算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day2:第17~26题
写在前面
- 本系列包含《剑指Offer》66道算法题,预计一周刷完,这是第二篇。
系列汇总:剑指Offer 66题 Java 刷题笔记汇总 - 所有题目均可在牛客网在线编程平台进行调试。
网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/coding-interviews - 本系列包含题目,解题思路及代码(Java)。
代码同步发布在GitHub:https://github.com/JohnnyJYWu/offer-Java
上一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day1:第1~16题
下一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day3:第27~37题
Day2:第17~26题
今天的题涉及递归及二叉树较多,需要深入理解其逻辑和原理。
- T17. 树的子结构
- T18. 二叉树的镜像
- T19. 顺时针打印矩阵
- T20. 包含 min 函数的栈
- T21. 栈的压入、弹出序列
- T22. 从上往下打印二叉树
- T23. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- T24. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- T25. 复杂链表的复制
- T26. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
T17. 树的子结构
题目描述
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
解题思路
设置终止条件进行判断,将B树与A树,A树左子树,A树右子树进行比较,递归进行即可。
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null || root2 == null) return false;
return isSubtree(root1, root2) //root2与root1比较
|| HasSubtree(root1.left, root2) //root2与root1左子树比较,递归逻辑
|| HasSubtree(root1.right, root2); //root2与root1右比较,递归逻辑
//以上三种情况任一为true,即证明root2是root1的子结构
}
private boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
//终止判定
if(root1 == null && root2 == null) return true;//为null,能执行到此步且相同,为子结构
if(root1 == null) return false;//root1为null,root2不为null,不同,不为子结构
if(root2 == null) return true;//root1不为null,root2为null,能执行到此步说明相同,为子结构
if(root1.val != root2.val) return false;//root1,root2都不为null,val不同,不为子结构
//能执行到此步,说明未判定完,继续对root1,root2的左右子树分别递归此方法进行判断,均为true则为子结构
return isSubtree(root1.left, root2.left) && isSubtree(root1.right, root2.right);
}
T18. 二叉树的镜像
题目描述
操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
解题思路
交换每个结点的左右子树,并对该结点的左右子结点分别进行此操作,递归进行即可。
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return;
//交换左右子树
swap(root);
//分别对root左右子树进行交换,递归调用此方法即可
Mirror(root.left);
Mirror(root.right);
}
private void swap(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
}
T19. 顺时针打印矩阵
题目描述
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
解题思路
顺时针绕圈打印即可,从外向里每次循环绕一圈。
注意:一定细心,出错基本都是马虎造成的。
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(matrix == null || matrix[0] == null) return list;
int rowTop = 0, rowBottom = matrix.length - 1;
int colLeft = 0, colRight = matrix[0].length - 1;
while(colLeft <= colRight && rowTop <= rowBottom) {//跳出条件
for(int i = colLeft; i <= colRight; i ++) {//添加上边一行,从左到右
list.add(matrix[rowTop][i]);
}
for(int i = rowTop + 1; i <= rowBottom; i ++) {//添加右边一列,从上到下,注意去掉已添加的【右上角】。
list.add(matrix[i][colRight]);
}
if(rowTop != rowBottom) {//若相等则已到同一行,无可继续添加的
for(int i = colRight - 1; i >= colLeft; i --) {//添加下边一行,从右到左,注意去掉已添加的【右下角】。
list.add(matrix[rowBottom][i]);
}
}
if(colLeft != colRight) {//若相等则已到同一列,无可继续添加的
for(int i = rowBottom - 1; i > rowTop; i --) {//添加左边一列,从下到上,注意去掉已添加的【左下角】及【左上角】。
list.add(matrix[i][colLeft]);
}
}
colLeft ++;
colRight --;
rowTop ++;
rowBottom --;
}
return list;
}
T20. 包含 min 函数的栈
题目描述
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))。
解题思路
定义两个栈,stack存入栈的数,minStack存该数入栈后栈内的最小数min。
注意:两个栈大小是相同的,同步入栈及出栈。即哪怕入栈的数不是最小的,也把那个最小的再入一次minStack。
private Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
private int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//minStack用于存储任一元素入栈时,当前栈内的最小值,与stack是同步入栈出栈的,即两个栈内元素数目相同
private Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<>();
public void push(int node) {
stack.push(node);
if(min > node) {
min = node;
}
minStack.push(min);
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
min = minStack.peek();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return min;
}
T21. 栈的压入、弹出序列
题目描述
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。(注意:这两个序列的长度是相等的)
解题思路
建个栈,模拟出入栈顺序即可。
注意:每次入栈后,要对出栈顺序的数组进行检测,循环把该出栈的出了,再进行下次入栈。
public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushA, int[] popA) {//pushA和popA长度相同
//建个栈,模拟入栈出栈操作即可
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int popIndex = 0;
for(int pushIndex = 0; pushIndex < pushA.length; pushIndex ++) {
stack.push(pushA[pushIndex]);//按pushA顺序入栈
while(popIndex < popA.length && popA[popIndex] == stack.peek()) {//相同说明可出栈,即模拟popA顺序进行出栈操作
stack.pop();
popIndex ++;
}
}
//若栈空,说明pushA入栈能按popA顺序出栈
return stack.isEmpty();
}
T22. 从上往下打印二叉树
题目描述
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个结点,同层结点从左至右打印。
解题思路
二叉树层输出,使用**广度优先搜索(BFS)**即可。
使用队列实现,边出队边输出,同时将其左右子结点压入队列。
public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
//使用队列实现,不断按层压入及输出
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode tmp = queue.poll();
//先左后右按顺序压入子结点
if(tmp.left != null) queue.add(tmp.left);
if(tmp.right != null) queue.add(tmp.right);
list.add(tmp.val);
}
return list;
}
T23. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
题目描述
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则输出Yes,否则输出No。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
解题思路
二叉搜索树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;它的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)。
后序遍历:左 -> 右 -> 根。
因此,后序遍历最后一个数为根结点。通过根结点可把后序遍历分为两部分,前半部分为小于根结点的左子树,后半部分为大于根结点的右子树。然后根据此原理,递归对左右子树分别用此方法进行验证即可。
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if(sequence == null || sequence.length == 0) return false;
return verify(sequence, 0, sequence.length - 1);
}
private boolean verify(int[] sequence, int first, int last) {
//终止条件
if(first >= last) return true;
int rootValue = sequence[last];//后序遍历的根结点为最后一个
int index = first;
while(sequence[index] <= rootValue && index < last) {//比根结点小的为左子树,大的为右子树
index ++;
}
//此时sequence[index]是第一个比根结点大的值
//可将sequence[0]~sequence[index-1]认为是左子树,sequence[index]~sequence[last-1]认为是右子树
for(int i = index; i < last; i ++) {
if(sequence[i] < rootValue) {//若右子树中存在比根结点小的,则不是二叉搜索树
return false;
}
}
//此时分别对根结点的左右子树进行迭代判断,全部为true则是后序遍历
return verify(sequence, first, index - 1)
&& verify(sequence, index, last - 1);//last为根结点
}
T24. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目描述
输入一颗二叉树的跟结点和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。(注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大的数组靠前)
解题思路
深度优先搜索(DFS),通过减法的思想不断用target减去当前结点值,能减为0则是一条路径。
注意:路径要求最后到达叶子结点。
迭代过程中需把当前值在path中移除以保证路径正确,相当于回退到上一步的路径。(详见代码)
private ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root, int target) {
if(root == null) return result;
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
findPathDFS(root, target, path);
return result;
}
private void findPathDFS(TreeNode node, int target, ArrayList<Integer> path) {
if(node == null) return;
path.add(node.val);
target -= node.val;//减法的思想,目标值能减为0则是一条路径
if(target == 0 && node.left == null && node.right == null) {//已经到达叶子结点且targe正好减完
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
} else if(target > 0) {//若>0则继续对其左右子结点进行迭代判断
findPathDFS(node.left, target, path);
findPathDFS(node.right, target, path);
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);//此步重要,迭代过程中需把当前值在path中移除以保证路径正确,相当于回退到上一步的路径
}
T25. 复杂链表的复制
题目描述
输入一个复杂链表(每个结点中有结点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个结点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个结点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的head。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的结点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)
解题思路
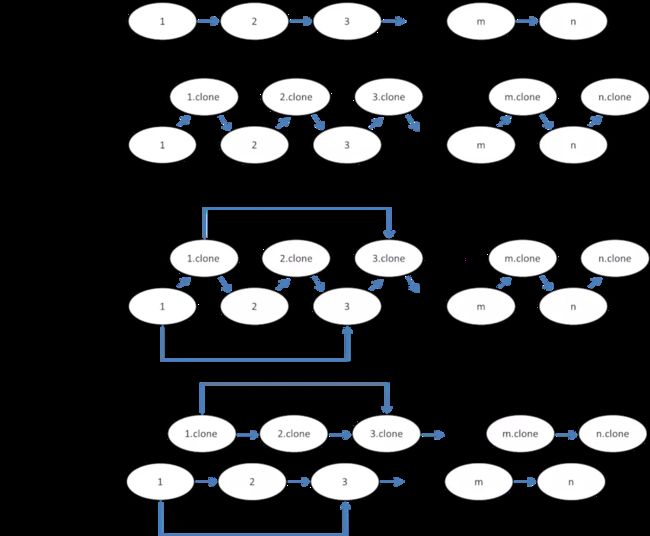
step1:在每个结点的后面(或者说每个结点与下一个结点中间)插入新结点。该新结点为克隆结点,这么做是为了连接random结点。
step2:连接random结点。
step3:拆分链表,下边为原链表,上边为clone链表。
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null) return null;
//step1:在每个结点的后面(或者说每个结点与下一个结点中间)插入【新结点】
//该新结点为克隆结点,这么做是为了连接random结点
RandomListNode tmp = pHead;
while(tmp != null) {
RandomListNode cloneNode = new RandomListNode(tmp.label);
//插入clone结点
cloneNode.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = cloneNode;
//移到原链表的下一个结点
tmp = cloneNode.next;
}
//step2:连接random结点
tmp = pHead;
while(tmp != null) {
RandomListNode cloneNode = tmp.next;
if(tmp.random != null) {
cloneNode.random = tmp.random.next;//tmp.random是原链表的结点,tmp.random.next才是那个结点的clone结点
}
tmp = cloneNode.next;
}
//step3:拆分链表(详见图片)
tmp = pHead;
RandomListNode cloneHead = tmp.next;
while(tmp.next != null) {
RandomListNode node = tmp.next;
tmp.next = node.next;
tmp = node;
}
return cloneHead;
}
T26. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
题目描述
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
解题思路
由于二叉搜索树左子结点 < 根结点 < 右子结点的性质,题目实质上是二叉搜索树的中序遍历,改结点的指针。left代表双向链表的prev指针,right代表next指针。
private TreeNode pre = null;//用于记录上一个结点
private TreeNode head = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null) return null;
inOrder(pRootOfTree);
return head;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) return;
//实质上是中序遍历,改结点的指针。left代表双向链表的prev指针,right代表next
//左
inOrder(node.left);
//根
//改指针的指向(只需与上一个结点相连即可)
node.left = pre;//连上一个
if(pre != null) {//如果上一个不为null,连此时这个
pre.right = node;
}
pre = node;//将pre移向此时这个结点,为下一次迭代做准备
if(head == null) head = node;//只在第一次找到最小结点时作为头结点
//右
inOrder(node.right);
}
项目地址:https://github.com/JohnnyJYWu/offer-Java
上一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day1:第1~16题
下一篇:算法 | 一周刷完《剑指Offer》 Day3:第27~37题
希望这篇文章对你有帮助~
