接下来我们需要编写Hibernate配置文件-hibernate.cfg.xml
root
0707
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bs
true
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
update
true
3、现在基本配置已经完成了,我们可以进行dao层的开发了,编写UserDao.java文件
package com.sw.dao;
import com.sw.domain.User;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月10日
*@Explain:Dao层接口
*/
public interface UserDao {
public final static String SERVICE_NAME = "UserDaoImpl";
//登录
public User findUserByUsername(String username);
}4、接下来需要编写实现类-UserDaoImpl.java
package com.sw.dao.impl;
import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport;
import com.sw.dao.UserDao;
import com.sw.domain.User;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月10日
*@Explain:Dao层实现
*/
public class UserDaoImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport implements UserDao {
@Override
public User findUserByUsername(String username) {
Session session=null;
User user=new User();
try {
session=this.getHibernateTemplate().getSessionFactory().openSession();
Criteria criteria=(Criteria) session.createCriteria(User.class);
//加入条件查询
criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("username", username));
user=(User) criteria.uniqueResult();
} finally {
if(session!=null){
session.close();
}
}
return user;
}
}5、接下来我们需要通过Spring来管理SsqlsessionFactoty,同时需要通过spring管理dao层的方法,编写applicatiobContext.xml文件
classpath:/hibernate/hibernate.cfg.xml
6、接下来我们需要编写spring配置文件加载的工具类,在之前的ssm以及ssm2中已经讲到,这里不再重复。
加载配置文件类:
package com.sw.container;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月15日
*@Explain:服务类,用用户加载applicationContext.xml文件
*/
public class ServiceProvideCord {
protected static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public static void load(String[] fileName){
applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(fileName);
}
}获取bean服务的类:
package com.sw.container;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月15日
*@Explain:Service层服务类
*/
@SuppressWarnings("static-access")
public class SwServiceProvider {
private static ServiceProvideCord serviceProvideCord;
//静态加载
static{
serviceProvideCord = new ServiceProvideCord();
serviceProvideCord.load(new String[]{"classpath:/spring/applicationContext-service.xml",
"classpath:/spring/applicationContext-dao.xml",
"classpath:/spring/applicationContext-transaction.xml",
"classpath:/spring/applicationContext-action.xml"});
}
public static Object getService(String serviceName){
//服务名称为空
if(StringUtils.isBlank(serviceName)){
throw new RuntimeException("当前服务名称不存在...");
}
Object object = null;
if(serviceProvideCord.applicationContext.containsBean(serviceName)){
//获取bean
object = serviceProvideCord.applicationContext.getBean(serviceName);
}
if(object==null){
throw new RuntimeException("服务名称为【"+serviceName+"】下的服务节点不存在...");
}
return object;
}
}7、如上,我们已经完成了编写,可以进行测试了。
package com.sw.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.sw.container.SwServiceProvider;
import com.sw.dao.UserDao;
import com.sw.domain.User;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月18日
*@Explain:hibernate(dao)测试
*/
public class DaoTest {
@Test
public void testFindUserByName() {
UserDao userDao= (UserDao) SwServiceProvider.getService(UserDao.SERVICE_NAME);
User user=(User) userDao.findUserByUsername("bs");
if(user!=null){
String string=user.getPassword();
System.out.println(string);
}else{
System.out.println("");
}
}
}测试结果如下:
如上所示,表明model层的开发已经无误;记下来进行service层的开发。
Service
service层的开发主要包括Spring对hibernate的事务管理以及容器对service方法的管理。
1、编写service层接口
package com.sw.service;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月10日
*@Explain:Service层接口
*/
public interface UserService {
public final static String SERVICE_NAME = "UserServiceImpl";
//登录查询
public String findUserByUsername(String username);
}2、实现service层接口
package com.sw.service.impl;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.sw.container.SwServiceProvider;
import com.sw.dao.UserDao;
import com.sw.domain.User;
import com.sw.service.UserService;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月10日
*@Explain:Service层实现
*/
//指定事务提交级别
@Transactional(readOnly=true)
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
//验证
@Override
public String findUserByUsername(String username) {
UserDao userDao= (UserDao) SwServiceProvider.getService("UserDaoImpl");
User user = userDao.findUserByUsername(username);
String pass;
if(user!=null){
pass = user.getPassword();
}else{
pass = "";
}
return pass;
}
}3、接下来我们需要将service方法放到spring中管理,编写applicationContext-service.xml文件
4、接着需要通过spring管理hibernate的事务,编写配置文件applicationContext-transaction.xml文件
5、如上,service层的配置已经完成,加下来进行相关测试。
package com.sw.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.sw.container.SwServiceProvider;
import com.sw.service.UserService;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月18日
*@Explain:Service测试
*/
public class ServiceTest {
@Test
public void testFindUserByUsername() {
UserService userService=(UserService)SwServiceProvider.getService(UserService.SERVICE_NAME);
String pass=userService.findUserByUsername("bs");
System.out.println(pass);
}
}测试结果如下:
如图,系统正常运行。
View
最后我们需要进行Struts2的开发,主要包括页面的开发、action的开发以及将actioin放到spring中管理。
1、首先我们编写界面文件login.html
Insert title here
successlogin.html:
success
登录成功
errlogin.html:
err
登录失败
2、接下来需要编写Vo对象,用于映射form表单提交的值,UserForm.java:
package com.sw.web.form;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年5月10日
*@Explain:Vo对象-映射form表单
*/
public class UserForm {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}3、接下来需要编写基础action,继承于request,BaseAction.java:
package com.sw.web.action;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletRequestAware;
import org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletResponseAware;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年4月27日
*@Explain:封装Request与Response
*/
public class BaseAction extends ActionSupport implements ServletRequestAware,ServletResponseAware{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected HttpServletRequest request;
protected HttpServletResponse response;
@Override
public void setServletResponse(HttpServletResponse response) {
this.response = response;
}
@Override
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
this.request = request;
}
}4、最后编写处理登录动作的action。LoginAction.java:
package com.sw.web.action;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven;
import com.sw.container.SwServiceProvider;
import com.sw.service.UserService;
import com.sw.web.form.UserForm;
/*
*@Author swxctx
*@time 2017年4月27日
*@Explain:登录Action
*/
public class LoginAction extends BaseAction implements ModelDriven{
//modeldriven-收集页面数据
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/*创建vo对象*/
UserForm userForm = new UserForm();
/*加载applicationContext.xml*/
private UserService userService = (UserService)SwServiceProvider.getService(UserService.SERVICE_NAME);
@Override
public UserForm getModel() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return userForm;
}
/*处理*/
@Override
public String execute() throws Exception {
/*调用service层LoginCheck函数校验*/
String pass= userService.findUserByUsername(userForm.getUsername());
if(userForm.getPassword().equals(pass)){
return "success";
}else{
return "error";
}
}
}
6、在spring中配置以后,直接在struts.xml中引用即可,编写struts.xml文件如下:
/login/successlogin.html
/login/errlogin.html
7、最后一步,我们还需要对web.xml进行编写,如下:
ssh-template
contextConfigLocation
classpath:/spring/applicationContext-*.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
struts2
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
config
struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,/struts/struts.xml
struts2
/*
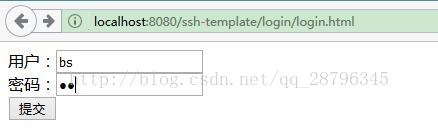
至此,ssh的整合已经全部完成,我们可以打开服务器进行测试了,测试结果如下:
登录界面:
登录成功:
登录失败:
结语:
就我自己而言,比较喜欢使用配置文件的方式,虽然这样开发速度比较慢,同时代码也比较乱,但是我觉适合自己的开发方式可能速度也不一定会慢吧,掌握了配置文件的方式,再去掌握注解的方式。相信也会快很多吧,其实原理都是差不多的,都是从那个点出发,只不过中间的过程有些许不同, 但是最终完成的都是通过spring管理;ssh的开发,对比ssm、ssm2的开发,其实基本上没有多大的差别,ssh的dao层也就是ssm以及ssm2的mapper,在之前ssm以及ssm2我们使用的是Mybatis的Mapper开发方式,所以也就仅仅这里有一些差别,在其他地方其原理都是一样,如果Mybatis使用传统dao的开发方式,那么起开发也就是一样的。总之,个人觉得原理比较重要,学习了各个框架以后,再了解各个框架之间为什么要整合,那么也就自然会整合了,以上纯属个人观点,请多指教。